Dark launch is a deployment strategy where new features are released to a limited audience or hidden from public view to test performance and gather feedback without impacting all users. This approach allows for fine-tuning and issue resolution before a full-scale release, minimizing risk and ensuring a smoother user experience. Discover how dark launch can enhance your product rollout and optimize development processes in the rest of this article.
Table of Comparison
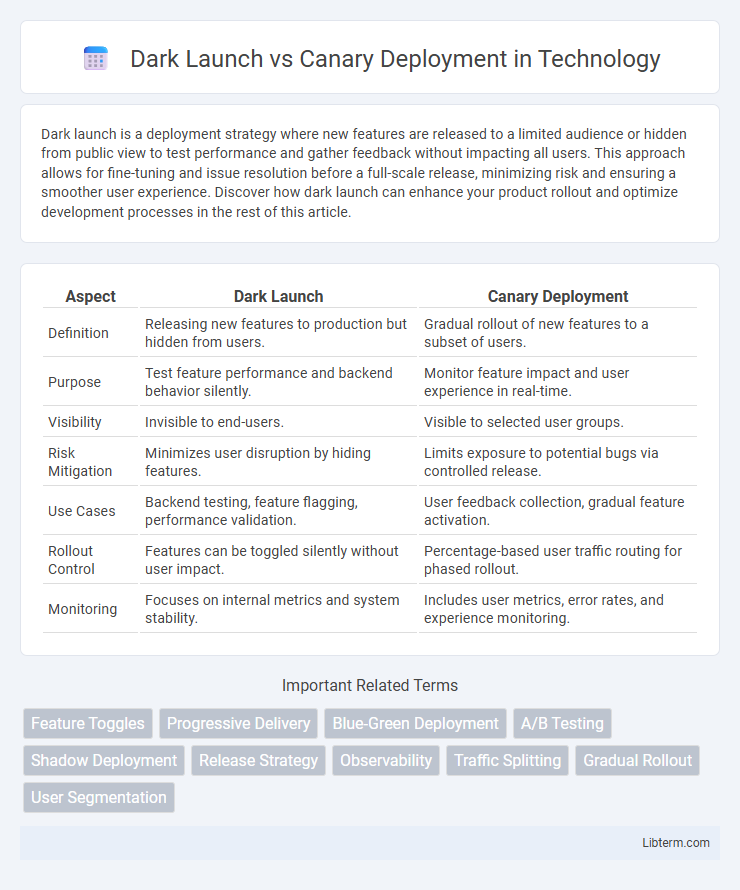
| Aspect | Dark Launch | Canary Deployment |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Releasing new features to production but hidden from users. | Gradual rollout of new features to a subset of users. |
| Purpose | Test feature performance and backend behavior silently. | Monitor feature impact and user experience in real-time. |
| Visibility | Invisible to end-users. | Visible to selected user groups. |
| Risk Mitigation | Minimizes user disruption by hiding features. | Limits exposure to potential bugs via controlled release. |
| Use Cases | Backend testing, feature flagging, performance validation. | User feedback collection, gradual feature activation. |
| Rollout Control | Features can be toggled silently without user impact. | Percentage-based user traffic routing for phased rollout. |
| Monitoring | Focuses on internal metrics and system stability. | Includes user metrics, error rates, and experience monitoring. |
Understanding Dark Launch and Canary Deployment
Dark Launch involves releasing new features to a limited set of users without making them widely visible, allowing teams to test functionality and gather feedback while minimizing risks. Canary Deployment gradually rolls out updates to a small subset of users, monitoring performance and stability before full-scale release to detect issues early. Both strategies prioritize controlled, incremental exposure to enhance release quality and reduce disruption in production environments.
Key Differences Between Dark Launch and Canary Deployment
Dark Launch enables features to be deployed in production but hidden from users, allowing testing with real data without user exposure. Canary Deployment releases a new version to a small subset of users to monitor performance and stability before wider rollout. The key difference lies in user exposure: Dark Launch hides features entirely, while Canary Deployment involves targeted user exposure to new features.
Benefits of Dark Launch in Modern Software Delivery
Dark Launch enables controlled feature exposure, allowing teams to test new functionalities with real users while minimizing risk by hiding features from the broader audience. This approach gathers valuable user feedback and performance data without impacting overall system stability or user experience. By decoupling deployment from release, Dark Launch facilitates faster iteration and safer rollouts in modern software delivery pipelines.
Advantages of Canary Deployment Strategies
Canary deployment strategies enable incremental software rollouts by releasing updates to a small subset of users, reducing the risk of widespread system failures. This approach allows real-time monitoring and quick rollback if issues arise, ensuring higher system stability and user satisfaction. Targeted exposure during canary deployments also facilitates precise performance analysis and feedback collection before full-scale release.
Risks and Challenges of Dark Launch
Dark Launch poses significant risks such as unintended user exposure to incomplete features, leading to potential confusion or negative feedback that can harm brand reputation. It challenges teams with the difficulty of isolating and managing hidden features in production, increasing the chance of unnoticed bugs or performance issues affecting overall system stability. Unlike Canary Deployment, which limits exposure to a small, controlled user group, Dark Launch often relies on feature toggles that can complicate rollback processes and delay issue detection.
Potential Pitfalls in Canary Deployments
Canary deployments can introduce risks such as incomplete monitoring leading to unnoticed errors impacting a subset of users, and configuration mismatches causing inconsistent behavior between canary and production environments. Traffic segmentation challenges may result in uneven load distribution, while rollback complexities increase downtime if issues arise late in the canary phase. Ensuring comprehensive automated testing and real-time analytics is crucial to mitigate these pitfalls and maintain service reliability.
Use Cases: When to Choose Dark Launch
Dark Launch is ideal for testing new features in production without user impact, allowing controlled activation to specific user segments for real-time feedback and risk mitigation. It suits scenarios requiring feature validation, operational monitoring, and gradual rollout readiness without full exposure. Enterprises adopt Dark Launch when ensuring stability in sensitive environments or when stakeholder approval is pending before wide release.
Use Cases: When to Choose Canary Deployment
Canary Deployment is ideal for updating critical production services with a need for controlled, incremental exposure to new features, minimizing user impact during rollback. It suits scenarios where performance monitoring and real-time feedback are essential for validating updates before full release. Organizations prioritize this method when aiming to ensure system stability while gradually introducing potentially risky changes.
Best Practices for Implementing Dark Launch and Canary Deployment
Implementing dark launch requires feature toggles to control user exposure, rigorous monitoring to detect issues early, and gradual ramp-up strategies to minimize risks. Canary deployment best practices include selecting a representative subset of users, automated rollback mechanisms in case of failures, and comprehensive performance tracking to ensure system stability. Both approaches benefit from continuous integration and continuous delivery (CI/CD) pipelines to streamline deployment and enable rapid iteration.
Choosing the Right Strategy for Your Deployment Needs
Dark Launch enables feature testing in production by releasing functionality to a limited subset of users without full visibility, ideal for minimizing risk and gathering real-world data. Canary Deployment gradually rolls out updates to a small group of users before broader release, allowing performance monitoring and issue detection in a controlled environment. Selecting the right strategy depends on factors such as risk tolerance, user impact, and the need for immediate feedback versus controlled exposure.
Dark Launch Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com