Scrum is an agile framework designed to help teams work collaboratively, delivering products incrementally through defined roles, events, and artifacts. It emphasizes flexibility, continuous feedback, and iterative progress to improve productivity and adapt to changing requirements. Discover how Scrum can transform your project management by exploring the key principles and practices in the rest of this article.
Table of Comparison
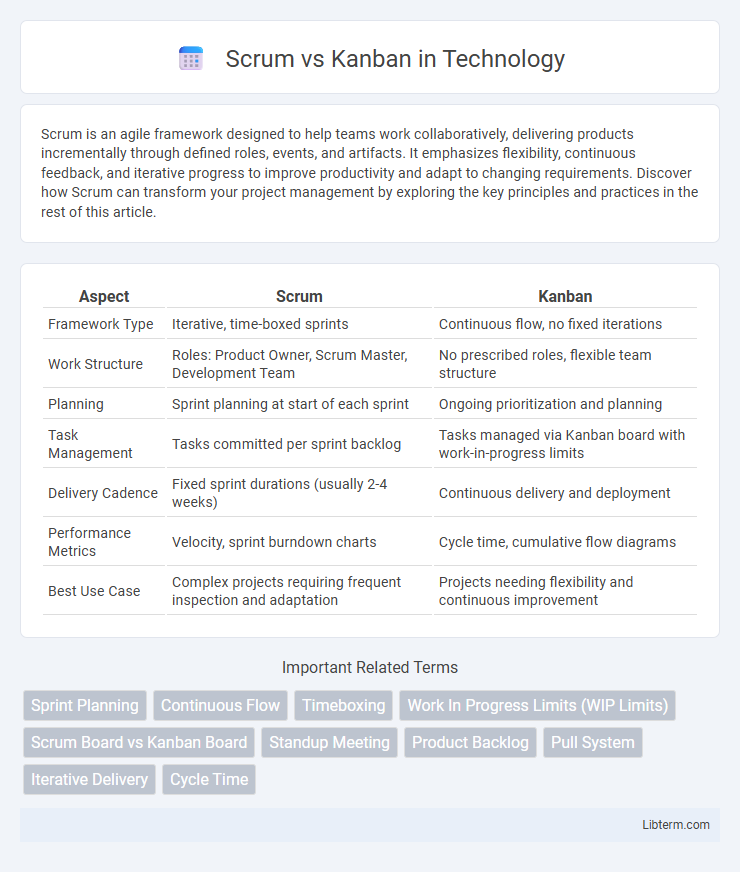
| Aspect | Scrum | Kanban |
|---|---|---|
| Framework Type | Iterative, time-boxed sprints | Continuous flow, no fixed iterations |
| Work Structure | Roles: Product Owner, Scrum Master, Development Team | No prescribed roles, flexible team structure |
| Planning | Sprint planning at start of each sprint | Ongoing prioritization and planning |
| Task Management | Tasks committed per sprint backlog | Tasks managed via Kanban board with work-in-progress limits |
| Delivery Cadence | Fixed sprint durations (usually 2-4 weeks) | Continuous delivery and deployment |
| Performance Metrics | Velocity, sprint burndown charts | Cycle time, cumulative flow diagrams |
| Best Use Case | Complex projects requiring frequent inspection and adaptation | Projects needing flexibility and continuous improvement |
Introduction to Agile Frameworks
Scrum and Kanban are two popular Agile frameworks designed to improve project management and product development efficiency. Scrum emphasizes fixed-length sprints, defined roles such as Scrum Master and Product Owner, and regular ceremonies including sprint planning, daily stand-ups, and retrospectives. Kanban focuses on continuous delivery through visual workflow management using boards and limits on work-in-progress to optimize task flow and reduce bottlenecks.
