The Sixth Man plays a pivotal role in basketball by providing crucial energy and scoring off the bench, often changing the game's momentum. This player's versatility and ability to adapt to various positions can give your team a strategic edge during critical moments. Discover how the Sixth Man can transform your team's dynamic by continuing to read the rest of the article.
Table of Comparison
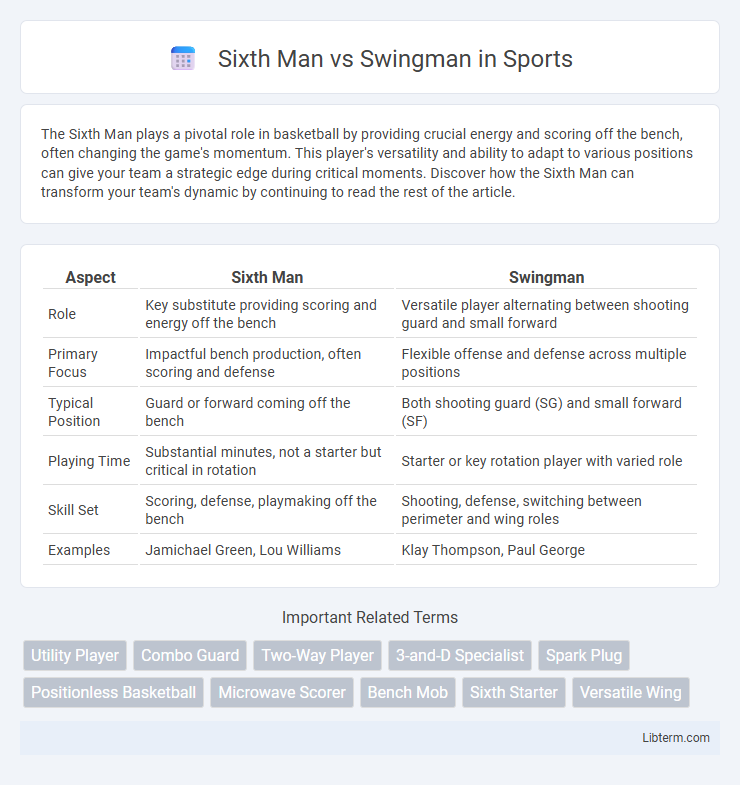
| Aspect | Sixth Man | Swingman |
|---|---|---|
| Role | Key substitute providing scoring and energy off the bench | Versatile player alternating between shooting guard and small forward |
| Primary Focus | Impactful bench production, often scoring and defense | Flexible offense and defense across multiple positions |
| Typical Position | Guard or forward coming off the bench | Both shooting guard (SG) and small forward (SF) |
| Playing Time | Substantial minutes, not a starter but critical in rotation | Starter or key rotation player with varied role |
| Skill Set | Scoring, defense, playmaking off the bench | Shooting, defense, switching between perimeter and wing roles |
| Examples | Jamichael Green, Lou Williams | Klay Thompson, Paul George |
Understanding the Roles: Sixth Man vs Swingman
The Sixth Man serves as a versatile and crucial player off the bench, often providing energy, scoring, and defensive stability in crucial moments. The Swingman, typically capable of playing both shooting guard and small forward positions, offers flexibility on the court with a mix of perimeter shooting, slashing ability, and defensive versatility. Understanding the distinct roles highlights that sixth men are key impact substitutes, while swingmen are adaptable starters or key rotation players who bridge multiple positions.
Key Differences Between Sixth Man and Swingman
The key differences between a sixth man and a swingman lie in their roles and versatility on a basketball team. A sixth man primarily serves as the first substitute, providing scoring and energy off the bench, whereas a swingman can play multiple positions, typically both shooting guard and small forward, adapting to various defensive and offensive roles. The sixth man emphasizes impact during limited minutes, while the swingman offers positional flexibility and matchup advantages across the lineup.
