Authentication is the process of verifying the identity of a user or system to ensure secure access to resources. Strong authentication methods, such as multi-factor authentication, enhance protection against unauthorized access and data breaches. Discover how implementing robust authentication techniques can safeguard Your digital environment by reading the full article.
Table of Comparison
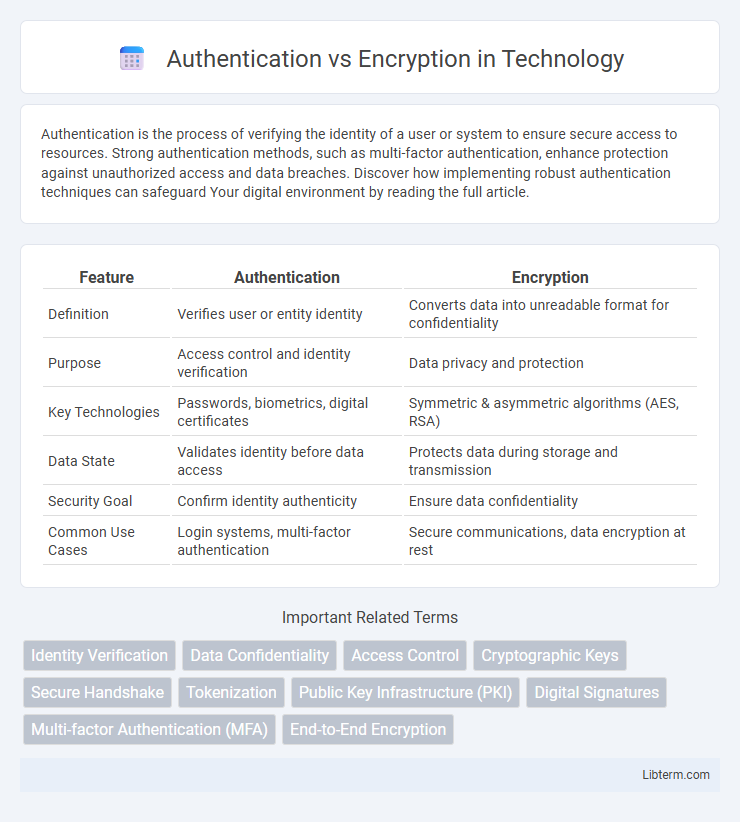
| Feature | Authentication | Encryption |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Verifies user or entity identity | Converts data into unreadable format for confidentiality |
| Purpose | Access control and identity verification | Data privacy and protection |
| Key Technologies | Passwords, biometrics, digital certificates | Symmetric & asymmetric algorithms (AES, RSA) |
| Data State | Validates identity before data access | Protects data during storage and transmission |
| Security Goal | Confirm identity authenticity | Ensure data confidentiality |
| Common Use Cases | Login systems, multi-factor authentication | Secure communications, data encryption at rest |
Introduction to Authentication and Encryption
Authentication verifies the identity of users or devices to ensure authorized access, employing methods such as passwords, biometrics, or digital certificates. Encryption converts data into a coded format to protect confidentiality during storage or transmission, using algorithms like AES or RSA. Both processes are fundamental to cybersecurity, with authentication establishing trust and encryption securing data integrity.
Defining Authentication: Purpose and Methods
Authentication confirms the identity of a user or system to ensure authorized access to resources by verifying credentials such as passwords, biometrics, or digital certificates. Its primary purpose is to prevent unauthorized access and protect sensitive information from identity-related threats. Common methods include multi-factor authentication, token-based authentication, and certificate-based authentication, each enhancing security by validating user legitimacy before granting access.
Understanding Encryption: Key Concepts and Types
Encryption transforms readable data into an encoded format, protecting information confidentiality by allowing only authorized parties with decryption keys to access the original content. Symmetric encryption uses a single key for both encryption and decryption, while asymmetric encryption employs a pair of public and private keys to enhance security and enable secure key exchange. Common algorithms include AES for symmetric encryption and RSA or ECC for asymmetric encryption, each serving critical roles in data protection across various applications.
Main Differences Between Authentication and Encryption
Authentication verifies the identity of users or systems by confirming credentials, ensuring that access is granted only to authorized entities. Encryption transforms data into unreadable ciphertext to protect confidentiality during storage or transmission, making information inaccessible to unauthorized parties. While authentication validates who is involved, encryption safeguards what is communicated or stored, highlighting their complementary roles in cybersecurity.
How Authentication Works in Digital Security
Authentication in digital security verifies the identity of users or devices by using mechanisms like passwords, biometrics, or digital certificates to ensure access is granted only to authorized entities. It often employs protocols such as multi-factor authentication and public key infrastructure (PKI) to enhance security by requiring multiple forms of verification and cryptographic methods. This process establishes trust and integrity before allowing access, differentiating it from encryption, which focuses on protecting data confidentiality during transmission or storage.
Encryption Algorithms and Their Applications
Encryption algorithms, such as AES (Advanced Encryption Standard), RSA (Rivest-Shamir-Adleman), and ECC (Elliptic Curve Cryptography), play a crucial role in securing data confidentiality by transforming readable data into an unreadable format. AES is widely used for symmetric key encryption in applications like securing wireless networks and data storage, while RSA and ECC are essential for asymmetric encryption in digital signatures and secure key exchange in protocols like TLS. These algorithms ensure data integrity and privacy across various domains, including online banking, email communication, and cloud computing environments.
Role of Authentication in Access Control
Authentication serves as the critical first step in access control by verifying the identity of users or systems before granting permissions, ensuring that only authorized entities gain entry. This process relies on credentials such as passwords, biometrics, or multi-factor authentication to establish trust and prevent unauthorized access. Unlike encryption, which protects data confidentiality during transmission or storage, authentication specifically focuses on validating identity to enforce access policies effectively.
Encryption in Data Protection and Privacy
Encryption transforms data into a secure format, making it unreadable to unauthorized users, ensuring confidentiality and privacy in data protection. It employs algorithms like AES and RSA to safeguard sensitive information during storage and transmission, preventing data breaches and cyberattacks. Encryption is a fundamental technology in protecting personal data, financial transactions, and communication channels across digital systems.
Common Misconceptions: Authentication vs Encryption
Authentication verifies the identity of a user or device, ensuring that access is granted only to authorized entities. Encryption protects data confidentiality by converting information into a coded format, preventing unauthorized access during transmission or storage. Common misconceptions confuse authentication as data protection and encryption as identity verification, but both serve distinct security functions essential for comprehensive cybersecurity.
Choosing the Right Solution: When to Use Authentication or Encryption
Choosing between authentication and encryption depends on the security goal: authentication verifies the identity of users or systems, ensuring data integrity and access control, while encryption protects data confidentiality by converting information into unreadable formats for unauthorized users. Authentication is crucial in scenarios requiring user verification, such as login systems and access management, whereas encryption is essential for safeguarding sensitive data during transmission or storage, like in VPNs and secure email communication. Combining both techniques often provides a comprehensive security approach, ensuring data is both confidential and accessible only to authorized entities.
Authentication Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com