Vertical integration streamlines your supply chain by consolidating multiple production stages under one organization, reducing costs and increasing control over quality. This strategy enhances market competitiveness and fosters smoother coordination between suppliers and distributors. Explore the rest of the article to understand how vertical integration can transform your business operations.
Table of Comparison
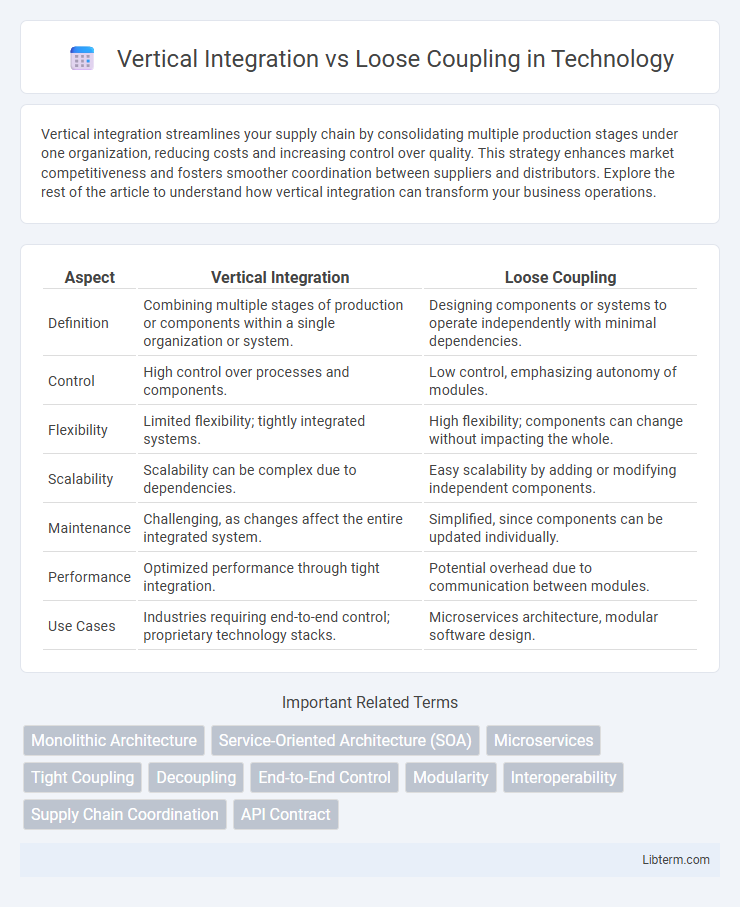
| Aspect | Vertical Integration | Loose Coupling |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Combining multiple stages of production or components within a single organization or system. | Designing components or systems to operate independently with minimal dependencies. |
| Control | High control over processes and components. | Low control, emphasizing autonomy of modules. |
| Flexibility | Limited flexibility; tightly integrated systems. | High flexibility; components can change without impacting the whole. |
| Scalability | Scalability can be complex due to dependencies. | Easy scalability by adding or modifying independent components. |
| Maintenance | Challenging, as changes affect the entire integrated system. | Simplified, since components can be updated individually. |
| Performance | Optimized performance through tight integration. | Potential overhead due to communication between modules. |
| Use Cases | Industries requiring end-to-end control; proprietary technology stacks. | Microservices architecture, modular software design. |
Introduction to Vertical Integration and Loose Coupling
Vertical integration involves consolidating multiple stages of production or service processes within a single organization to enhance control, reduce costs, and improve efficiency. Loose coupling refers to designing systems or organizational units with minimal dependencies, allowing each component to operate independently and adapt quickly to changes. Understanding vertical integration and loose coupling helps businesses optimize operational flexibility and control based on strategic goals.
Defining Vertical Integration in Business Systems
Vertical integration in business systems refers to the strategic consolidation of multiple stages of production or distribution within a single company, enhancing control over the supply chain and reducing reliance on external suppliers. This approach streamlines operations by aligning processes vertically, from raw material acquisition through manufacturing to final product delivery. By integrating these stages, companies can achieve cost efficiencies, improve coordination, and maintain higher quality standards across the entire system.
What is Loose Coupling? An Overview
Loose coupling is a design principle in software architecture where components or systems have minimal dependencies on each other, allowing independent modification and scalability. It enhances flexibility by enabling components to interact through well-defined interfaces without requiring intimate knowledge of each other's internal workings. This approach contrasts with vertical integration, promoting system resilience and easier maintenance in complex, distributed environments.
Key Differences Between Vertical Integration and Loose Coupling
Vertical integration centralizes control by combining multiple stages of production or distribution within a single organization, enhancing coordination and reducing dependency on external entities. Loose coupling allows independent components or systems to interact with minimal dependencies, promoting flexibility, scalability, and easier adaptability to change. Key differences include the level of control, with vertical integration emphasizing unified management, whereas loose coupling prioritizes modularity and autonomy among interconnected units.
Advantages of Vertical Integration
Vertical integration enhances operational efficiency by streamlining supply chain management and reducing production costs, leading to increased profit margins. It ensures greater control over quality and production timelines, minimizing risks associated with supplier dependency and improving product consistency. Firms practicing vertical integration can achieve competitive advantages through exclusive access to critical resources and improved market responsiveness.
Benefits of Loose Coupling
Loose coupling enhances system flexibility by allowing independent component updates without affecting the entire architecture, which reduces downtime and accelerates deployment cycles. It supports scalability and easier maintenance by isolating changes to specific modules, minimizing risks and improving fault tolerance. These benefits drive innovation and adaptability, crucial for dynamic environments and evolving business requirements.
Challenges and Risks of Vertical Integration
Vertical integration poses significant challenges such as high operational costs and reduced flexibility in responding to market changes, increasing vulnerability to economic downturns. The concentration of control within a single entity can lead to inefficiencies, diminished innovation, and potential regulatory scrutiny. These risks often outweigh the benefits, making vertical integration a complex strategic decision.
Drawbacks of Loose Coupling Approaches
Loose coupling can lead to increased complexity in managing dependencies and communication between components, resulting in potential performance bottlenecks. The need for extensive interface design and versioning control may introduce overhead in development and maintenance processes. Furthermore, debugging and tracing issues become more challenging due to the distributed nature of loosely coupled systems.
Real-World Examples: Vertical Integration vs Loose Coupling
Vertical integration is exemplified by Apple's control over its entire supply chain, enabling seamless hardware-software integration and enhanced product consistency. In contrast, loose coupling is evident in microservices architecture used by companies like Netflix, allowing independent service updates and scalability without centralized control. These approaches highlight the trade-offs between control and flexibility in system design.
Choosing the Right Strategy: Factors to Consider
Choosing between vertical integration and loose coupling depends on factors such as control, flexibility, and scalability requirements. Vertical integration offers enhanced control and streamlined processes, ideal for companies prioritizing uniformity and cost reduction. Loose coupling supports adaptability and easier integration with diverse systems, fitting businesses that demand rapid innovation and modular growth.
Vertical Integration Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com