Pentest and code review are essential practices for identifying security vulnerabilities and improving the overall robustness of your software applications. Penetration testing simulates real-world attacks to uncover exploitable weaknesses, while code review focuses on detecting flaws in the source code that could lead to security breaches. Explore the rest of the article to learn how combining these techniques strengthens your security posture effectively.
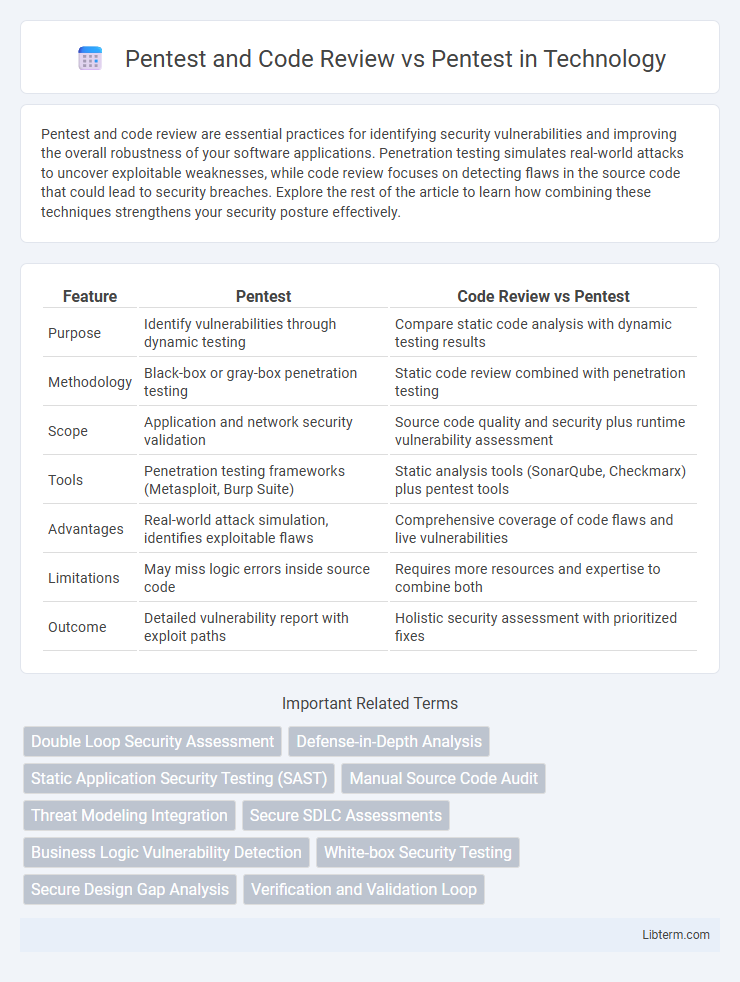
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Pentest | Code Review vs Pentest |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Identify vulnerabilities through dynamic testing | Compare static code analysis with dynamic testing results |
| Methodology | Black-box or gray-box penetration testing | Static code review combined with penetration testing |
| Scope | Application and network security validation | Source code quality and security plus runtime vulnerability assessment |
| Tools | Penetration testing frameworks (Metasploit, Burp Suite) | Static analysis tools (SonarQube, Checkmarx) plus pentest tools |
| Advantages | Real-world attack simulation, identifies exploitable flaws | Comprehensive coverage of code flaws and live vulnerabilities |
| Limitations | May miss logic errors inside source code | Requires more resources and expertise to combine both |
| Outcome | Detailed vulnerability report with exploit paths | Holistic security assessment with prioritized fixes |
Introduction to Penetration Testing and Code Review
Penetration testing identifies vulnerabilities by simulating real-world cyberattacks to evaluate system security, while code review analyzes the source code for potential flaws and weaknesses without executing the program. Both approaches complement each other; penetration testing targets runtime behavior and system misconfigurations, whereas code review focuses on secure coding practices, logic errors, and potential backdoors within the application. Effective security assessments integrate penetration testing and code review to uncover a broader spectrum of risks and strengthen overall application resilience.
