Denial-of-Service attacks overwhelm networks or servers with excessive traffic, rendering services unavailable to legitimate users and disrupting business operations. These attacks can target websites, email servers, or other critical systems, causing significant downtime and financial loss. Explore the rest of the article to learn how to protect your network from such threats effectively.
Table of Comparison
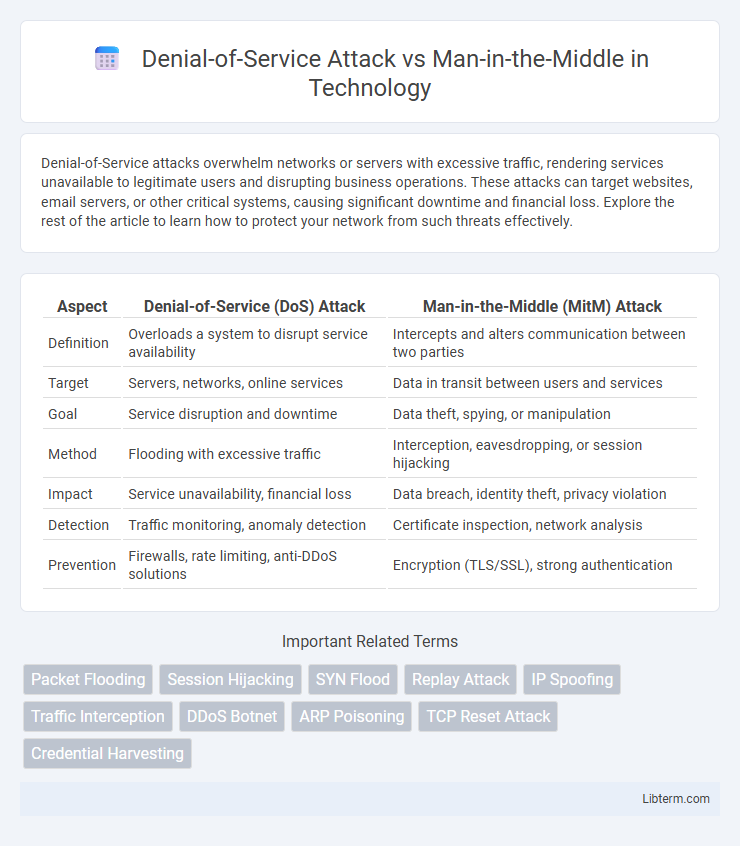
| Aspect | Denial-of-Service (DoS) Attack | Man-in-the-Middle (MitM) Attack |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Overloads a system to disrupt service availability | Intercepts and alters communication between two parties |
| Target | Servers, networks, online services | Data in transit between users and services |
| Goal | Service disruption and downtime | Data theft, spying, or manipulation |
| Method | Flooding with excessive traffic | Interception, eavesdropping, or session hijacking |
| Impact | Service unavailability, financial loss | Data breach, identity theft, privacy violation |
| Detection | Traffic monitoring, anomaly detection | Certificate inspection, network analysis |
| Prevention | Firewalls, rate limiting, anti-DDoS solutions | Encryption (TLS/SSL), strong authentication |
Introduction to Denial-of-Service (DoS) Attacks
Denial-of-Service (DoS) attacks target network availability by overwhelming a system or server with excessive traffic, causing disruption or total service unavailability. These attacks exploit vulnerabilities in bandwidth, processing power, or application resources, rendering legitimate user access impossible. Unlike Man-in-the-Middle attacks that intercept communication, DoS attacks focus solely on resource exhaustion to disrupt normal operations.
Understanding Man-in-the-Middle (MitM) Attacks
Man-in-the-Middle (MitM) attacks involve an attacker secretly intercepting and possibly altering communication between two parties without their knowledge. Unlike Denial-of-Service (DoS) attacks that focus on overwhelming systems to disrupt service, MitM attacks aim to eavesdrop, steal sensitive data, or inject false information during active communication. Understanding attack vectors such as session hijacking, IP spoofing, and Wi-Fi eavesdropping is crucial to implementing effective MitM prevention strategies like encryption and authentication protocols.
