DNS load balancing distributes incoming network traffic across multiple servers by resolving domain names to different IP addresses in a round-robin or weighted manner, enhancing availability and performance. This method helps prevent server overload, reduce latency, and ensure seamless user experiences during peak traffic times. Discover how DNS load balancing can optimize Your network infrastructure in the full article.
Table of Comparison
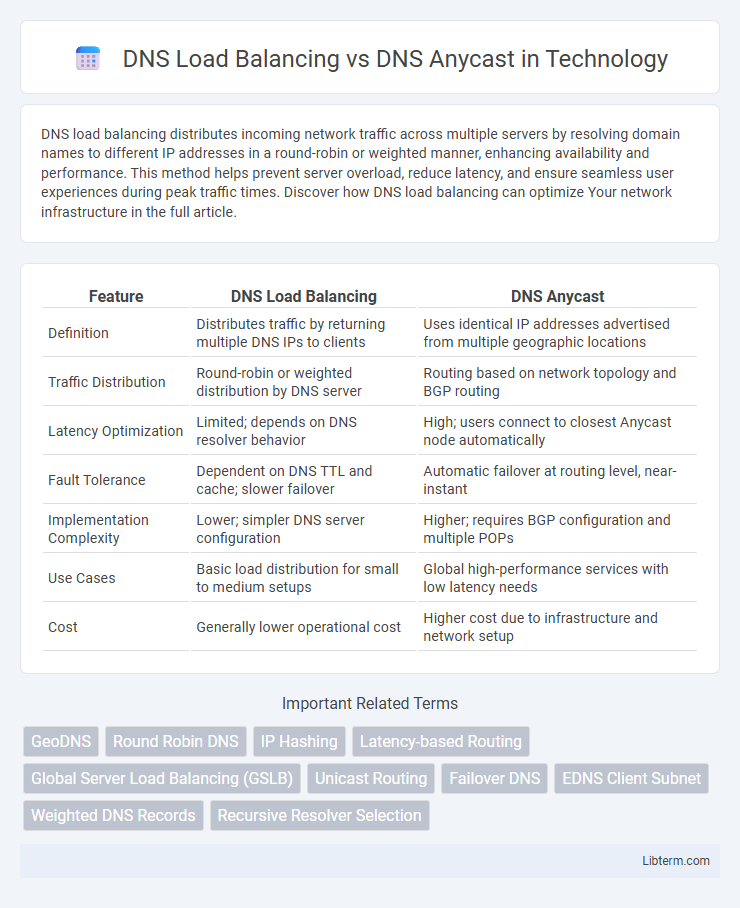
| Feature | DNS Load Balancing | DNS Anycast |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Distributes traffic by returning multiple DNS IPs to clients | Uses identical IP addresses advertised from multiple geographic locations |
| Traffic Distribution | Round-robin or weighted distribution by DNS server | Routing based on network topology and BGP routing |
| Latency Optimization | Limited; depends on DNS resolver behavior | High; users connect to closest Anycast node automatically |
| Fault Tolerance | Dependent on DNS TTL and cache; slower failover | Automatic failover at routing level, near-instant |
| Implementation Complexity | Lower; simpler DNS server configuration | Higher; requires BGP configuration and multiple POPs |
| Use Cases | Basic load distribution for small to medium setups | Global high-performance services with low latency needs |
| Cost | Generally lower operational cost | Higher cost due to infrastructure and network setup |
Introduction to DNS Load Balancing and Anycast
DNS Load Balancing distributes incoming domain name system queries across multiple servers to optimize response times and ensure high availability, often using round-robin or weighted approaches. DNS Anycast assigns the same IP address to multiple geographically dispersed servers, directing user requests to the nearest or best-performing server based on network topology, thereby improving latency and fault tolerance. Both techniques enhance DNS reliability and performance but utilize different routing and distribution mechanisms.
What is DNS Load Balancing?
DNS Load Balancing distributes incoming DNS queries across multiple servers to enhance reliability and optimize resource utilization by using techniques such as round-robin, weighted, or geographic routing. This method improves fault tolerance and reduces latency by directing traffic to the most available or closest server based on real-time load conditions. DNS Load Balancing contrasts with DNS Anycast, which routes users to the nearest data center using the same IP address advertised from multiple locations, focusing more on routing efficiency rather than dynamic load distribution.
