A power block serves as the core component of a thermal power plant, efficiently converting fuel energy into mechanical and electrical energy through interconnected systems. Maximizing the performance of your power block can lead to improved plant efficiency, reduced operational costs, and lower emissions. Explore the full article to understand how optimizing power block design and maintenance can boost energy production.
Table of Comparison
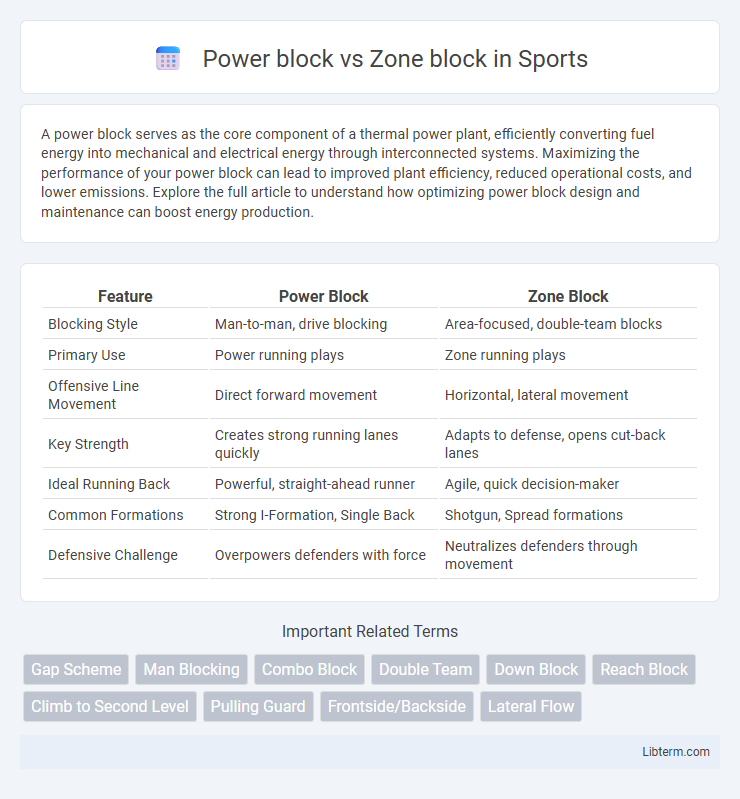
| Feature | Power Block | Zone Block |
|---|---|---|
| Blocking Style | Man-to-man, drive blocking | Area-focused, double-team blocks |
| Primary Use | Power running plays | Zone running plays |
| Offensive Line Movement | Direct forward movement | Horizontal, lateral movement |
| Key Strength | Creates strong running lanes quickly | Adapts to defense, opens cut-back lanes |
| Ideal Running Back | Powerful, straight-ahead runner | Agile, quick decision-maker |
| Common Formations | Strong I-Formation, Single Back | Shotgun, Spread formations |
| Defensive Challenge | Overpowers defenders with force | Neutralizes defenders through movement |
Understanding Power Blocking and Zone Blocking
Power blocking emphasizes driving defenders backward using man-on-man blocking schemes, maximizing physical strength and aggression to create running lanes. Zone blocking relies on coordinated group movement, where offensive linemen block specific areas or zones rather than individual defenders, promoting agility and teamwork in reacting to defensive shifts. Understanding the distinction between power blocking's focus on sheer force and zone blocking's emphasis on spatial control is essential for tailoring offensive strategies in football.
Key Differences Between Power Block and Zone Block
The Power Block technique emphasizes maximum force through aggressive, low-stance blocking aimed at overpowering the opponent, while the Zone Block strategy prioritizes controlling space and leveraging quick, coordinated movements to create gaps in the defensive line. Power Block relies heavily on individual strength and direct impact, whereas Zone Block depends on timing, teamwork, and exploiting defensive alignments. Understanding these distinctions is crucial for offensive line strategies in football, affecting both run-blocking efficiency and pass protection schemes.
Historical Evolution of Blocking Schemes in Football
Power block and zone block represent two fundamental offensive line techniques whose historical evolution traces back to early 20th-century football strategies. The power block emphasizes driving the defensive linemen off the line of scrimmage with aggressive, straight-ahead blocking, evolving from the physical ground-and-pound style predominant in the 1920s and 1930s. Zone blocking, which emerged primarily in the 1950s and gained widespread popularity in the 1980s, focuses on lateral movement and teamwork among linemen to create cutback lanes, reflecting a strategic shift toward speed and agility in offensive play design.
Core Principles of Power Blocking
Power blocking emphasizes creating strong, driving blocks that generate maximum momentum for offensive linemen, focusing on aggressive contact and driving defenders away from the play's point of attack. The core principles include maintaining a low pad level, delivering powerful initial punches, and sustaining leverage to control defenders throughout the block. This technique contrasts with zone blocking, which prioritizes lateral movement and teamwork to create cutback lanes by using coordinated, area-based blocking schemes.
Core Principles of Zone Blocking
Zone blocking emphasizes coordinated movement, where offensive linemen work in unison to block specific areas rather than individual defenders, creating running lanes through collective angles and leverage. Unlike power blocking, which relies on straight-ahead, man-to-man blocks and physical dominance to push defenders backward, zone blocking employs lateral movement and quick footwork to stretch the defense horizontally. This technique enhances the running back's ability to read openings and make decisive cuts based on the defensive alignment, improving adaptability and efficiency in the running game.
Advantages of Power Blocking Schemes
Power blocking schemes offer significant advantages in strength training by maximizing muscle recruitment and promoting balanced hypertrophy across large muscle groups. This method enhances neuromuscular efficiency and allows for greater overload potential, leading to improved power output and overall athletic performance. Power blocks also reduce fatigue accumulation compared to zone blocking, enabling athletes to sustain higher intensity levels during workouts.
Benefits of Zone Blocking Approaches
Zone blocking approaches enhance offensive line flexibility, allowing linemen to work in unison to create running lanes by blocking areas rather than specific defenders. This method improves adaptability against complex defensive fronts, increasing overall rushing yardage and control of the line of scrimmage. Compared to power blocking, zone blocking reduces penetration by defenders and maximizes yards after contact through coordinated movement and leverage.
Challenges and Limitations of Each System
Power block systems face challenges such as limited scalability and less precise targeting, resulting in potential underutilization of resources and higher operational costs. Zone block systems encounter difficulties in managing complex routing and increased maintenance requirements due to their segmented architecture. Both systems struggle with integration issues when adapting to rapidly changing energy demands and infrastructure upgrades.
When to Use Power Block vs. Zone Block
Power block exercises suit lifters aiming to build maximal strength and explosive power by targeting larger muscle groups through compound movements like deadlifts and squats. Zone block techniques are ideal for athletes or bodybuilders seeking precise muscle activation and isolation, emphasizing controlled range of motion to enhance muscle hypertrophy and endurance. Choose power block routines to improve overall force output and performance in sports requiring strength, while zone block is better for focused muscle development and injury prevention during rehabilitation.
Impact on Player Roles and Team Performance
Power block schemes emphasize physicality and leverage, typically assigning offensive linemen to dominate defenders through strong, straight-ahead blocking, which benefits power runners and short-yardage situations. Zone block schemes rely on lateral movement and coordination, requiring linemen and backs to work cohesively in reading and reacting to defensive fronts, promoting versatility and creativity in playmaking. Teams employing power blocking often excel in controlling the line of scrimmage and time of possession, while zone blocking can enhance explosive plays and adaptability against diverse defenses.
Power block Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com