Effective infrastructure monitoring ensures continuous performance, availability, and security of your IT systems by tracking the health of servers, networks, and applications in real-time. By identifying potential issues before they impact operations, you can maintain optimal efficiency and reduce downtime, safeguarding your organization's productivity. Discover how advanced monitoring tools and strategies can enhance your infrastructure's reliability throughout the rest of this article.
Table of Comparison
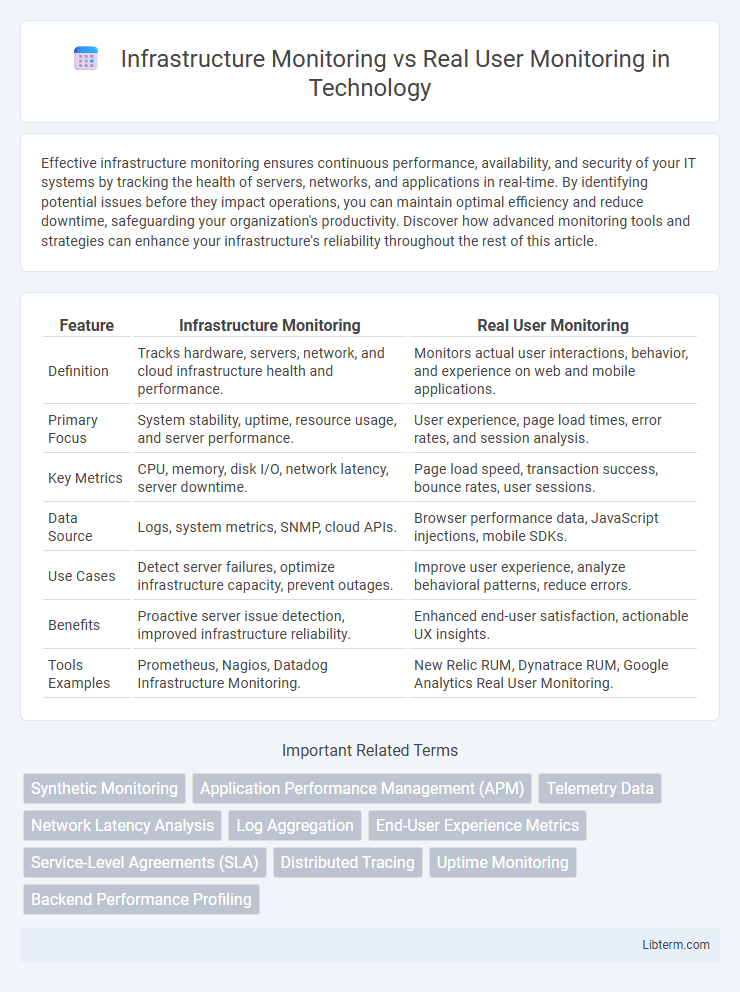
| Feature | Infrastructure Monitoring | Real User Monitoring |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Tracks hardware, servers, network, and cloud infrastructure health and performance. | Monitors actual user interactions, behavior, and experience on web and mobile applications. |
| Primary Focus | System stability, uptime, resource usage, and server performance. | User experience, page load times, error rates, and session analysis. |
| Key Metrics | CPU, memory, disk I/O, network latency, server downtime. | Page load speed, transaction success, bounce rates, user sessions. |
| Data Source | Logs, system metrics, SNMP, cloud APIs. | Browser performance data, JavaScript injections, mobile SDKs. |
| Use Cases | Detect server failures, optimize infrastructure capacity, prevent outages. | Improve user experience, analyze behavioral patterns, reduce errors. |
| Benefits | Proactive server issue detection, improved infrastructure reliability. | Enhanced end-user satisfaction, actionable UX insights. |
| Tools Examples | Prometheus, Nagios, Datadog Infrastructure Monitoring. | New Relic RUM, Dynatrace RUM, Google Analytics Real User Monitoring. |
Introduction to Infrastructure Monitoring and Real User Monitoring
Infrastructure Monitoring tracks the health and performance of IT components such as servers, networks, and databases to ensure system reliability and uptime. Real User Monitoring (RUM) captures and analyzes actual user interactions within web applications, providing insights into user experience and frontend performance metrics. Together, these monitoring types offer comprehensive visibility by addressing backend infrastructure stability and real-time user behavior performance.