How DNS Anycast Works
DNS Anycast works by assigning the same IP address to multiple DNS servers distributed across various geographic locations, enabling user queries to be routed to the nearest or best-performing server based on network topology and routing protocols like BGP. This method reduces latency and improves redundancy by automatically directing traffic to available servers in the event of a failure. Unlike DNS Load Balancing, which distributes queries at the application level, DNS Anycast leverages network-layer routing to provide efficient, resilient DNS resolution globally.
Key Differences Between DNS Load Balancing and Anycast
DNS Load Balancing distributes traffic by assigning different IP addresses to a single domain name, directing users to multiple servers based on algorithms like round-robin or weighted responses, optimizing resource use at the application layer. DNS Anycast routes queries to the nearest instance of a DNS server using the same IP address advertised from multiple geographic locations, enhancing resilience and reducing latency at the network layer. Load balancing manages client distribution dynamically to handle capacity, while Anycast focuses on network topology to provide fault tolerance and high availability.
Performance Benefits: Load Balancing vs. Anycast
DNS load balancing distributes incoming traffic across multiple servers to optimize response times and prevent overload by dynamically adjusting based on server health and capacity. DNS Anycast routes user requests to the geographically nearest or fastest data center using the same IP address, minimizing latency and enhancing global performance consistency. While load balancing excels in managing server workloads and improving redundancy, Anycast provides superior latency reduction and resilience through network-level traffic distribution.
Scalability and Flexibility Comparison
DNS Load Balancing distributes traffic across multiple servers using multiple IP addresses to enhance scalability by balancing loads dynamically based on server availability and response times. DNS Anycast routes user requests to the nearest data center or server based on network topology, offering high scalability by reducing latency and improving redundancy with static IP addresses advertised in multiple locations. Flexibility is higher in DNS Load Balancing due to its ability to customize traffic distribution policies, while DNS Anycast provides less configuration flexibility but excels in automatic failover and consistent global performance.
Security Implications: Load Balancing and Anycast
DNS load balancing distributes traffic across multiple servers, reducing the risk of individual server overload but may expose attack vectors through DNS response manipulation or spoofing due to reliance on client-side DNS resolution. DNS Anycast enhances security by broadcasting the same IP address from multiple geographically dispersed locations, enabling rapid mitigation of DDoS attacks through network-level traffic absorption and improved resilience. Both methods improve availability, yet Anycast provides stronger protection against volumetric attacks by leveraging routing protocols rather than relying solely on DNS-based distribution mechanisms.
Use Cases for DNS Load Balancing
DNS Load Balancing is ideal for distributing client requests across multiple servers to enhance availability and optimize performance in high-traffic web applications, content delivery networks (CDNs), and geographically dispersed data centers. It enables dynamic traffic management by assigning different IP addresses to a single domain name, allowing for efficient resource utilization and fault tolerance. Use cases include ecommerce platforms handling fluctuating loads, SaaS applications requiring consistent uptime, and global services needing localized response routing.
Use Cases for DNS Anycast
DNS Anycast is ideal for global content delivery networks (CDNs) requiring low-latency and high-availability by routing user queries to the nearest or best-performing data center. It excels in mitigating distributed denial-of-service (DDoS) attacks by dispersing traffic across multiple nodes simultaneously. Enterprises leveraging cloud services benefit from DNS Anycast to provide fault tolerance and consistent user experience across diverse geographic regions.
Choosing the Right DNS Solution for Your Needs
DNS Load Balancing distributes incoming traffic across multiple servers using DNS responses with different IP addresses, optimizing resource usage and reducing latency for specific regions. DNS Anycast routes user requests to the nearest or best-performing server using the same IP address advertised from multiple locations, enhancing global availability and mitigating DDoS attacks. Choosing the right DNS solution depends on your infrastructure scale, geographic distribution, and specific goals such as performance optimization with Load Balancing or improved redundancy and security with Anycast.
DNS Load Balancing Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com