Partitioning your hard drive can enhance system organization and improve data management by dividing a single physical disk into multiple logical sections. Proper partitioning helps optimize performance, allows for different operating systems to coexist, and simplifies backup processes. Explore the rest of this article to discover how effective partitioning can benefit your computer setup.
Table of Comparison
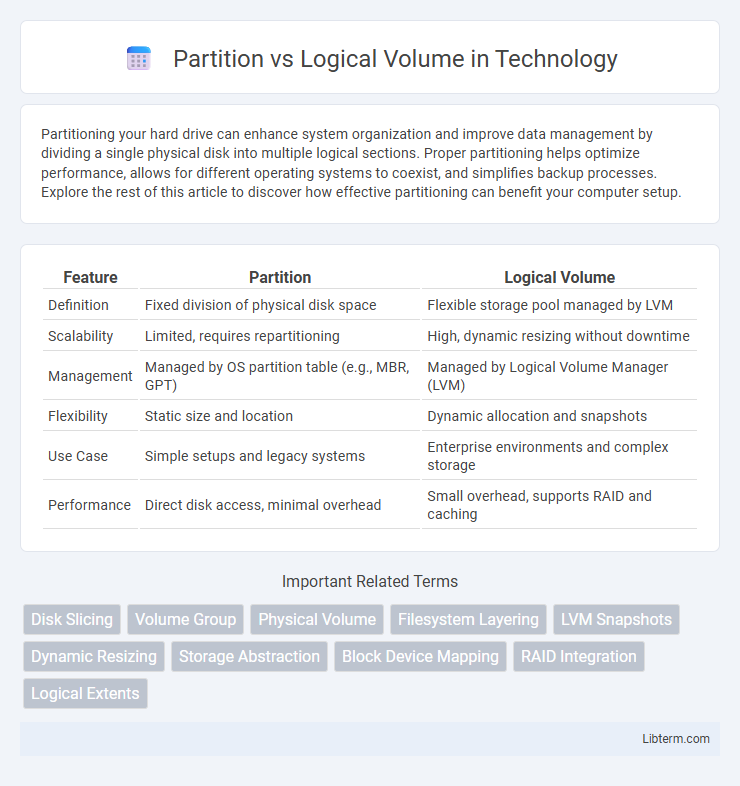
| Feature | Partition | Logical Volume |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Fixed division of physical disk space | Flexible storage pool managed by LVM |
| Scalability | Limited, requires repartitioning | High, dynamic resizing without downtime |
| Management | Managed by OS partition table (e.g., MBR, GPT) | Managed by Logical Volume Manager (LVM) |
| Flexibility | Static size and location | Dynamic allocation and snapshots |
| Use Case | Simple setups and legacy systems | Enterprise environments and complex storage |
| Performance | Direct disk access, minimal overhead | Small overhead, supports RAID and caching |
Understanding Partitions and Logical Volumes
Partitions divide a physical hard drive into separate, fixed-size sections that operate independently for file storage and system purposes, often managed via partition tables like MBR or GPT. Logical volumes abstract physical storage by combining multiple partitions or drives into flexible, resizable storage units using Logical Volume Manager (LVM), enhancing data management and scalability. Understanding partitions emphasizes discrete storage allocation, while logical volumes enable dynamic volume resizing and pooling of storage resources across devices.
Key Differences Between Partitions and Logical Volumes
Partitions are fixed-size divisions of a physical disk that allocate storage space to specific sections, while logical volumes use a flexible volume management system to pool storage from multiple physical devices. Logical volumes enable dynamic resizing, snapshots, and easier management across multiple disks, unlike traditional partitions which have static boundaries and limited flexibility. Key differences include the fixed size of partitions versus the dynamic allocation of logical volumes, and the advanced features such as striping and mirroring offered by logical volume managers (LVM) for performance and redundancy.
Advantages of Using Partitions
Partitions provide a straightforward method to divide a physical disk into isolated sections, enabling better organization and management of data. They offer compatibility with most operating systems and boot loaders, ensuring easy system setup and recovery without complex configuration. Partitioning also allows dedicated space allocation for different file systems or OS installations, enhancing system stability and security.
Benefits of Logical Volume Management (LVM)
Logical Volume Management (LVM) offers flexible disk space allocation by allowing dynamic resizing of volumes without data loss, unlike traditional partitions with fixed sizes. It enables efficient storage management through features like volume snapshots for backups and aggregation of multiple physical disks into a single logical volume, enhancing performance and redundancy. LVM simplifies disk management tasks, improves scalability, and maximizes storage utilization in complex systems.
Flexibility and Scalability: LVM vs Partitions
Logical Volume Management (LVM) offers superior flexibility and scalability compared to traditional disk partitions by allowing dynamic resizing of volumes without unmounting or rebooting the system. Partitions are fixed in size and require complex procedures to resize or reorganize, often leading to downtime and potential data loss. LVM supports advanced features such as volume snapshots, pooling multiple physical volumes, and easy volume migration, enabling efficient storage management in evolving environments.
Performance Considerations: Partition vs Logical Volume
Partitions generally provide faster disk access due to direct mapping on physical storage, while logical volumes introduce a layer of abstraction that may slightly impact performance but offer greater flexibility. Logical Volume Manager (LVM) allows dynamic resizing and snapshot capabilities with minimal overhead, benefiting workloads requiring frequent adjustments. Performance can depend on the underlying storage system and use case, with partitions excelling in static, high-throughput environments and logical volumes favored for adaptability and complex storage management.
Data Management and Backup Strategies
Partitions divide a physical hard drive into fixed segments, enabling straightforward data management but limiting flexibility during resizing or reallocation. Logical volumes, managed by volume managers like LVM, allow dynamic resizing, snapshots, and easier data migration, enhancing backup strategies and disaster recovery plans. Using logical volumes improves data redundancy and simplifies creating consistent backups by enabling snapshot-based backup solutions without downtime.
Use Cases: When to Choose Partitions
Partitions are ideal for simple, straightforward disk management tasks such as isolating different operating systems or creating separate spaces for system and data files on a single drive. They provide a fixed-size division of disk space that ensures compatibility with legacy systems and boot loaders, making them suitable for multi-boot environments. Use partitions when predictability, ease of setup, and compatibility across various platforms are the primary requirements.
Use Cases: When to Opt for Logical Volumes
Logical volumes offer superior flexibility for managing storage in environments with frequently changing data needs, such as virtualization, databases, and large-scale enterprise systems. They support dynamic resizing, snapshots, and easier migration across physical disks, making them ideal for applications requiring high availability and efficient storage allocation. Partitions remain suitable for simpler, static setups like single-boot systems or fixed-size storage devices where minimal management overhead is desired.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Storage Approach
Choosing between partitioning and logical volume management depends on flexibility and scalability needs. Partitions offer simplicity and straightforward management for fixed storage requirements, while logical volumes provide dynamic resizing, snapshot capabilities, and easier reallocation of space across multiple physical drives. For environments requiring adaptable storage solutions and efficient space utilization, logical volumes are the preferred approach.
Partition Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com