A disk is a storage device used to save and retrieve digital data, commonly found in computers and external devices. It plays a crucial role in maintaining your files, applications, and system information securely and efficiently. Explore the rest of the article to understand the different types of disks and how they impact your technology experience.
Table of Comparison
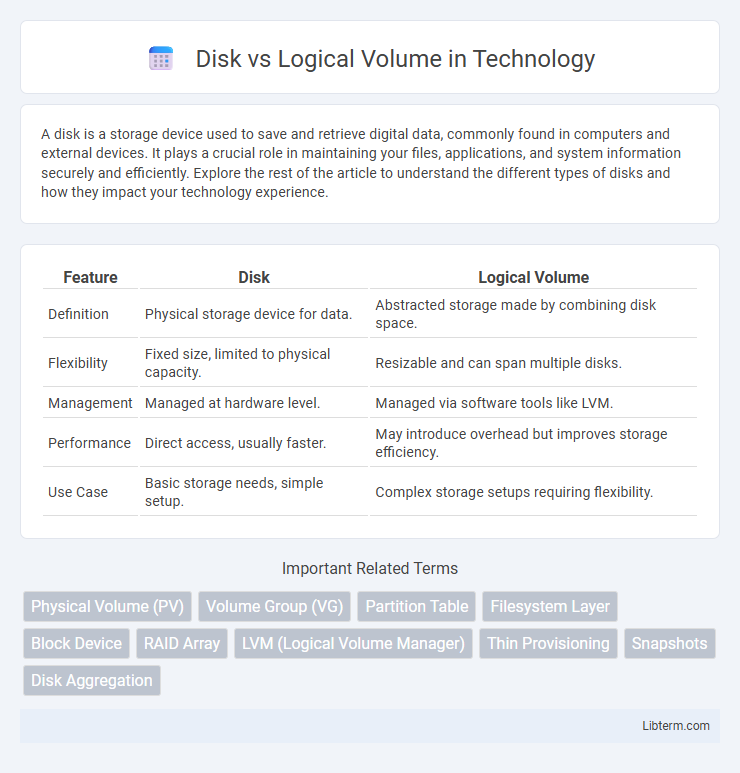
| Feature | Disk | Logical Volume |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Physical storage device for data. | Abstracted storage made by combining disk space. |
| Flexibility | Fixed size, limited to physical capacity. | Resizable and can span multiple disks. |
| Management | Managed at hardware level. | Managed via software tools like LVM. |
| Performance | Direct access, usually faster. | May introduce overhead but improves storage efficiency. |
| Use Case | Basic storage needs, simple setup. | Complex storage setups requiring flexibility. |
Introduction to Disk and Logical Volume
A disk is a physical storage device used to store data persistently, such as hard drives or solid-state drives, while a logical volume is a virtual storage abstraction created by combining or partitioning disk space to optimize flexibility and management. Logical volumes allow dynamic resizing and easier allocation compared to fixed physical disks, enhancing storage efficiency in environments using Logical Volume Managers (LVM). This abstraction separates physical hardware constraints from storage management, enabling advanced features like snapshot creation and improved data organization.
Understanding Physical Disks
Physical disks represent the actual hardware storage devices, such as HDDs or SSDs, that provide the foundational layer for data storage. Unlike logical volumes, which are virtualized storage units created by combining or partitioning physical disks, physical disks have fixed capacities and performance characteristics dictated by their mechanical or flash-based technology. Understanding the physical disk's parameters, including size, speed (RPM for HDDs), and interface type (SATA, NVMe), is crucial for optimizing system storage configurations and ensuring data reliability.
What is a Logical Volume?
A Logical Volume (LV) is a virtual storage unit created within a volume group, allowing flexible disk space management beyond traditional physical disk partitions. Unlike a physical disk, a logical volume can span multiple physical disks and be resized dynamically without downtime. Logical volumes enable efficient storage allocation, improving system scalability and simplifying data management in environments using Logical Volume Manager (LVM).
Key Differences Between Disk and Logical Volume
A disk is a physical storage device that stores data, while a logical volume is a virtual storage unit created by combining or partitioning one or more physical disks. Logical volumes offer flexibility by allowing dynamic resizing and easier management of storage compared to fixed-size physical disks. Disks represent the hardware layer, whereas logical volumes provide an abstraction layer that enables efficient storage allocation and improved data organization.
Storage Management: Disk vs Logical Volume
Disks represent physical storage devices used to store data, while logical volumes are virtual storage units created by combining or partitioning these physical disks for flexible management. Logical Volume Managers (LVM) enable dynamic resizing, snapshots, and efficient allocation of disk space, optimizing storage utilization compared to static disk partitions. This abstraction layer simplifies storage maintenance, improves performance, and enhances data redundancy across multiple physical disks.
Performance Comparison: Disk vs Logical Volume
Disk performance depends on physical hardware characteristics such as spindle speed, seek time, and interface type (e.g., SATA, SSD, NVMe), directly impacting read/write speeds and latency. Logical volumes introduce abstraction layers for flexibility and management but may cause slight overhead due to additional mapping and possible fragmentation. High-performance environments often favor direct disk access for minimal latency, while logical volumes offer scalability and resilience with marginal performance trade-offs.
Scalability and Flexibility
Logical volumes offer superior scalability and flexibility compared to physical disks by allowing dynamic resizing and aggregation of multiple disk spaces into a single storage pool. They enable on-the-fly adjustment of volume sizes without physical hardware changes, supporting efficient storage management in growing environments. Disk-based storage lacks this adaptability, often requiring downtime and manual intervention for capacity upgrades or reconfiguration.
Data Protection and Recovery
Disks provide basic data protection through hardware features like RAID but lack flexibility in recovery options. Logical volumes enhance data protection by enabling snapshots, cloning, and dynamic resizing, which improve recovery speed and minimize downtime. Combining multiple physical disks into logical volumes facilitates efficient backup management and disaster recovery strategies.
Use Cases: When to Choose Each
Disks are ideal for straightforward storage needs, such as single operating systems or dedicated applications requiring direct access to physical storage devices. Logical volumes provide flexibility for complex environments involving dynamic resizing, snapshots, and aggregation of multiple disks to optimize storage utilization in virtualized or multi-tenant systems. Choose disks for simplicity and performance, while logical volumes suit scalable, high-availability, and easily manageable storage architectures.
Conclusion: Selecting the Right Storage Option
Choosing between a physical disk and a logical volume depends on storage flexibility, scalability, and management needs. Disks offer straightforward, dedicated storage with predictable performance, while logical volumes provide dynamic resizing, easier backup, and multipath redundancy. Enterprises prioritizing agility and efficient storage utilization benefit most from logical volumes, whereas environments requiring simplicity and dedicated access may opt for physical disks.
Disk Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com