A data diode is a cybersecurity device designed to enforce one-way data flow, preventing data leaks and unauthorized access by allowing information to travel in only one direction. It is commonly used in high-security environments like military, industrial control systems, and critical infrastructure to ensure robust data protection. Discover how a data diode can safeguard Your sensitive information and improve your network security by reading the rest of this article.
Table of Comparison
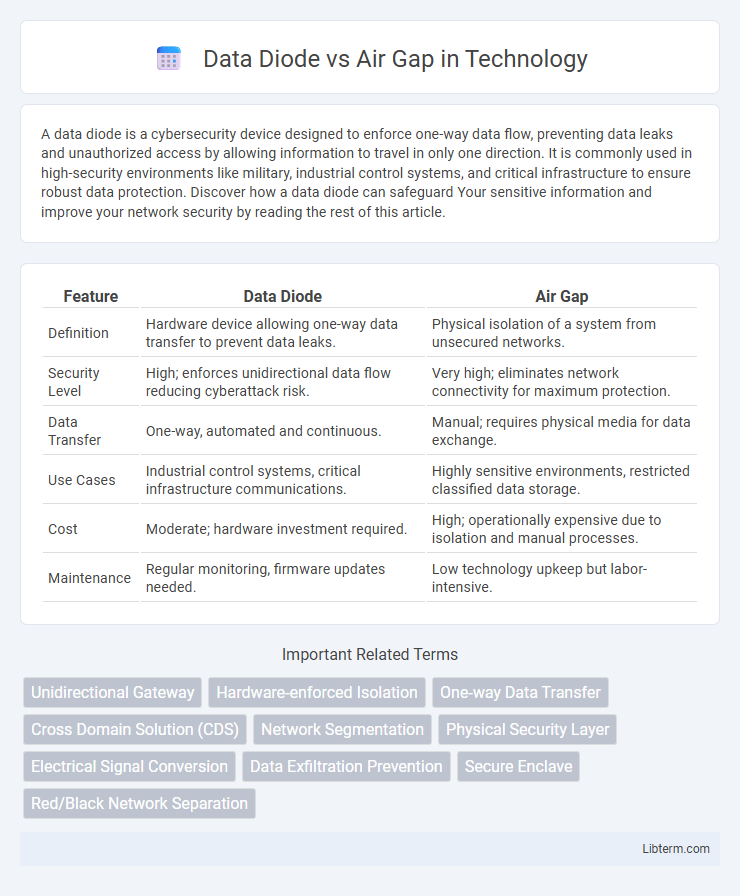
| Feature | Data Diode | Air Gap |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Hardware device allowing one-way data transfer to prevent data leaks. | Physical isolation of a system from unsecured networks. |
| Security Level | High; enforces unidirectional data flow reducing cyberattack risk. | Very high; eliminates network connectivity for maximum protection. |
| Data Transfer | One-way, automated and continuous. | Manual; requires physical media for data exchange. |
| Use Cases | Industrial control systems, critical infrastructure communications. | Highly sensitive environments, restricted classified data storage. |
| Cost | Moderate; hardware investment required. | High; operationally expensive due to isolation and manual processes. |
| Maintenance | Regular monitoring, firmware updates needed. | Low technology upkeep but labor-intensive. |
Introduction to Data Diode and Air Gap Technologies
Data Diode technology ensures unidirectional data flow by physically restricting data transmission to one direction, providing high-security protection between networks to prevent data breaches. Air Gap technology involves physically isolating a computer or network from unsecured networks, creating a complete disconnection to eliminate any potential external cyber threats. Both technologies are critical in safeguarding sensitive information but differ in their approach: Data Diodes allow controlled data flow with strict security, while Air Gaps rely on physical separation for isolation.
