A hardware wallet provides secure, offline storage for your cryptocurrency private keys, significantly reducing the risk of hacking or theft compared to online wallets. These devices use robust encryption and physical security measures to safeguard your digital assets. Discover how a hardware wallet can enhance your crypto security and protect your investments by exploring the rest of this article.
Table of Comparison
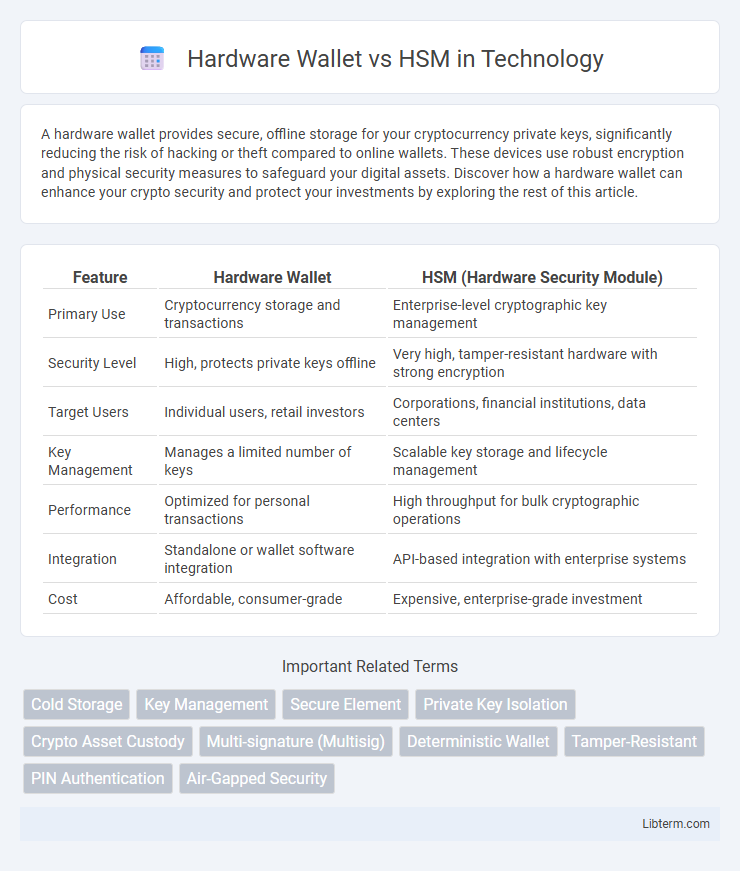
| Feature | Hardware Wallet | HSM (Hardware Security Module) |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Use | Cryptocurrency storage and transactions | Enterprise-level cryptographic key management |
| Security Level | High, protects private keys offline | Very high, tamper-resistant hardware with strong encryption |
| Target Users | Individual users, retail investors | Corporations, financial institutions, data centers |
| Key Management | Manages a limited number of keys | Scalable key storage and lifecycle management |
| Performance | Optimized for personal transactions | High throughput for bulk cryptographic operations |
| Integration | Standalone or wallet software integration | API-based integration with enterprise systems |
| Cost | Affordable, consumer-grade | Expensive, enterprise-grade investment |
Introduction to Hardware Wallets and HSMs
Hardware wallets are physical devices designed to securely store cryptocurrency private keys offline, preventing unauthorized access and cyber threats. Hardware Security Modules (HSMs) are specialized physical computing devices used by enterprises to manage cryptographic keys and perform encryption, decryption, and authentication functions with high security standards. Both hardware wallets and HSMs protect sensitive cryptographic material but differ in scope, with hardware wallets targeting individual users and HSMs serving large-scale organizational security needs.
Core Functions and Use Cases
Hardware wallets provide secure, offline storage for individual cryptocurrency private keys, enabling safe transaction signing and protection against hacking. Hardware Security Modules (HSMs) serve enterprise-level cryptographic key management, offering high-throughput encryption, digital signing, and key lifecycle control in data centers and financial institutions. Core functions of hardware wallets focus on personal asset security and ease of use, while HSMs prioritize regulatory compliance, scalability, and integration into complex IT infrastructures.
