A Content Delivery Network (CDN) enhances website performance by distributing content across multiple servers worldwide, reducing latency and improving load times for users. It protects your site from traffic surges and potential cyberattacks by handling data efficiently and securely. Discover how integrating a CDN can transform your online presence in the rest of this article.
Table of Comparison
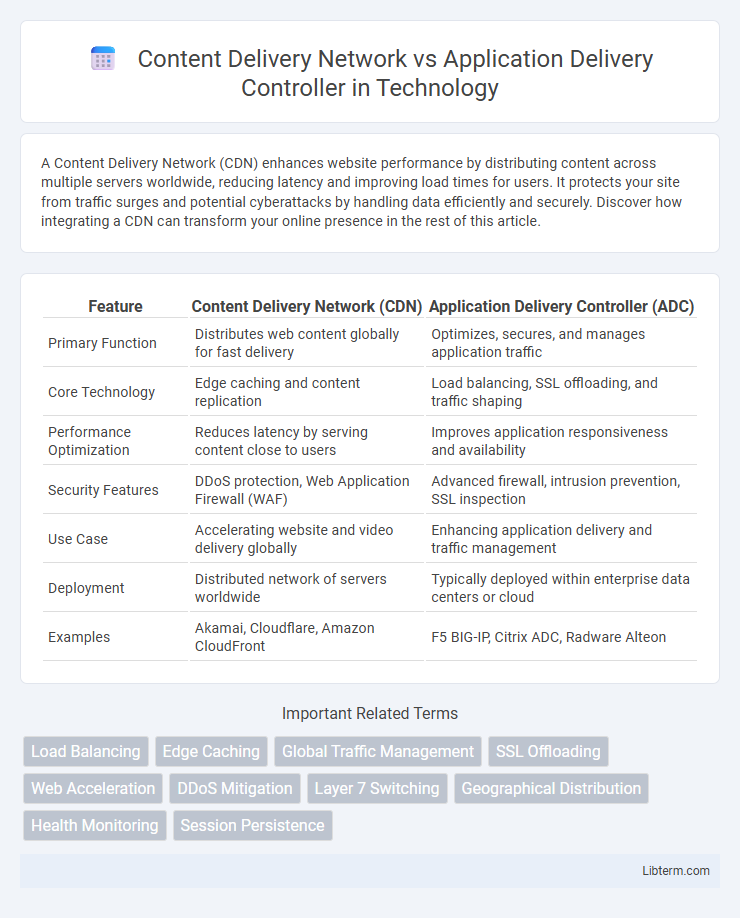
| Feature | Content Delivery Network (CDN) | Application Delivery Controller (ADC) |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Function | Distributes web content globally for fast delivery | Optimizes, secures, and manages application traffic |
| Core Technology | Edge caching and content replication | Load balancing, SSL offloading, and traffic shaping |
| Performance Optimization | Reduces latency by serving content close to users | Improves application responsiveness and availability |
| Security Features | DDoS protection, Web Application Firewall (WAF) | Advanced firewall, intrusion prevention, SSL inspection |
| Use Case | Accelerating website and video delivery globally | Enhancing application delivery and traffic management |
| Deployment | Distributed network of servers worldwide | Typically deployed within enterprise data centers or cloud |
| Examples | Akamai, Cloudflare, Amazon CloudFront | F5 BIG-IP, Citrix ADC, Radware Alteon |
Introduction to Content Delivery Networks (CDN)
Content Delivery Networks (CDNs) enhance web performance by distributing content across multiple geographically dispersed edge servers, reducing latency and improving load times for users worldwide. CDNs cache static assets such as images, videos, and scripts closer to end-users, optimizing bandwidth and minimizing server overload. Unlike Application Delivery Controllers (ADCs) that focus on optimizing and securing application traffic within data centers, CDNs primarily accelerate content delivery and improve user experience by leveraging global network infrastructure.
What is an Application Delivery Controller (ADC)?
An Application Delivery Controller (ADC) is a network device that manages and optimizes the delivery of applications by load balancing traffic, accelerating application performance, and providing security features such as SSL offloading and web application firewalls. Unlike Content Delivery Networks (CDNs) that primarily distribute and cache static content geographically, ADCs dynamically control application traffic within data centers or cloud environments to ensure high availability and improved user experience. Key functionalities of ADCs include traffic shaping, protocol optimization, and application acceleration tailored to enhance the responsiveness and reliability of enterprise applications.