Defining Penetration Testing: Purpose and Scope
Penetration testing evaluates the security of an entire system by simulating real-world attacks to identify vulnerabilities across networks, applications, and infrastructure. Code review focuses on analyzing source code to detect security flaws, logic errors, and coding standards violations primarily within software development. The purpose of penetration testing is to assess overall system resilience and exploit potential, while code review aims to improve code quality and prevent specific vulnerabilities at the development stage.
Code Review Explained: Methodology and Goals
Code Review involves systematically examining source code to identify security vulnerabilities, ensure adherence to coding standards, and detect logic errors before deployment. The methodology includes static analysis, manual inspection by security experts, and the use of automated tools to highlight potential risks such as buffer overflows, injection flaws, and insecure cryptographic practices. The primary goals are to improve code quality, enhance software security, and reduce the attack surface by addressing issues early in the development lifecycle compared to Pentest, which focuses on identifying vulnerabilities in running applications through dynamic testing.
Combining Pentest and Code Review: A Holistic Approach
Combining penetration testing and code review forms a holistic security approach by addressing vulnerabilities from both external and internal perspectives. Penetration testing simulates real-world attacks to identify exploitable weaknesses, while code review analyzes source code for logic flaws, security misconfigurations, and insecure coding patterns. Integrating these practices enhances overall security posture by ensuring comprehensive detection, prevention, and remediation of software vulnerabilities.
Pentest Only: Strengths and Limitations
Pentest focuses on identifying real-world vulnerabilities by simulating cyberattacks, offering practical insights into system weaknesses and exploitability that static code reviews may overlook. It reveals security flaws in configurations, network defenses, and authentication mechanisms, providing a more comprehensive view of an application's security posture. Limitations include its reliance on the tester's skills, potential scope constraints, and the inability to guarantee complete coverage of all possible vulnerabilities.
Comparative Analysis: Pentest vs Pentest with Code Review
Pentest combined with code review provides deeper vulnerability detection by analyzing both system behavior and underlying source code, unlike standalone pentesting which primarily focuses on external attack vectors. Code review exposes hidden security flaws such as logic errors and insecure coding practices that penetration testing might miss during runtime assessments. Integrating both approaches results in a comprehensive security evaluation, improving overall risk mitigation strategies.
Identifying Vulnerabilities: Black Box vs White Box Techniques
Pentest and Code Review offer complementary approaches to identifying vulnerabilities, with Pentest typically employing Black Box techniques that simulate real-world attacks by testing systems without prior knowledge, revealing exploitable security flaws in live environments. In contrast, Code Review uses White Box techniques involving thorough analysis of source code to detect latent vulnerabilities, logic errors, and insecure coding practices early in the development lifecycle. Combining Black Box Pentest and White Box Code Review enables comprehensive vulnerability detection across both operational systems and application internals, enhancing overall cybersecurity posture.
Risk Mitigation: Enhanced Security through Dual Assessment
Pentest combined with code review amplifies risk mitigation by identifying both external vulnerabilities and internal coding flaws, leading to enhanced security. This dual assessment uncovers hidden logic errors, insecure coding practices, and potential exploits that standalone pentesting might miss. Organizations benefit from a comprehensive defense strategy that reduces attack surfaces and improves overall software integrity.
When to Use Pentest Alone vs Combined Approach
Pentest alone is ideal for identifying real-world vulnerabilities through simulated attacks, providing a practical assessment of security defenses. Use a combined approach of Pentest and Code Review to uncover both implementation flaws and logical errors in the source code, enabling a comprehensive security evaluation. Organizations requiring deep insight into security risks benefit from the combined strategy, especially when safeguarding critical applications or handling sensitive data.
Conclusion: Maximizing Application Security
Combining Pentest and Code Review maximizes application security by addressing both external vulnerabilities and internal code weaknesses. Pentests simulate real-world attacks to identify exploitable flaws, while Code Reviews ensure secure coding practices and detect logic errors before deployment. Leveraging both methodologies provides comprehensive risk mitigation and strengthens overall defense posture.
Pentest and Code Review Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com