Security Architecture Comparison
Hardware wallets utilize secure elements and isolated environments to protect private keys from malware and physical tampering, offering robust encryption and user-controlled key management. Hardware Security Modules (HSMs) provide enterprise-grade security with tamper-resistant hardware, access control, and cryptographic key lifecycle management, designed to protect keys in high-volume transaction environments. Both architectures emphasize physical security, but HSMs integrate advanced audit capabilities and compliance certifications, whereas hardware wallets prioritize user-friendly interfaces and portable defense mechanisms.
Key Management and Storage Mechanisms
Hardware wallets store private keys in a tamper-resistant environment, isolated from network access, using secure elements or dedicated chips that protect keys via encryption and physical safeguards. Hardware Security Modules (HSMs) provide enterprise-grade key management with high availability, centralized control, and robust cryptographic operations, often incorporating multi-factor authentication and strict access policies to protect keys during generation, storage, and usage. While hardware wallets prioritize user-controlled key custody for digital assets, HSMs cater to large-scale organizational needs requiring regulated, auditable key management across complex infrastructures.
User Accessibility and Interface
Hardware wallets offer user-friendly interfaces with touchscreen displays or simple button controls, making them accessible for both beginners and experienced cryptocurrency holders. HSMs (Hardware Security Modules) typically require specialized knowledge and command-line interaction, posing a steeper learning curve for general users. The intuitive design of hardware wallets ensures easier management of private keys, whereas HSMs prioritize enterprise-level security with limited user interaction.
Supported Cryptocurrencies and Assets
Hardware wallets typically support a wide range of cryptocurrencies, including popular assets like Bitcoin, Ethereum, and various ERC-20 tokens, as well as many altcoins, offering users versatility in managing diverse portfolios. Hardware Security Modules (HSMs) primarily focus on securing cryptographic keys for enterprise-level applications and may support fewer directly managed cryptocurrencies but excel in handling large-scale, multi-asset custody with strong compliance and audit features. While hardware wallets prioritize user-friendly interfaces and compatibility with multiple blockchain networks, HSMs provide robust, scalable security solutions geared towards institutional asset management and customized cryptographic operations.
Regulatory Compliance and Certifications
Hardware wallets and Hardware Security Modules (HSMs) differ significantly in regulatory compliance and certifications, with HSMs often adhering to rigorous industry standards such as FIPS 140-2/140-3 and Common Criteria, ensuring robust security for enterprise and government environments. Hardware wallets, designed primarily for individual cryptocurrency storage, may offer some security certifications but typically lack the extensive regulatory compliance required for institutional use. Organizations subject to strict regulatory frameworks prioritize HSMs due to their certified tamper-resistance and standardized cryptographic processing, essential for meeting compliance mandates like GDPR, HIPAA, and PCI DSS.
Integration and Deployment Scenarios
Hardware wallets provide seamless integration with personal devices through USB or Bluetooth, making them ideal for individual cryptocurrency storage and secure private key management with minimal setup. Hardware Security Modules (HSMs) are designed for enterprise environments, offering robust API support for integration with large-scale financial systems, automated key management, and compliance with regulatory standards. Deployment scenarios for hardware wallets favor decentralized users seeking portable security, while HSMs are deployed in data centers or cloud infrastructures requiring high-throughput cryptographic operations and centralized control.
Cost and Maintenance Considerations
Hardware wallets typically offer a lower initial cost and minimal maintenance, making them accessible for individual users managing personal crypto assets. HSMs (Hardware Security Modules) incur significantly higher upfront expenses and require specialized maintenance, often demanding dedicated IT personnel and regular firmware updates to ensure compliance and security standards. The total cost of ownership for HSMs includes ongoing support contracts and potential hardware replacement, which contrasts with the relatively straightforward upkeep of hardware wallets.
Choosing Between Hardware Wallet and HSM
Choosing between a hardware wallet and a hardware security module (HSM) depends on the specific security needs and use cases of the user or organization. Hardware wallets are optimal for individual cryptocurrency holders seeking secure, offline private key storage with user-friendly interfaces, while HSMs provide enterprise-grade cryptographic key management and high-performance hardware security for large-scale operations. Evaluating factors such as transaction volume, compliance requirements, and integration capabilities helps determine the most appropriate solution for safeguarding digital assets.
Hardware Wallet Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com