Backend as a Service (BaaS) streamlines app development by providing ready-to-use backend infrastructure, including databases, authentication, and cloud storage, allowing developers to focus on frontend functionality. This service enhances scalability, reduces development time, and ensures seamless integration with various platforms and devices. Discover how BaaS can transform your development process by reading the full article.
Table of Comparison
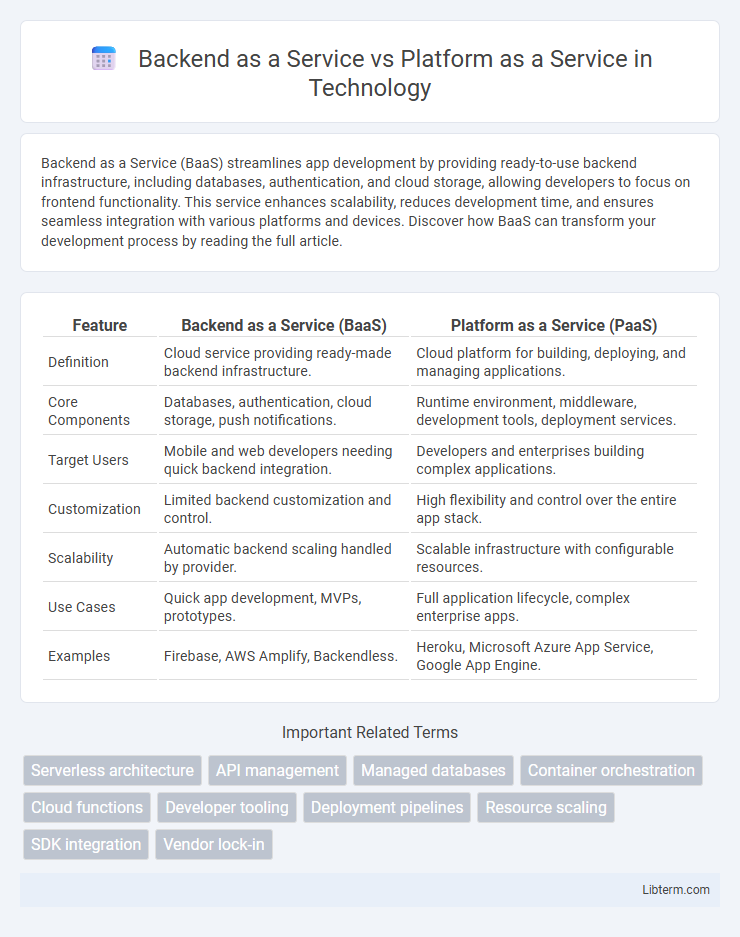
| Feature | Backend as a Service (BaaS) | Platform as a Service (PaaS) |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Cloud service providing ready-made backend infrastructure. | Cloud platform for building, deploying, and managing applications. |
| Core Components | Databases, authentication, cloud storage, push notifications. | Runtime environment, middleware, development tools, deployment services. |
| Target Users | Mobile and web developers needing quick backend integration. | Developers and enterprises building complex applications. |
| Customization | Limited backend customization and control. | High flexibility and control over the entire app stack. |
| Scalability | Automatic backend scaling handled by provider. | Scalable infrastructure with configurable resources. |
| Use Cases | Quick app development, MVPs, prototypes. | Full application lifecycle, complex enterprise apps. |
| Examples | Firebase, AWS Amplify, Backendless. | Heroku, Microsoft Azure App Service, Google App Engine. |
Introduction to Backend as a Service (BaaS) and Platform as a Service (PaaS)
Backend as a Service (BaaS) provides developers with ready-to-use cloud-based backend infrastructure, including database management, authentication, and cloud storage, enabling rapid app development without managing servers. Platform as a Service (PaaS) offers a comprehensive development environment with tools, runtime, and middleware, allowing developers to build, test, and deploy applications on a managed platform. Both BaaS and PaaS streamline development workflows but differ in scope: BaaS focuses on pre-built backend functionalities, while PaaS provides a full platform for application lifecycle management.