Key Differences Between Infrastructure Monitoring and Real User Monitoring
Infrastructure Monitoring tracks the performance and health of servers, networks, and hardware components to ensure system stability and uptime. Real User Monitoring collects data on actual user interactions, measuring experience metrics such as page load times, transaction success rates, and user behavior patterns. The key difference lies in Infrastructure Monitoring's focus on backend system performance, while Real User Monitoring centers on front-end user experience and application responsiveness.
Core Components of Infrastructure Monitoring
Infrastructure Monitoring primarily focuses on core components such as servers, network devices, databases, and cloud resources to ensure optimal system performance and availability. It involves tracking metrics like CPU utilization, memory usage, disk I/O, and network latency to detect hardware failures, bottlenecks, or capacity issues. By continuously analyzing these components, Infrastructure Monitoring enables proactive maintenance and minimizes downtime, distinct from Real User Monitoring which centers on actual user interactions and experience.
Essential Features of Real User Monitoring
Real User Monitoring (RUM) captures actual user interactions by tracking metrics such as page load time, response time, and user behavior across devices and browsers, enabling precise performance analysis from the end-user perspective. Unlike Infrastructure Monitoring, which focuses on server health, CPU usage, and network performance, RUM provides insights into frontend performance issues and user experience bottlenecks in real-time. Essential features of RUM include session replay, geographic data analysis, error tracking, and user journey visualization, all crucial for optimizing site performance and user satisfaction.
Use Cases for Infrastructure Monitoring
Infrastructure monitoring enables IT teams to track server health, network performance, and database availability in real time, ensuring optimal system uptime and quick issue resolution. It supports capacity planning and resource optimization by analyzing metrics such as CPU usage, memory consumption, and disk I/O across physical and virtual environments. Use cases include detecting hardware failures, mitigating network bottlenecks, and maintaining compliance through continuous visibility into cloud infrastructure and on-premises data centers.
When to Choose Real User Monitoring
Real User Monitoring (RUM) is essential when businesses need to capture actual user interactions and experience across various devices, browsers, and geographies, providing real-time data on performance and usability. It is particularly valuable for websites and applications with diverse user bases requiring insights into load times, errors, and transaction paths from the end-user perspective. Unlike Infrastructure Monitoring, which tracks server and network health, RUM prioritizes user-centric metrics to optimize frontend performance and enhance customer satisfaction.
Benefits of Combining Both Monitoring Approaches
Combining Infrastructure Monitoring and Real User Monitoring enhances overall system visibility by correlating backend performance metrics with actual user experience data, enabling faster issue detection and resolution. This integrated approach improves operational efficiency through proactive infrastructure management aligned with real-time user interaction insights, reducing downtime and optimizing resource allocation. Organizations benefit from comprehensive analytics that drive informed decision-making and elevate service reliability across the entire technology stack.
Challenges in Implementing Monitoring Solutions
Infrastructure Monitoring faces challenges such as managing diverse and complex hardware environments, ensuring real-time data collection across distributed systems, and handling large volumes of performance metrics for accurate analysis. Real User Monitoring struggles with capturing comprehensive user interactions across various devices and browsers, dealing with privacy regulations like GDPR, and integrating user experience data with backend performance metrics for holistic insights. Both solutions require scalable architectures and seamless integration with existing IT frameworks to provide actionable alerts while minimizing false positives.
Best Practices for Monitoring Strategy Integration
Combining Infrastructure Monitoring and Real User Monitoring (RUM) enhances end-to-end visibility by correlating system performance metrics with actual user experiences. Best practices for monitoring strategy integration include establishing a unified dashboard to align backend infrastructure health with frontend user interactions, enabling faster root cause analysis. Implementing automated alerting mechanisms based on cross-layer insights ensures proactive problem resolution and continuous optimization of both application infrastructure and user satisfaction.
Future Trends in Infrastructure and Real User Monitoring
Future trends in infrastructure monitoring emphasize AI-driven automation for predictive maintenance and extensive integration with cloud-native environments to enhance scalability and resilience. Real User Monitoring (RUM) is evolving towards deeper analytics powered by machine learning, capturing complex user interactions and behavioral patterns in real time for improved user experience personalization. Both domains increasingly leverage edge computing and observability platforms that unify metrics, logs, and traces to deliver holistic insights across distributed systems and user journeys.
Infrastructure Monitoring Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com