Software engineering involves the systematic application of engineering principles to software development, ensuring the creation of reliable, efficient, and scalable programs. It encompasses various processes such as requirements analysis, design, coding, testing, and maintenance, all aimed at delivering high-quality software solutions. Discover how mastering software engineering can elevate your projects by exploring the detailed insights in the rest of this article.
Table of Comparison
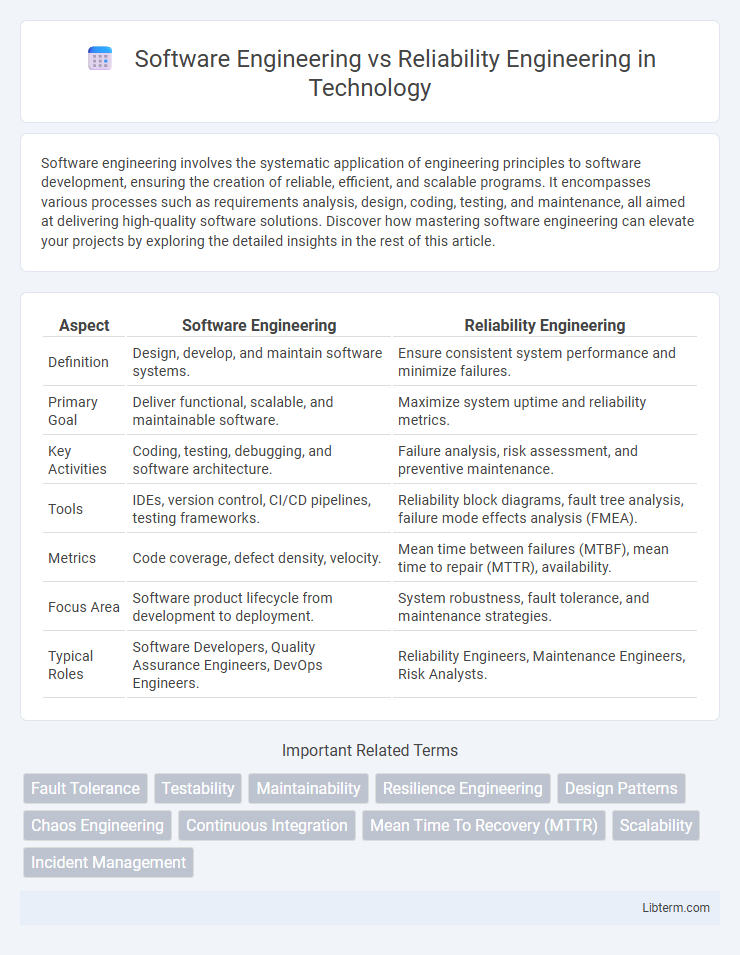
| Aspect | Software Engineering | Reliability Engineering |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Design, develop, and maintain software systems. | Ensure consistent system performance and minimize failures. |
| Primary Goal | Deliver functional, scalable, and maintainable software. | Maximize system uptime and reliability metrics. |
| Key Activities | Coding, testing, debugging, and software architecture. | Failure analysis, risk assessment, and preventive maintenance. |
| Tools | IDEs, version control, CI/CD pipelines, testing frameworks. | Reliability block diagrams, fault tree analysis, failure mode effects analysis (FMEA). |
| Metrics | Code coverage, defect density, velocity. | Mean time between failures (MTBF), mean time to repair (MTTR), availability. |
| Focus Area | Software product lifecycle from development to deployment. | System robustness, fault tolerance, and maintenance strategies. |
| Typical Roles | Software Developers, Quality Assurance Engineers, DevOps Engineers. | Reliability Engineers, Maintenance Engineers, Risk Analysts. |
Introduction to Software Engineering and Reliability Engineering
Software engineering encompasses the systematic design, development, testing, and maintenance of software applications to meet user requirements and quality standards. Reliability engineering focuses on ensuring that software systems function consistently and without failure over time, emphasizing fault tolerance, error detection, and risk assessment. Both disciplines are critical for delivering robust, high-quality software, with software engineering driving development processes and reliability engineering guaranteeing long-term system dependability.