Key Functions of CDNs vs ADCs
Content Delivery Networks (CDNs) primarily optimize web content delivery by caching static resources across geographically distributed servers, reducing latency and improving load times for end-users globally. Application Delivery Controllers (ADCs) focus on load balancing, traffic management, and ensuring high availability and security for applications in data centers or cloud environments. While CDNs accelerate content distribution at the edge, ADCs provide advanced application-level control, including SSL offloading, authentication, and application firewalling.
Performance Enhancement: CDN vs ADC
Content Delivery Networks (CDNs) improve performance by caching content on geographically distributed servers, reducing latency and accelerating static content delivery for global users. Application Delivery Controllers (ADCs) optimize dynamic application traffic through load balancing, SSL offloading, and application acceleration, enhancing backend server efficiency and responsiveness. Combining CDN and ADC technologies delivers superior performance by addressing both content distribution and application-level optimization.
Security Features in CDN and ADC
Content Delivery Networks (CDNs) enhance security by providing DDoS mitigation, web application firewalls (WAF), and SSL/TLS encryption to protect data in transit and shield origin servers from attacks. Application Delivery Controllers (ADCs) offer advanced security features such as intrusion detection and prevention systems (IDPS), granular access controls, and application-layer firewall capabilities to safeguard backend applications. Both CDN and ADC complement each other in securing web infrastructure by distributing traffic while enforcing robust application-level security policies.
Scalability and Flexibility Comparison
Content Delivery Networks (CDNs) excel in scalability by distributing web content across numerous global servers, enabling rapid and efficient content delivery under heavy traffic loads. Application Delivery Controllers (ADCs) offer greater flexibility through advanced load balancing, application acceleration, and security functions that optimize application performance and reliability. While CDNs primarily focus on geographical scalability for static and dynamic content, ADCs provide granular control and adaptability for diverse application delivery requirements.
Use Cases for Content Delivery Networks
Content Delivery Networks (CDNs) are primarily used to enhance website performance by distributing content across multiple geographically dispersed servers, reducing latency and improving load times for end users. Typical use cases include accelerating web page delivery, streaming video content, and mitigating Distributed Denial of Service (DDoS) attacks through traffic filtering and load balancing. In contrast, Application Delivery Controllers (ADCs) offer advanced application-level routing, security, and optimization features for enterprise applications, focusing on server health monitoring, SSL offloading, and granular traffic management.
Application Scenarios for Application Delivery Controllers
Application Delivery Controllers (ADCs) excel in optimizing web application performance, enhancing security, and ensuring high availability by managing traffic load balancing, SSL offloading, and application acceleration. Common application scenarios for ADCs include e-commerce platforms requiring secure, fast transaction processing, enterprise data centers needing robust application firewall and access control, and cloud environments where dynamic resource allocation and scalability are critical. ADCs also support content switching and application-layer security, making them indispensable for organizations prioritizing user experience and protection against DDoS attacks and application-layer threats.
Cost Considerations: CDN vs ADC
Content Delivery Network (CDN) typically offers lower upfront and operational costs due to its distributed architecture leveraging existing internet infrastructure, making it cost-effective for scaling content delivery across global regions. In contrast, Application Delivery Controller (ADC) involves higher capital expenditure with specialized hardware or software licenses, plus maintenance expenses reflecting advanced application-layer management features and local traffic optimization. Organizations must weigh CDN's cost-efficiency for broad content distribution against ADC's higher investment for granular traffic control and enhanced security within enterprise environments.
Choosing the Right Solution for Your Business
Choosing the right solution between a Content Delivery Network (CDN) and an Application Delivery Controller (ADC) depends on your business's specific needs for performance, security, and scalability. CDNs excel at optimizing content distribution globally by caching static assets and reducing latency, ideal for businesses with high traffic and widespread audiences. ADCs offer advanced traffic management, load balancing, and security at the application layer, making them suitable for enterprises requiring granular control over application delivery and reliability.
Content Delivery Network Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com