Key Differences Between DoS and MitM Attacks
Denial-of-Service (DoS) attacks aim to overwhelm a target system or network with excessive traffic to render services unavailable, focusing on resource exhaustion rather than data interception. Man-in-the-Middle (MitM) attacks involve intercepting and potentially altering communication between two parties without detection, targeting data confidentiality and integrity. Key differences include DoS attacks disrupting service availability, whereas MitM attacks compromise communication security and confidentiality.
Attack Vectors and Techniques
Denial-of-Service (DoS) attacks overwhelm a target system, network, or service with excessive traffic, exploiting bandwidth saturation, resource exhaustion, or protocol vulnerabilities such as SYN floods and UDP amplification. Man-in-the-Middle (MitM) attacks intercept and manipulate communications between two parties using techniques like session hijacking, DNS spoofing, and SSL stripping to eavesdrop or alter data in real time. While DoS attacks focus on disruption through volume-based vectors, MitM attacks emphasize stealth and interception through sophisticated exploitation of communication protocols.
Common Targets and Impacts
Denial-of-Service (DoS) attacks commonly target network infrastructure, web servers, and online services, overwhelming them with traffic to disrupt availability and cause downtime. Man-in-the-Middle (MitM) attacks focus on intercepting communications between users and systems, compromising data confidentiality and integrity across financial services, email exchanges, and VPN connections. The impact of DoS attacks primarily involves service interruption and financial loss from downtime, while MitM attacks lead to data breaches, identity theft, and unauthorized access to sensitive information.
Detection Methods for DoS and MitM
Detection methods for Denial-of-Service (DoS) attacks primarily rely on traffic analysis tools that monitor abnormal spikes in data packets, sudden bandwidth consumption, or excessive connection requests, triggering alerts through intrusion detection systems (IDS) like Snort or Zeek. Man-in-the-Middle (MitM) attacks often require detection techniques such as SSL/TLS certificate validation, protocol anomaly detection, or network behavior analysis to identify unauthorized interception or manipulation of communication between parties. Both DoS and MitM detection benefit significantly from real-time monitoring systems and machine learning algorithms that recognize patterns indicative of malicious activity.
Prevention and Mitigation Strategies
Denial-of-Service (DoS) attack prevention prioritizes robust network architecture and traffic filtering techniques like rate limiting and firewalls to prevent service disruption. Man-in-the-Middle (MitM) attack mitigation emphasizes strong encryption protocols such as TLS, secure authentication mechanisms, and continuous network monitoring to detect unauthorized interception. Both attack types benefit from comprehensive cybersecurity policies, regular software updates, and employee awareness training to minimize risk and ensure system integrity.
Real-World Examples and Case Studies
The 2016 Dyn cyberattack exemplifies a Denial-of-Service (DoS) attack, where a massive botnet disrupted internet access across major websites by overwhelming DNS infrastructure. In contrast, the 2013 Target data breach illustrates a Man-in-the-Middle (MitM) attack, where attackers intercepted and stole credit card information through compromised vendor credentials and network traffic. These cases highlight DoS attacks' focus on service disruption versus MitM attacks' emphasis on covert data interception and theft.
Security Best Practices for Organizations
Denial-of-Service (DoS) attacks and Man-in-the-Middle (MitM) attacks require distinct security best practices to safeguard organizational networks effectively. Employing robust firewall configurations, intrusion detection systems, and rate limiting techniques helps mitigate DoS attacks by controlling traffic flow and detecting anomalies early. For defending against MitM attacks, organizations should implement end-to-end encryption, use secure communication protocols like TLS, and enforce multi-factor authentication to ensure data integrity and confidentiality.
Future Trends in Cyber Attack Methods
Denial-of-Service (DoS) attacks are evolving with the integration of AI-driven botnets that can launch highly adaptive and distributed traffic floods, overwhelming networks with unprecedented scale and speed. Man-in-the-Middle (MitM) attacks are increasingly leveraging quantum computing advancements and sophisticated encryption-cracking algorithms to intercept and manipulate data in real-time, bypassing traditional security protocols. Future cyber attack methods will heavily focus on combining DoS and MitM techniques with emerging technologies like 5G and IoT to exploit vast attack surfaces, making threat detection and mitigation more complex.
Denial-of-Service Attack Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com