Avro and JSON are widely used data serialization formats that enable efficient data exchange and storage. Avro offers compact binary serialization with schema evolution support, while JSON provides human-readable text format ideal for web applications. Explore the key differences and best use cases to enhance your data processing strategies in the full article.
Table of Comparison
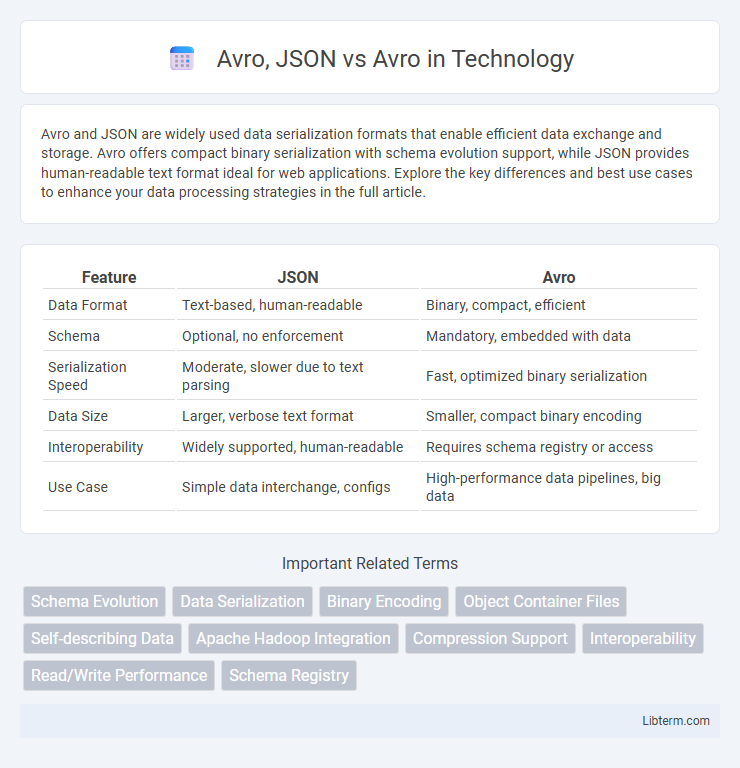
| Feature | JSON | Avro |
|---|---|---|
| Data Format | Text-based, human-readable | Binary, compact, efficient |
| Schema | Optional, no enforcement | Mandatory, embedded with data |
| Serialization Speed | Moderate, slower due to text parsing | Fast, optimized binary serialization |
| Data Size | Larger, verbose text format | Smaller, compact binary encoding |
| Interoperability | Widely supported, human-readable | Requires schema registry or access |
| Use Case | Simple data interchange, configs | High-performance data pipelines, big data |
Introduction to Data Serialization Formats
Avro and JSON are popular data serialization formats used for efficient data storage and communication. Avro provides compact binary encoding and schema evolution support, making it ideal for big data processing frameworks like Apache Hadoop and Kafka. JSON offers human-readable text format and ease of integration but often results in larger payloads and slower parsing compared to Avro's binary serialization.
What is Avro?
Avro is a compact, fast, binary data serialization system designed for Hadoop and Apache Kafka environments, enabling efficient storage and exchange of data. JSON is a human-readable data format, whereas Avro uses a schema-based approach, supporting rich data structures with schemas stored alongside the data for robust serialization and deserialization. Avro's design reduces data size and speeds up processing compared to JSON, making it ideal for big data and streaming applications.
Key Features of Avro
Avro offers compact, fast, and efficient binary serialization with a schema that evolves without breaking compatibility, making it ideal for big data processing. Unlike JSON, which is human-readable but verbose and slower to parse, Avro uses a schema-based approach to provide smaller data size and faster serialization/deserialization. Key features of Avro include its support for rich data structures, dynamic typing, and seamless integration with Apache Hadoop and streaming platforms like Apache Kafka.
Overview of JSON
JSON (JavaScript Object Notation) is a lightweight data interchange format that is easy to read and write, commonly used for API communication and configuration files. JSON's simple text-based structure supports hierarchical key-value pairs but lacks a standardized schema, which can lead to data inconsistency. Unlike Avro, JSON does not provide efficient serialization or built-in schema evolution, impacting performance in large-scale data processing scenarios.
JSON vs Avro: Data Structure
JSON stores data in a human-readable text format using key-value pairs and arrays, which offers flexibility but can lead to larger file sizes due to verbose syntax. Avro, designed for efficient serialization, uses a compact binary data structure that relies on a predefined schema, enabling faster data processing and reduced storage requirements. Unlike JSON, Avro enforces schema validation, ensuring data consistency and enabling seamless schema evolution in big data applications.
Performance Comparison: Avro vs JSON
Avro outperforms JSON in serialization and deserialization speed due to its compact binary format, reducing I/O and network overhead. JSON, being a text-based format, requires more CPU resources for parsing and generating, which impacts performance in high-throughput systems. Avro's schema-based compression also minimizes data size, enhancing transmission efficiency compared to the verbose JSON format.
Schema Evolution and Validation
Avro uses a robust schema evolution mechanism that allows backward and forward compatibility by embedding the schema with the data, enabling seamless validation during serialization and deserialization processes. JSON lacks a built-in schema, making schema evolution and data validation more error-prone and reliant on external tools or manual processes. Avro's strict adherence to schemas ensures data integrity and efficient validation, which is critical for evolving data systems in big data environments.
Interoperability and Language Support
Avro offers superior interoperability and language support compared to JSON, as it provides a compact binary format with schema evolution capabilities that ensure consistent data interpretation across diverse systems. Avro supports multiple programming languages including Java, Python, C, C++, and Ruby, enhancing seamless integration in polyglot environments, whereas JSON is text-based and widely supported but lacks formal schema definition, leading to potential compatibility issues. The use of Avro schemas enables precise data validation and efficient serialization, making it a preferred choice for distributed data pipelines and real-time streaming applications.
Use Cases: When to Use Avro or JSON
Avro excels in big data environments like Apache Hadoop and Kafka due to its compact binary serialization and efficient schema evolution capabilities, making it ideal for high-throughput data pipelines and storage. JSON is preferable for web APIs, configuration files, and human-readable data exchange where ease of use and readability are priorities. Choose Avro when data compactness, schema evolution, and integration with big data tools are critical, while JSON fits scenarios demanding simple text-based interchange and broad language compatibility.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Format
Avro offers schema-based serialization with compact binary encoding, ideal for high-performance data storage and transmission, while JSON provides human-readable, flexible data interchange suited for configuration and simple APIs. Choosing between Avro and JSON depends on the need for efficient serialization and strict schema enforcement versus readability and ease of use in dynamic data environments. For big data and streaming applications, Avro's strong typing and compression optimize performance, whereas JSON excels in interoperability and debugging scenarios.
Avro, JSON Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com