Ensuring data integrity is crucial for maintaining accurate, consistent, and reliable information across databases and systems. It involves protecting data from unauthorized alterations, corruption, or loss through validation, error checking, and secure access controls. Discover how understanding the key principles of data integrity can safeguard Your information and boost confidence in your digital operations by reading the full article.
Table of Comparison
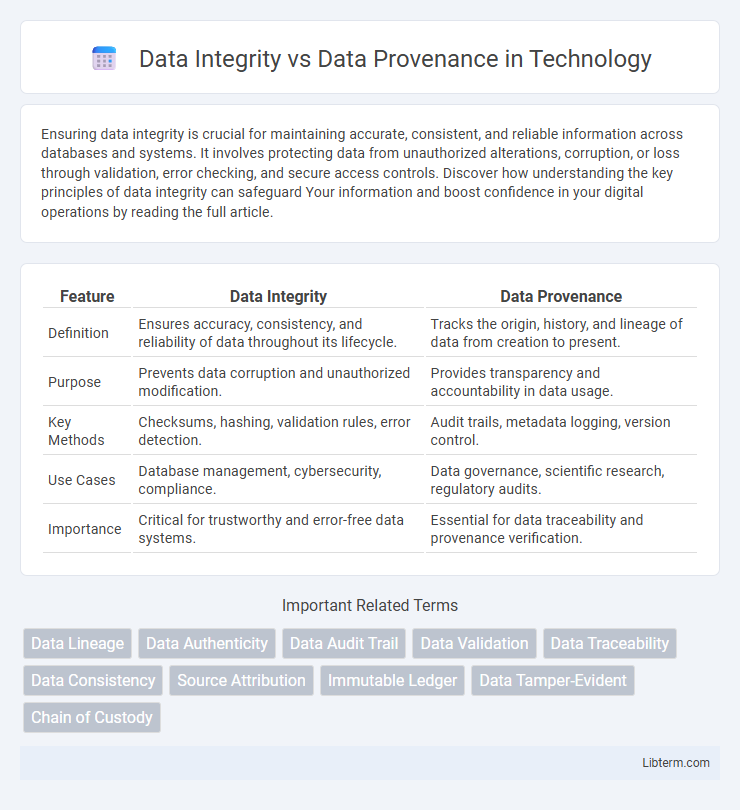
| Feature | Data Integrity | Data Provenance |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Ensures accuracy, consistency, and reliability of data throughout its lifecycle. | Tracks the origin, history, and lineage of data from creation to present. |
| Purpose | Prevents data corruption and unauthorized modification. | Provides transparency and accountability in data usage. |
| Key Methods | Checksums, hashing, validation rules, error detection. | Audit trails, metadata logging, version control. |
| Use Cases | Database management, cybersecurity, compliance. | Data governance, scientific research, regulatory audits. |
| Importance | Critical for trustworthy and error-free data systems. | Essential for data traceability and provenance verification. |
Introduction to Data Integrity and Data Provenance
Data integrity ensures the accuracy and consistency of data throughout its lifecycle, safeguarding against unauthorized alterations, corruption, or loss. Data provenance records the history and origin of data, detailing the processes and transformations applied from its creation to current state. Understanding data provenance supports verifying data integrity by providing traceability and auditability in various applications such as scientific research, data governance, and compliance.
Defining Data Integrity: Key Concepts
Data Integrity refers to the accuracy, consistency, and reliability of data throughout its lifecycle, ensuring that information remains unaltered and trustworthy from creation to storage and retrieval. It involves key concepts such as validation, error detection, and prevention mechanisms that protect against unauthorized modification or corruption. Maintaining data integrity is essential for compliance, decision-making, and operational efficiency across various industries.
Understanding Data Provenance: An Overview
Data provenance refers to the detailed documentation of the origin, history, and movement of data throughout its lifecycle, ensuring traceability and accountability in data management. It plays a critical role in verifying data integrity by providing transparent records of data transformations, sources, and handling processes, which help detect anomalies and ensure authenticity. Understanding data provenance is essential for compliance with regulatory standards, enhancing data quality, and supporting trust in data-driven decisions across various industries.
Core Differences Between Data Integrity and Data Provenance
Data integrity refers to the accuracy, consistency, and reliability of data throughout its lifecycle, ensuring that information remains unaltered and trustworthy. Data provenance traces the origin, history, and the processes through which data has passed, providing a detailed record of data lineage and transformations. The core difference lies in data integrity emphasizing the preservation of data correctness, while data provenance focuses on documenting the data's source and evolution over time.
Importance of Data Integrity in Digital Systems
Data integrity ensures the accuracy, consistency, and reliability of data throughout its lifecycle, making it essential for maintaining trust in digital systems. It prevents data corruption, unauthorized modifications, and errors, which can lead to faulty decisions, security breaches, and compliance issues. Maintaining robust data integrity protocols supports regulatory adherence, enhances operational efficiency, and safeguards critical information assets in industries such as finance, healthcare, and cloud computing.
Role of Data Provenance in Data Lifecycle Management
Data provenance plays a critical role in data lifecycle management by providing detailed records of data origin, transformations, and movement throughout its lifecycle. This traceability enhances data integrity by ensuring transparency, enabling verification of data authenticity, and supporting compliance with regulatory standards. Effective data provenance mechanisms facilitate audit trails, improve data governance, and enable accurate impact analysis during data updates or migrations.
Common Challenges in Ensuring Data Integrity
Ensuring data integrity faces common challenges such as unauthorized access, accidental modifications, and data corruption during transmission or storage. Businesses must implement robust validation, encryption, and audit trails to maintain accurate and consistent data states. In contrast to data provenance, which tracks data origins and history, data integrity focuses specifically on the protection against data tampering and errors throughout its lifecycle.
Technologies Supporting Data Provenance
Technologies supporting data provenance include blockchain, which provides immutable ledgers ensuring traceability and verification of data origin. Provenance metadata frameworks like W3C PROV enable standardized documentation of data lifecycle events across systems. Advanced cryptographic techniques and audit trails further enhance transparency and reliability in tracking data lineage and transformations.
Real-World Applications: Integrity vs. Provenance
Data integrity ensures accuracy and consistency of data throughout its lifecycle, crucial for financial transactions, healthcare records, and audit trails where trustworthiness is mandatory. Data provenance tracks the origin and lineage of data, enabling validation of sources and enhancing transparency in scientific research, supply chain management, and compliance reporting. Together, these concepts support robust data governance frameworks that safeguard decision-making and regulatory adherence.
Best Practices for Integrating Data Integrity and Provenance
Implement robust cryptographic hashing techniques to ensure data integrity, enabling verification that information remains unaltered during storage and transmission. Integrate comprehensive metadata capture for data provenance, documenting the origin, transformations, and custody of data to establish a transparent audit trail. Employ automated data governance frameworks that combine integrity checks with provenance tracking to enhance compliance, accountability, and trustworthiness in data management processes.
Data Integrity Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com