Centralized management streamlines decision-making by consolidating authority within a single leadership structure, enhancing organizational consistency and accountability. This approach can improve efficiency and reduce redundancies across various departments. Explore the rest of the article to discover how centralized management can transform your business operations.
Table of Comparison
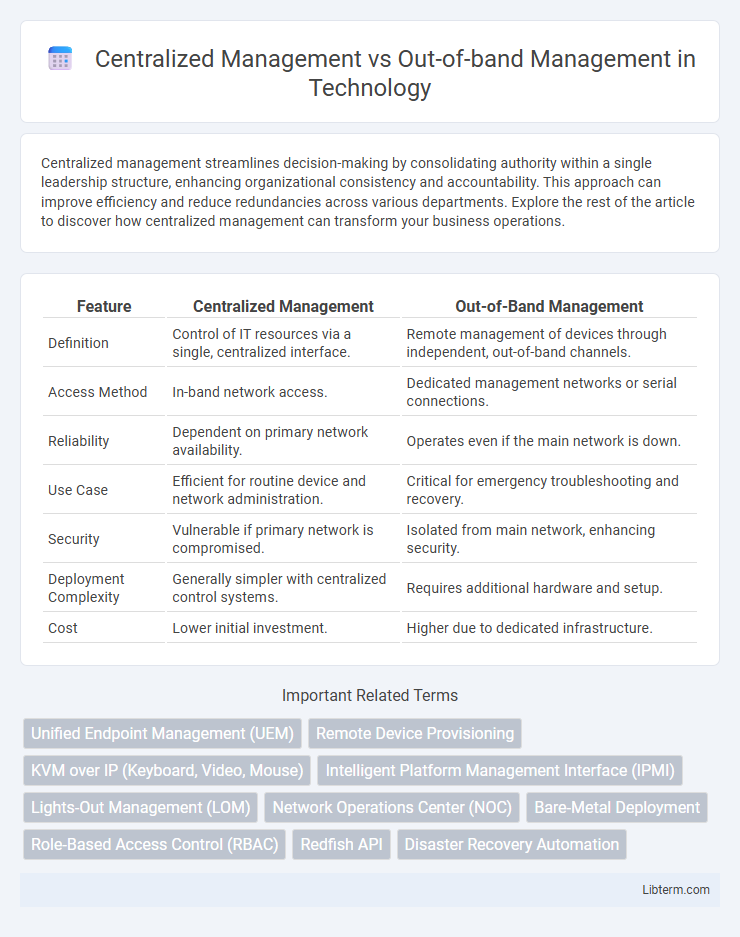
| Feature | Centralized Management | Out-of-Band Management |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Control of IT resources via a single, centralized interface. | Remote management of devices through independent, out-of-band channels. |
| Access Method | In-band network access. | Dedicated management networks or serial connections. |
| Reliability | Dependent on primary network availability. | Operates even if the main network is down. |
| Use Case | Efficient for routine device and network administration. | Critical for emergency troubleshooting and recovery. |
| Security | Vulnerable if primary network is compromised. | Isolated from main network, enhancing security. |
| Deployment Complexity | Generally simpler with centralized control systems. | Requires additional hardware and setup. |
| Cost | Lower initial investment. | Higher due to dedicated infrastructure. |
Understanding Centralized Management
Centralized management consolidates control and monitoring of IT systems into a single interface, improving efficiency and simplifying administration across networks. It enables real-time visibility, policy enforcement, and streamlined updates, reducing operational complexity and downtime. By centralizing data collection and decision-making processes, organizations enhance security, compliance, and resource optimization in large-scale environments.
Overview of Out-of-Band Management
Out-of-band management provides a dedicated, independent channel for accessing network devices and servers, ensuring control even when the primary network is down or unresponsive. This method enhances reliability and security by isolating management traffic from regular data flow, allowing administrators to perform remote troubleshooting, updates, and recovery without impacting production networks. Out-of-band management is essential for maintaining uptime and rapid incident response in complex IT environments and critical infrastructure.
Key Differences Between Centralized and Out-of-Band Management
Centralized management consolidates control of IT resources through a single interface, allowing administrators to monitor and configure systems within the main network environment. Out-of-band management provides a separate, dedicated channel for managing devices independently of the primary network, ensuring access during network outages or failures. The key difference lies in centralized management's reliance on live network connectivity, while out-of-band management offers resilience and remote troubleshooting capabilities through an isolated communication path.
Advantages of Centralized Management
Centralized management streamlines IT operations by consolidating control into a single platform, enhancing efficiency and reducing administrative complexity. It improves resource allocation and policy enforcement across multiple devices and locations, leading to stronger security and compliance. Centralized management also enables real-time monitoring and rapid incident response, minimizing downtime and operational costs.
Benefits of Out-of-Band Management
Out-of-band management provides uninterrupted access to network devices even during system failures or outages, enhancing remote troubleshooting capabilities. It improves security by isolating management traffic from regular data traffic, reducing exposure to cyber threats. This approach enables faster recovery times and greater control over critical infrastructure, minimizing downtime and operational disruptions.
Security Considerations in Both Approaches
Centralized management consolidates control over network devices through a single interface, enhancing security by enabling unified policy enforcement and real-time monitoring, but introduces risks of a single point of failure and potential attacks on the central system. Out-of-band management utilizes a dedicated, isolated network for device access, significantly reducing exposure to common network threats and improving incident response capabilities, yet requires additional infrastructure and careful segmentation to prevent unauthorized access. Both approaches necessitate robust authentication, encryption, and access controls to mitigate risks and ensure secure remote management in enterprise environments.
Scalability and Flexibility Comparison
Centralized management offers high scalability by allowing IT administrators to control multiple devices from a single interface, streamlining large-scale network operations. Out-of-band management enhances flexibility by providing direct, independent access to individual devices, even during network failures, ensuring continuous control and troubleshooting capabilities. While centralized management excels in managing extensive infrastructures efficiently, out-of-band management provides critical flexibility for emergency interventions and isolated device handling.
Costs and Resource Allocation
Centralized management consolidates IT control into a single platform, reducing operational costs and streamlining resource allocation by minimizing the need for multiple management tools. Out-of-band management, while offering superior control during network outages, often incurs higher expenses due to dedicated hardware and separate network paths. Organizations must weigh upfront investments against ongoing savings and operational efficiency to determine the optimal balance for infrastructure management.
Best Use Cases for Centralized vs Out-of-Band Management
Centralized management excels in environments requiring unified control and streamlined monitoring of multiple devices through a single interface, making it ideal for large-scale enterprise networks and data centers. Out-of-band management is best suited for critical situations where remote access to network devices is necessary despite primary network failures, providing independent access via separate channels to ensure uninterrupted troubleshooting and maintenance. Deploying centralized management enhances efficiency for routine administration, while out-of-band management ensures resilience and rapid recovery during network outages.
Choosing the Right Management Strategy for Your Organization
Centralized management streamlines IT operations by consolidating control into a single platform, enhancing efficiency and policy enforcement across dispersed assets. Out-of-band management provides robust remote access independent of the primary network, ensuring uninterrupted troubleshooting and recovery during system failures. Organizations should evaluate their operational complexity, security requirements, and downtime tolerance to select a strategy that optimizes control, resilience, and resource allocation.
Centralized Management Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com