Rollback is a critical process in database management that reverses transactions to maintain data integrity after errors or system failures occur. This mechanism ensures your database remains consistent by undoing changes that could compromise accuracy or reliability. Explore the rest of the article to understand how rollback functions safeguard your data and improve system resilience.
Table of Comparison
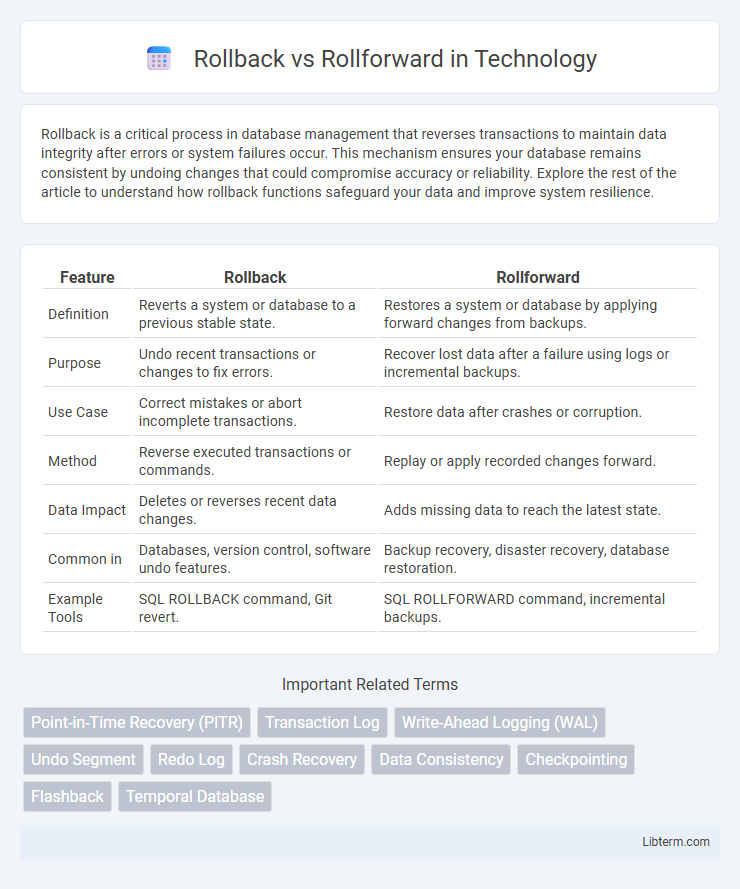
| Feature | Rollback | Rollforward |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Reverts a system or database to a previous stable state. | Restores a system or database by applying forward changes from backups. |
| Purpose | Undo recent transactions or changes to fix errors. | Recover lost data after a failure using logs or incremental backups. |
| Use Case | Correct mistakes or abort incomplete transactions. | Restore data after crashes or corruption. |
| Method | Reverse executed transactions or commands. | Replay or apply recorded changes forward. |
| Data Impact | Deletes or reverses recent data changes. | Adds missing data to reach the latest state. |
| Common in | Databases, version control, software undo features. | Backup recovery, disaster recovery, database restoration. |
| Example Tools | SQL ROLLBACK command, Git revert. | SQL ROLLFORWARD command, incremental backups. |
Introduction to Data Recovery Techniques
Rollback and rollforward are crucial data recovery techniques used to restore databases to a consistent state after failures. Rollback involves undoing uncommitted transactions to maintain data integrity, while rollforward applies committed transaction logs to update the database to the latest state. These methods ensure minimal data loss and support database resilience during recovery operations.
Understanding Rollback: Definition and Purpose
Rollback is a database recovery process that reverses transactions to restore the database to a previous consistent state, ensuring data integrity after errors or system failures. It undoes uncommitted changes by reverting the database to its state before a transaction began, preventing partial or corrupt data entries. Rollback is essential for maintaining transactional atomicity and enforcing consistency in relational database management systems (RDBMS).
Exploring Rollforward: Definition and Functionality
Rollforward is a database recovery method that applies transaction logs or archived redo files to restore data to a specific point in time after a failure. This technique ensures data consistency by reapplying committed transactions that occurred after the last backup, minimizing data loss. Rollforward complements rollback by forwarding the database state to the desired recovery point, enhancing disaster recovery strategies in database management systems.
Key Differences Between Rollback and Rollforward
Rollback reverses a database transaction to its previous stable state before the changes were made, ensuring data integrity by undoing incomplete or erroneous operations. Rollforward, on the other hand, applies transaction logs or changes from backups to restore or reapply committed transactions up to a specific point in time, facilitating data recovery after failures. The key difference lies in rollback's function to undo recent changes, whereas rollforward re-applies changes to bring the database to a desired future or current state.
Common Use Cases for Rollback
Rollback is commonly used in database management to undo transactions that contain errors or inconsistencies, ensuring data integrity by reverting to a previous stable state. In software development, rollback helps reverse software updates or deployments that cause system failures or performance issues, minimizing downtime and operational impact. Backup restoration also employs rollback techniques to restore corrupted or lost data to a specific point in time, enhancing disaster recovery processes.
Typical Scenarios for Using Rollforward
Rollforward is typically used in disaster recovery scenarios where databases need to be restored to the most recent committed state after a crash or failure, ensuring minimal data loss. It applies transaction logs or incremental backups to bring the database forward from the last full backup point. This method is essential for maintaining data integrity in high-availability systems and during incremental database migrations.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Rollback
Rollback offers the advantage of quickly restoring a database to a previous consistent state, effectively undoing undesired or erroneous transactions to maintain data integrity. Its main disadvantage lies in potential data loss from transactions that occurred after the rollback point, which can impact system availability and require additional effort to reprocess lost data. Rollback operations are essential for error recovery but may cause temporary system downtime and increased complexity in managing transaction logs.
Pros and Cons of Rollforward
Rollforward recovery offers the advantage of applying committed transactions from backup logs to bring databases up to the point of failure, minimizing data loss and ensuring transactional consistency. However, it requires thorough log management and may involve longer recovery times if extensive log processing is needed, potentially delaying application availability. Its effectiveness depends on the availability of complete and intact transaction logs, making it vulnerable to scenarios where log files are corrupted or missing.
Choosing Between Rollback and Rollforward
Choosing between rollback and rollforward depends on the specific database recovery scenario and the availability of backup data. Rollback is ideal for undoing uncommitted transactions to maintain data integrity, while rollforward applies transaction logs to restore a database to a particular point in time after a failure. Evaluating factors such as the backup strategy, transaction log availability, and recovery objectives determines the most efficient method for database restoration.
Best Practices for Database Recovery Strategies
Rollback and rollforward are essential techniques in database recovery strategies, where rollback undoes uncommitted transactions to maintain data integrity, and rollforward applies committed transaction logs to restore databases to a consistent state after failure. Best practices include configuring frequent transaction log backups to minimize data loss during rollforward, using checkpointing to reduce rollback times, and ensuring atomicity by combining rollback for error correction with rollforward for disaster recovery. Implementing automated monitoring and alert systems enhances timely recovery actions, optimizing database availability and reliability in production environments.
Rollback Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com