Historical Origins of Sixth Man and Swingman Terms
The term "Sixth Man" originated in the 1960s to describe the first substitute player who provides crucial energy and scoring off the bench, popularized by Boston Celtics coach Red Auerbach. The "Swingman" term emerged later, referring to a versatile player capable of switching between shooting guard and small forward positions, reflecting basketball's evolution toward positional flexibility. Both concepts highlight strategic roles that expanded traditional player classifications in professional basketball history.
Essential Skills: Sixth Man vs Swingman
Sixth men excel in versatility, often possessing strong ball-handling, perimeter shooting, and defensive capabilities to adapt to multiple roles off the bench. Swingmen blend the skills of shooting guards and small forwards, with emphasis on scoring ability, wing defense, and rebounding prowess to switch effectively between guard and forward positions. Both roles require high basketball IQ and stamina, but sixth men prioritize the ability to impact the game immediately in various scenarios, while swingmen specialize in seamless positional flexibility on both ends of the floor.
Impact on Team Strategy and Rotation
Sixth Man typically provides scoring and energy off the bench, allowing starters to rest while maintaining offensive efficiency and defensive intensity. Swingman, able to play both guard and forward positions, offers tactical versatility, enabling coaches to adjust matchups and defensive schemes seamlessly. Incorporating both roles diversifies rotation options, enhances lineup flexibility, and optimizes matchup exploitation during critical game moments.
Famous Sixth Men in Basketball History
The role of the Sixth Man in basketball, exemplified by legends like Jamal Crawford and Manu Ginobili, serves as a crucial offensive catalyst off the bench, providing scoring and energy while maintaining team momentum. Unlike Swingmen who primarily play both shooting guard and small forward positions, Sixth Men are specialized substitutes known for their ability to change the game's dynamic without starting. Iconic Sixth Men like Lou Williams and Kevin McHale highlight the strategic importance of this role in NBA history, consistently delivering elite performance and versatility that often leads to playoff success and championship runs.
Legendary Swingmen and Their Contributions
Legendary swingmen like Michael Jordan and Scottie Pippen revolutionized basketball by seamlessly blending the skills of shooting guards and small forwards, contributing to dynamic offenses and versatile defenses. Their ability to adapt to multiple positions allowed teams to exploit mismatches, drive scoring, and create unpredictable plays. The strategic impact of these swingmen elevated team performance and cemented their status as iconic figures in basketball history.
How Coaches Utilize Sixth Men and Swingmen
Coaches utilize sixth men to provide scoring bursts and maintain game tempo when starters rest, often deploying them as versatile players who can guard multiple positions and create offensive opportunities off the bench. Swingmen serve as adaptable athletes capable of shifting between shooting guard and small forward roles, enabling coaches to adjust defensive matchups and exploit mismatches against opponents. Strategic use of both sixth men and swingmen enhances team depth, allowing for flexible rotations that sustain intensity and tactical advantage throughout the game.
Sixth Man vs Swingman: Statistical Comparisons
Sixth Man players average around 10-15 points per game, contributing crucial bench scoring and energy with high usage rates despite fewer minutes than starters. Swingmen typically log 25-35 minutes per game, balancing perimeter shooting and defensive versatility, with statistical outputs including higher rebounds and assists due to extended playtime. Efficiency metrics such as Player Efficiency Rating (PER) often show Sixth Men maintaining comparable or superior per-minute productivity compared to Swingmen, highlighting their impact in limited roles.
Which Role Holds More Value in Modern Basketball?
The Sixth Man holds more value in modern basketball as a versatile scorer and playmaker who provides a strategic boost off the bench, often matching starter-level impact. Swingmen offer defensive flexibility and the ability to guard multiple positions, but the Sixth Man's role in sustaining offensive momentum and adaptability in rotations is crucial in today's pace-and-space era. Teams prioritize Sixth Men for their scoring depth and ability to shift game dynamics, making this role increasingly pivotal compared to traditional Swingmen.
Sixth Man Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com