Key Differences Between Software Engineering and Reliability Engineering
Software Engineering focuses on designing, developing, and maintaining software applications, emphasizing code quality, functionality, and performance. Reliability Engineering concentrates on ensuring systems operate consistently under specified conditions by analyzing failure modes, performing risk assessments, and implementing fault tolerance mechanisms. Key differences include Software Engineering's goal of feature delivery and usability versus Reliability Engineering's objective to maximize system uptime and minimize failure rates.
Core Responsibilities of Software Engineers
Software engineers focus on designing, developing, and maintaining software applications by writing clean and efficient code, debugging, and implementing algorithms to meet functional requirements. Their core responsibilities include collaborating with cross-functional teams, conducting code reviews, and ensuring software scalability and performance. Reliability engineers, in contrast, prioritize system stability and fault tolerance by designing resilient architectures and monitoring system health to minimize downtime and failures.
Core Responsibilities of Reliability Engineers
Reliability engineers focus on ensuring system dependability by analyzing failure modes, performing root cause analysis, and implementing preventive measures to minimize downtime and enhance performance. Their core responsibilities include designing reliability test plans, monitoring key performance indicators (KPIs) like mean time between failures (MTBF), and collaborating with cross-functional teams to improve product lifecycle and maintainability. In contrast, software engineers primarily develop, test, and maintain software applications, emphasizing functionality and code quality rather than system resilience and long-term reliability metrics.
Skills Required in Software Engineering vs Reliability Engineering
Software Engineering requires proficiency in programming languages, software development methodologies, version control systems, and debugging techniques, focusing on coding, design, and implementation. Reliability Engineering demands expertise in statistical analysis, failure mode effect analysis (FMEA), reliability testing, and risk assessment to predict and enhance system dependability. Both fields emphasize problem-solving and system optimization but apply distinct technical skills tailored to software functionality versus system longevity and robustness.
Importance of Collaboration Between Both Roles
Effective collaboration between Software Engineering and Reliability Engineering enhances system performance by integrating robust design with continuous quality assurance. Software Engineers develop functional code while Reliability Engineers focus on system stability, failure prediction, and resilience, ensuring seamless user experiences. This partnership reduces downtime, improves fault tolerance, and accelerates the release of reliable software products.
Tools and Methodologies in Software and Reliability Engineering
Software engineering utilizes tools such as integrated development environments (IDEs), version control systems like Git, and methodologies including Agile, Scrum, and DevOps to streamline coding, testing, and deployment processes. Reliability engineering employs statistical analysis tools, fault tree analysis (FTA), failure mode and effects analysis (FMEA), and methodologies centered on system dependability, maintainability, and availability to ensure consistent performance and minimize downtime. Both disciplines leverage automated testing frameworks and continuous integration pipelines, though reliability engineering emphasizes rigorous risk assessment and lifecycle management techniques tailored to critical system robustness.
Impact on Product Quality and Performance
Software Engineering focuses on designing, developing, and maintaining software systems to meet functional requirements, directly affecting product quality through code correctness, usability, and feature completeness. Reliability Engineering targets ensuring system dependability, availability, and fault tolerance by identifying potential failures and implementing robust monitoring and recovery mechanisms, significantly enhancing product performance and uptime. Both disciplines collaboratively improve product quality, with Software Engineering driving feature innovation and Reliability Engineering ensuring consistent and stable operation under varying conditions.
Career Opportunities and Industry Demand
Software Engineering offers diverse career opportunities across industries like technology, finance, and healthcare, driven by strong demand for application development, system design, and cybersecurity. Reliability Engineering specializes in ensuring system dependability and performance, with high demand in sectors such as aerospace, manufacturing, and automotive where safety and uptime are critical. Both fields present robust job prospects, but Reliability Engineering often requires deeper knowledge of failure analysis, maintenance strategies, and risk assessment.
Choosing the Right Path: Software Engineer or Reliability Engineer
Choosing between software engineering and reliability engineering hinges on your passion for either creating innovative software solutions or ensuring system robustness and uptime. Software engineers focus on designing, coding, and developing applications, while reliability engineers specialize in system performance, failure prevention, and risk mitigation. Prioritizing your career goals and interests in either rapid development or long-term system stability will guide the decision between these two critical tech roles.
Software Engineering Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com