Definition and Core Principles of Data Diode
Data diode is a cybersecurity device designed to enforce unidirectional data flow, ensuring that information moves securely from one network to another without risk of data leakage or external attacks. Unlike an air gap, which physically isolates networks by completely disconnecting them, a data diode provides a controlled, hardware-enforced one-way transmission path. This core principle of strict one-way communication makes data diodes essential for high-security environments that require reliable data transfer while preventing unauthorized access.
Definition and Core Principles of Air Gap
An air gap is a physical security measure that involves isolating a computer or network by completely disconnecting it from any external connections, ensuring no data transmission pathways exist. This separation relies on the core principle of absolute physical disconnection to prevent unauthorized access or cyber threats. Unlike data diodes, which allow one-way data flow, air gaps enforce total network isolation to protect sensitive information.
Key Differences Between Data Diode and Air Gap
Data diodes provide unidirectional data flow ensuring secure, automated transmission from a less secure to a more secure network, while air gaps rely on physical isolation with no direct electronic connection between networks. Data diodes enable real-time data transfer with protocol-level control, whereas air gaps require manual data transfer methods, increasing operational complexity. The key difference lies in data flow control: data diodes enforce unidirectional communication electronically, whereas air gaps prevent network connection entirely, maximizing security at the cost of convenience.
Security Advantages of Data Diode Solutions
Data diode solutions offer unidirectional data flow that inherently prevents data leakage and cyber intrusions by blocking reverse communication, enhancing network security compared to traditional air gaps. Unlike air gaps that rely solely on physical separation and are vulnerable to insider threats or bridging attacks, data diodes provide continuous, automated protection without human intervention. This technology supports secure real-time data transmission for critical infrastructure, ensuring integrity and confidentiality while minimizing operational disruptions.
Security Benefits and Limitations of Air Gap
Air gaps provide a robust physical security barrier by completely isolating critical systems from external networks, significantly reducing the risk of remote cyberattacks. However, air-gapped environments face operational limitations such as complex data transfer processes, increased downtime, and potential insider threats due to manual intervention. While data diodes enable secure, one-way data flow minimizing risk without sacrificing connectivity, air gaps excel in scenarios demanding absolute network isolation despite their logistical challenges.
Typical Use Cases for Data Diode
Data diodes are typically used in high-security environments such as military networks, critical infrastructure control systems, and financial institutions to ensure unidirectional data flow and prevent cyber threats from infiltrating sensitive networks. Unlike air gaps, which physically isolate systems, data diodes enable real-time data transmission while maintaining strict security by allowing data to move only in one direction. This makes data diodes ideal for applications requiring continuous data monitoring, secure data transfer, and compliance with regulatory mandates in sectors like energy, manufacturing, and government.
Typical Use Cases for Air Gap
Air gap security is typically used in highly sensitive environments such as military, critical infrastructure, and industrial control systems where physical separation prevents any direct digital connection, ensuring maximum protection against cyber threats. It is ideal for safeguarding classified data, preventing ransomware spread, and protecting legacy systems that cannot be easily updated. Unlike data diodes, air gaps provide absolute isolation but require manual data transfer methods, making them suitable for scenarios prioritizing security over convenience.
Challenges in Implementation and Maintenance
Implementing data diodes involves intricate hardware integration and strict configuration to ensure one-way data flow, presenting challenges in system compatibility and scalability. Air gap implementation requires physical isolation of networks, demanding rigorous procedural controls and frequent validation to prevent accidental bridging or insider threats. Maintenance of both technologies necessitates ongoing monitoring and testing to uphold security integrity and address potential vulnerabilities from human error or technological advances.
Choosing Between Data Diode and Air Gap: Factors to Consider
Choosing between a data diode and an air gap depends on the specific security requirements and operational constraints of the environment. Data diodes provide continuous, automated unidirectional data flow, ideal for real-time monitoring while maintaining high security against cyber threats. Air gaps ensure physical separation, offering the highest level of protection from network-based attacks but can hinder data transfer efficiency and require manual intervention.
Data Diode Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com