Blue-Green Deployment reduces downtime and minimizes risks by running two identical production environments, allowing seamless switching during updates. This strategy ensures continuous availability and quick rollback if issues arise, making your software releases more reliable. Discover how implementing Blue-Green Deployment can transform your deployment process by reading the full article.
Table of Comparison
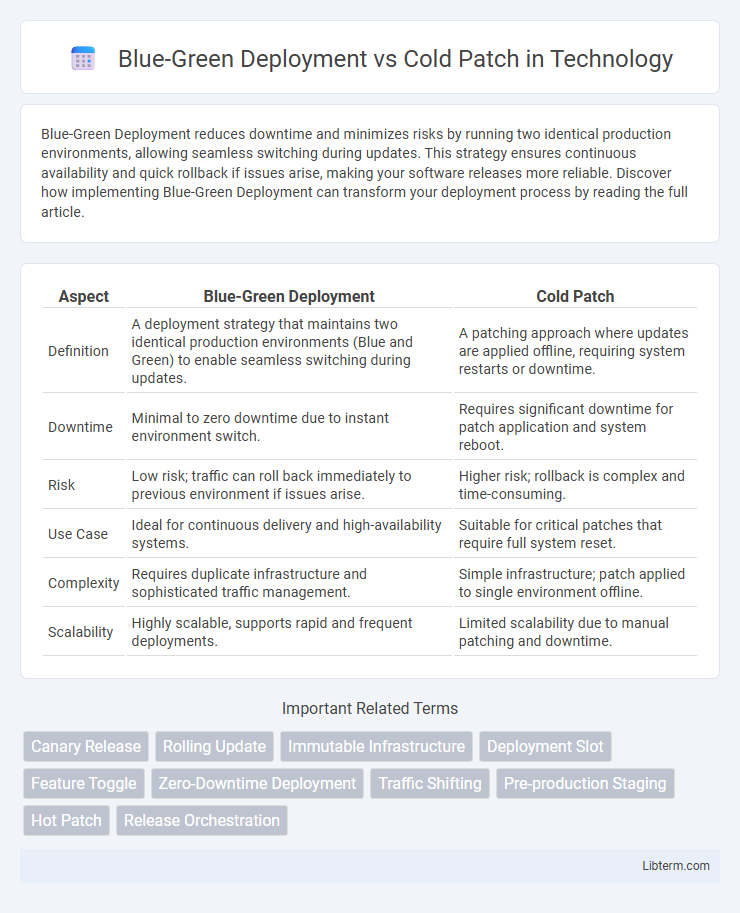
| Aspect | Blue-Green Deployment | Cold Patch |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | A deployment strategy that maintains two identical production environments (Blue and Green) to enable seamless switching during updates. | A patching approach where updates are applied offline, requiring system restarts or downtime. |
| Downtime | Minimal to zero downtime due to instant environment switch. | Requires significant downtime for patch application and system reboot. |
| Risk | Low risk; traffic can roll back immediately to previous environment if issues arise. | Higher risk; rollback is complex and time-consuming. |
| Use Case | Ideal for continuous delivery and high-availability systems. | Suitable for critical patches that require full system reset. |
| Complexity | Requires duplicate infrastructure and sophisticated traffic management. | Simple infrastructure; patch applied to single environment offline. |
| Scalability | Highly scalable, supports rapid and frequent deployments. | Limited scalability due to manual patching and downtime. |
Introduction to Deployment Strategies
Blue-Green Deployment involves maintaining two identical production environments, where one serves live traffic while the other deploys updates, enabling seamless switching with minimal downtime. Cold Patch deployment, by contrast, applies updates during system downtime or scheduled maintenance, often requiring service interruption to implement changes safely. These contrasting deployment strategies address different operational needs, balancing availability, risk, and system impact during software updates.
What is Blue-Green Deployment?
Blue-Green Deployment is a software release strategy that minimizes downtime and risk by maintaining two identical production environments, named Blue and Green. One environment (Blue) serves live traffic while the other (Green) hosts the new application version for testing and validation before switching user traffic. This approach enables seamless updates and quick rollback options compared to Cold Patch, which involves stopping services to apply immediate fixes without environment duplication.
Understanding Cold Patch Deployment
Cold Patch Deployment involves updating software by stopping the existing system completely before applying the update, ensuring no active processes interfere with the installation. This approach minimizes risks associated with runtime conflicts and data corruption but often results in downtime during the deployment window. Unlike Blue-Green Deployment, which swaps live environments to achieve zero-downtime updates, Cold Patch is simpler but best suited for less time-sensitive applications due to its inherent service interruption.
Key Differences Between Blue-Green and Cold Patch
Blue-Green Deployment minimizes downtime by running two identical production environments, switching traffic to the updated environment once testing is complete, ensuring seamless user experience. Cold Patch involves taking the system offline to apply updates or patches, resulting in service interruption during the deployment process. Key differences include downtime impact, with Blue-Green enabling near-zero downtime and Cold Patch requiring complete system shutdown, and the resource usage, where Blue-Green demands maintaining dual environments while Cold Patch operates within a single environment.
Pros and Cons of Blue-Green Deployment
Blue-Green Deployment offers seamless application updates by maintaining two identical production environments, minimizing downtime and reducing risk during releases. The main advantage is instant rollback capability, ensuring high availability and quick recovery from failures, but it requires double infrastructure resources, increasing costs and complexity. Compared to Cold Patch, which applies updates during system downtime with possible service disruption, Blue-Green Deployment prioritizes user experience and continuous uptime at the expense of higher operational demands.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Cold Patch
Cold Patch offers the advantage of minimal infrastructure changes, enabling quick fixes without the need for complex deployment strategies like Blue-Green Deployment. It is cost-effective for small-scale or infrequent updates but carries the risk of service downtime during the patching process. Unlike Blue-Green Deployment, Cold Patch lacks seamless rollback and zero-downtime capabilities, making it less suitable for high-availability systems.
Use Cases for Blue-Green Deployment
Blue-Green Deployment is ideal for high-availability applications requiring zero downtime updates, such as e-commerce platforms, financial services, and SaaS products. It allows seamless switching between two identical production environments, minimizing risk during releases and enabling quick rollback if issues arise. This approach supports continuous delivery pipelines and enhances system reliability for mission-critical services.
When to Choose Cold Patch Deployment
Cold Patch Deployment is ideal for environments requiring zero traffic routing to updated instances during maintenance, ensuring no service disruption. Use Cold Patch when application updates involve complex database changes or stateful services that cannot handle live traffic switching, unlike Blue-Green deployments. It suits scenarios demanding thorough validation before the new version serves user requests, minimizing risk in critical production systems.
Best Practices for Seamless Deployments
Blue-Green Deployment ensures zero downtime by switching traffic between two identical production environments, minimizing user impact during updates. Cold Patch involves updating systems offline, ideal for critical fixes but with temporary service interruption risks. Best practices for seamless deployments prioritize automated testing, thorough rollback plans, and incremental traffic shifting to balance stability and rapid recovery.
Conclusion: Selecting the Right Deployment Strategy
Choosing the right deployment strategy depends on the specific requirements for downtime tolerance, rollback flexibility, and resource availability. Blue-Green Deployment offers near-zero downtime and swift rollback by maintaining two identical environments, ideal for mission-critical applications requiring high availability. Cold Patch suits scenarios with acceptable downtime and limited infrastructure resources, providing a simpler but less seamless update process.
Blue-Green Deployment Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com