Load balancers distribute incoming network traffic across multiple servers to ensure high availability and reliability of applications. By efficiently managing resource allocation and minimizing response time, they prevent server overload and improve overall system performance. Discover how integrating load balancers can optimize Your infrastructure by reading the full article.
Table of Comparison
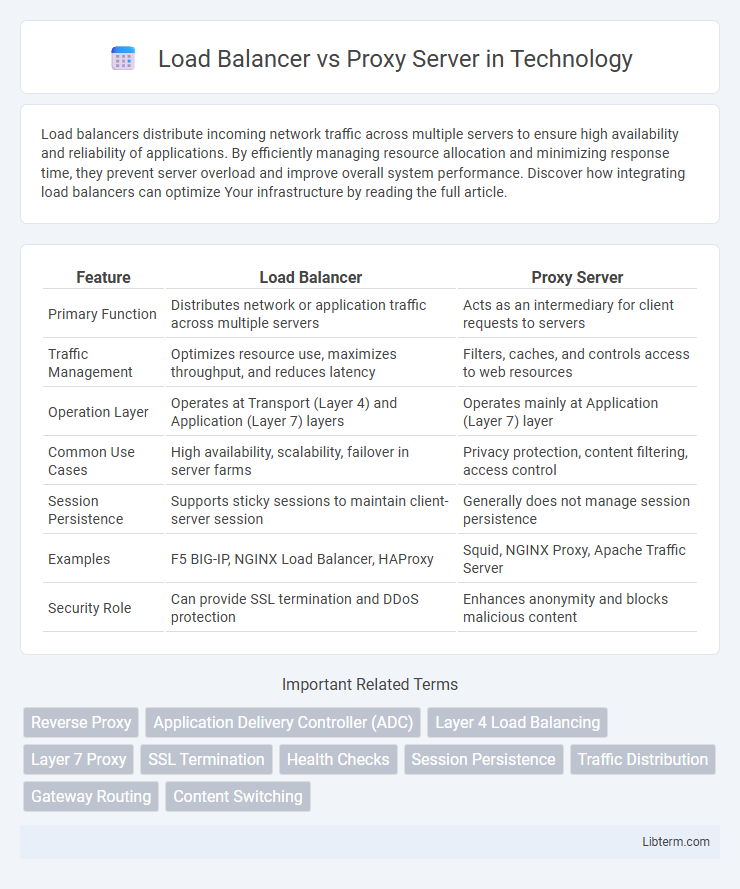
| Feature | Load Balancer | Proxy Server |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Function | Distributes network or application traffic across multiple servers | Acts as an intermediary for client requests to servers |
| Traffic Management | Optimizes resource use, maximizes throughput, and reduces latency | Filters, caches, and controls access to web resources |
| Operation Layer | Operates at Transport (Layer 4) and Application (Layer 7) layers | Operates mainly at Application (Layer 7) layer |
| Common Use Cases | High availability, scalability, failover in server farms | Privacy protection, content filtering, access control |
| Session Persistence | Supports sticky sessions to maintain client-server session | Generally does not manage session persistence |
| Examples | F5 BIG-IP, NGINX Load Balancer, HAProxy | Squid, NGINX Proxy, Apache Traffic Server |
| Security Role | Can provide SSL termination and DDoS protection | Enhances anonymity and blocks malicious content |
Introduction: Load Balancer vs Proxy Server
Load balancers distribute incoming network traffic across multiple servers to ensure high availability and reliability of applications. Proxy servers act as intermediaries between clients and servers, providing functions such as anonymity, content filtering, and security. Both technologies optimize network performance but serve distinct roles in traffic management and resource allocation.
What is a Load Balancer?
A load balancer is a network device or software that distributes incoming traffic across multiple servers to ensure optimal resource utilization, maximize throughput, minimize response time, and prevent server overload. It operates at various OSI layers, commonly Layer 4 (transport) and Layer 7 (application), enabling intelligent traffic routing based on factors like server health, session persistence, and request type. Load balancers enhance the availability and reliability of applications by balancing workloads, improving fault tolerance, and supporting seamless scalability in distributed systems.
What is a Proxy Server?
A proxy server acts as an intermediary between a client and the internet, forwarding client requests to target servers while masking the client's IP address for enhanced privacy and security. It can filter traffic, cache content to improve load times, and enforce access controls within a network. Unlike a load balancer that distributes network traffic across multiple servers to optimize resource use and prevent overload, a proxy server primarily manages and controls client-server communication.
Key Functions of Load Balancers
Load balancers distribute incoming network traffic across multiple servers to ensure high availability, reliability, and optimal resource utilization. They perform health checks to detect server failures and reroute traffic accordingly, preventing downtime and enhancing application performance. By managing session persistence and SSL termination, load balancers optimize user experience and reduce the processing burden on backend servers.
Primary Roles of Proxy Servers
Proxy servers primarily act as intermediaries between client devices and the internet, enhancing security by masking internal IP addresses and filtering traffic based on predefined rules. They also improve performance through caching frequently requested content, reducing bandwidth usage and load times. Unlike load balancers that distribute network traffic across multiple servers to optimize resource use and ensure redundancy, proxy servers focus on controlling and managing client access to external resources.
Differences in Traffic Management
Load balancers distribute incoming network traffic across multiple servers to optimize resource use, prevent overload, and increase fault tolerance, ensuring high availability and scalability. Proxy servers act as intermediaries between clients and servers, managing traffic by controlling, filtering, and monitoring requests for security, caching, or anonymity purposes. While load balancers focus on evenly distributing traffic to maintain performance, proxy servers primarily handle requests to enforce access policies or improve response times.
Security Features Comparison
Load balancers enhance security by distributing traffic across multiple servers, preventing overload and mitigating DDoS attacks through traffic filtering and SSL termination. Proxy servers act as intermediaries that conceal client IPs, enforce access controls, and filter requests to block malicious content or unauthorized access. Both devices bolster network security, but load balancers primarily focus on availability and traffic management, while proxy servers emphasize anonymity and granular content filtering.
Scalability and Performance
Load balancers distribute network or application traffic across multiple servers, enhancing scalability by preventing any single server from becoming a bottleneck and ensuring high availability. Proxy servers act as intermediaries between clients and servers, improving performance by caching content and filtering requests, but they do not inherently distribute load across multiple backend resources. For scalable architectures requiring efficient resource utilization and fault tolerance, load balancers are preferable, while proxies optimize individual connection performance and security.
Use Cases: When to Use Each
Load balancers optimize traffic distribution across multiple servers to enhance availability and scalability, ideal for high-traffic web applications and cloud environments requiring fault tolerance. Proxy servers manage client requests by acting as intermediaries, providing security, content filtering, and anonymity, often used in corporate networks and for accessing geo-restricted content. Choosing a load balancer suits scenarios demanding efficient resource utilization and redundancy, while proxy servers best serve needs for access control, privacy, and monitoring user activity.
Conclusion: Choosing Between Load Balancer and Proxy Server
Choosing between a load balancer and a proxy server depends on the specific needs of your network infrastructure; load balancers optimize traffic distribution across multiple servers to enhance performance and reliability, while proxy servers primarily manage client requests for security, anonymity, and content filtering. For environments requiring high availability and efficient resource utilization, load balancers are more effective. Proxy servers suit scenarios demanding access control, caching, and privacy.
Load Balancer Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com