Core Features of BaaS
Backend as a Service (BaaS) offers core features such as user authentication, database management, cloud storage, and server-side logic, enabling developers to build and scale mobile and web applications rapidly without managing infrastructure. Unlike Platform as a Service (PaaS), which provides a broader environment for application deployment and development, BaaS focuses specifically on backend functionalities, including real-time databases and push notifications. This specialization allows BaaS to streamline backend integration, reduce development time, and simplify maintenance.
Core Features of PaaS
Platform as a Service (PaaS) provides a comprehensive environment for application development, offering core features such as integrated development tools, scalable infrastructure, middleware, and runtime environments. Unlike Backend as a Service (BaaS), which primarily focuses on backend functionalities like database management, authentication, and cloud storage, PaaS enables full lifecycle management including application design, testing, deployment, and monitoring. PaaS solutions support multi-language development, automated scaling, and seamless integration with databases and DevOps tools, enhancing developer productivity and operational efficiency.
Key Differences Between BaaS and PaaS
Backend as a Service (BaaS) offers pre-built backend functionality such as user authentication, databases, and cloud storage, allowing developers to focus on front-end development without managing server infrastructure. Platform as a Service (PaaS) provides a broader environment for developing, testing, and deploying applications with tools, runtime, and middleware, giving more control over application architecture. The key difference lies in BaaS's emphasis on standardized backend services for rapid app development versus PaaS's comprehensive platform for custom application lifecycle management and deployment.
Advantages of Using BaaS
Backend as a Service (BaaS) offers developers ready-to-use backend infrastructure, enabling faster application development by eliminating the need to build and maintain servers, databases, and APIs. BaaS platforms provide scalable storage, user authentication, and real-time data synchronization, improving operational efficiency and reducing development costs. Compared to Platform as a Service (PaaS), BaaS focuses more on automating backend tasks, allowing frontend developers to concentrate on user experience and application functionality.
Advantages of Using PaaS
Platform as a Service (PaaS) offers developers a comprehensive environment with built-in infrastructure, middleware, and development tools, accelerating application development and deployment. PaaS supports scalability and integration with a wide range of services, enabling seamless management of complex applications without handling server maintenance. Unlike Backend as a Service (BaaS), PaaS provides greater control and flexibility over the application stack, facilitating custom workflows and enterprise-grade security features.
Common Use Cases for BaaS
Backend as a Service (BaaS) is commonly used to streamline mobile app development by providing ready-made backend functionalities such as user authentication, database management, and push notifications. It enables developers to focus on frontend development while relying on cloud-hosted services for server-side operations, ideal for startups and rapid prototyping. Unlike Platform as a Service (PaaS), which offers a broader environment for deploying and managing applications, BaaS targets developers needing scalable backend infrastructure without managing servers.
Common Use Cases for PaaS
Platform as a Service (PaaS) is commonly used for application development and deployment, offering tools for coding, testing, and collaboration that streamline software lifecycle management. It supports complex workflows, including AI integration, IoT applications, and multi-cloud environments, making it ideal for businesses requiring scalable infrastructure and flexible development environments. In contrast, Backend as a Service (BaaS) primarily focuses on providing ready-made backend components like databases, authentication, and cloud storage, reducing the need for custom server-side coding.
Factors to Consider When Choosing Between BaaS and PaaS
When choosing between Backend as a Service (BaaS) and Platform as a Service (PaaS), consider factors such as development speed, customization needs, and scalability requirements. BaaS offers rapid backend integration with pre-built services, ideal for projects needing quick deployment but less flexibility, while PaaS provides a more customizable environment for building and managing applications with greater control over infrastructure. Evaluate team expertise, project complexity, and long-term maintenance plans to determine the best fit between the two service models.
Conclusion: Which Solution Fits Your Project?
Backend as a Service (BaaS) offers pre-built backend functionalities ideal for rapid development and projects needing minimal server management, while Platform as a Service (PaaS) provides more control and flexibility for custom application infrastructure and complex deployments. Choosing between BaaS and PaaS depends on project requirements, scalability needs, and developer expertise, with BaaS suited for startups and quick MVPs and PaaS fitting enterprise-grade applications demanding customization. Evaluating factors like cost, time-to-market, and maintenance overhead ensures the optimal backend solution aligns with your project's goals.
Backend as a Service Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com