Core Principles: Scrum vs Kanban
Scrum centers on fixed-length sprints, roles such as Scrum Master and Product Owner, and ceremonies like daily stand-ups and sprint reviews to promote iterative progress and accountability. Kanban emphasizes continuous delivery through visualizing work on a board, limiting work in progress (WIP), and managing flow without prescribed roles or time-boxed events. Both frameworks prioritize transparency and efficiency but differ fundamentally in structure, with Scrum focusing on time-boxed iterations and Kanban on continuous improvement and flow management.
Roles and Responsibilities
Scrum defines specific roles including Product Owner, Scrum Master, and Development Team, each with clear responsibilities such as backlog management, process facilitation, and delivering increments. Kanban emphasizes flexible roles without formal titles, promoting shared responsibility among team members to visualize work, limit work in progress, and optimize flow. Scrum requires time-boxed events and role-driven accountability, while Kanban relies on continuous collaboration and evolutionary process improvements.
Workflow and Process Structure
Scrum follows a structured workflow with fixed-length sprints, defined roles, and time-boxed events designed to promote iterative progress and regular feedback. Kanban emphasizes a continuous flow process where work items move through predefined stages on a visual board, allowing teams to manage tasks flexibly without prescribed roles or time constraints. While Scrum prescribes ceremonies like sprint planning and retrospectives, Kanban focuses on workflow visualization and continuous delivery to optimize efficiency and limit work in progress.
Planning and Scheduling
Scrum employs time-boxed sprints typically lasting two to four weeks, with detailed sprint planning sessions to define tasks and commitments, ensuring a structured schedule and predictable delivery. Kanban utilizes a continuous flow approach without fixed sprint timelines, emphasizing real-time prioritization and flexible scheduling through work-in-progress limits to optimize efficiency. Scrum's planning is rigid and time-bound for iterative progress, whereas Kanban's scheduling remains adaptive, allowing teams to respond dynamically to workflow changes.
Flexibility and Adaptability
Scrum offers structured flexibility through fixed-length sprints and defined roles, promoting adaptability within time-boxed iterations. Kanban emphasizes continuous flow and visual workflow management, enabling real-time adjustments without rigid time constraints. Both methodologies enhance team responsiveness but differ in approach: Scrum adapts via sprint planning and retrospectives, while Kanban adapts through ongoing prioritization and workflow optimization.
Visual Management Tools
Scrum utilizes visual management tools such as task boards and sprint burndown charts to track progress within fixed time-boxed iterations, emphasizing sprint goals and team commitments. Kanban employs continuous flow visual boards with columns representing workflow stages, highlighting work-in-progress limits to optimize efficiency and identify bottlenecks in real-time. Both frameworks leverage visual management tools to enhance transparency, improve collaboration, and streamline task tracking but differ in their approach to work pacing and process structure.
Metrics and Performance Tracking
Scrum emphasizes velocity and sprint burndown charts to track performance, enabling teams to measure completed story points per sprint and identify scope changes. Kanban relies on cycle time, lead time, and cumulative flow diagrams to monitor work-in-progress and optimize continuous delivery efficiency. Both frameworks use metrics to enhance transparency, but Scrum focuses on time-boxed iterations, while Kanban prioritizes flow and throughput for adaptive workflow management.
Choosing the Right Framework
Scrum and Kanban are agile frameworks designed to enhance project management, but choosing the right one depends on the team's workflow and project needs. Scrum uses fixed-length sprints, roles, and ceremonies ideal for projects requiring structured planning and iterative delivery. Kanban offers continuous delivery and visual workflow management, making it suitable for teams needing flexibility and constant prioritization without rigid timeboxes.
Conclusion: Which Suits Your Team?
Scrum suits teams with projects requiring fixed-length sprints, clear roles, and regular reviews to maximize iterative progress and predictable delivery. Kanban is ideal for teams needing continuous workflow management, flexibility, and real-time task prioritization without strict time-boxing. Evaluating project complexity, team size, and delivery cadence determines whether Scrum's structured framework or Kanban's flow-based approach aligns better with your team's goals.
Scrum Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com