Systemd is a powerful system and service manager for Linux operating systems, designed to bootstrap the user space and manage system processes efficiently. It replaces traditional init systems to provide parallel startup of services, automated dependency handling, and extensive logging capabilities. Explore the rest of the article to discover how systemd can enhance your system's performance and reliability.
Table of Comparison
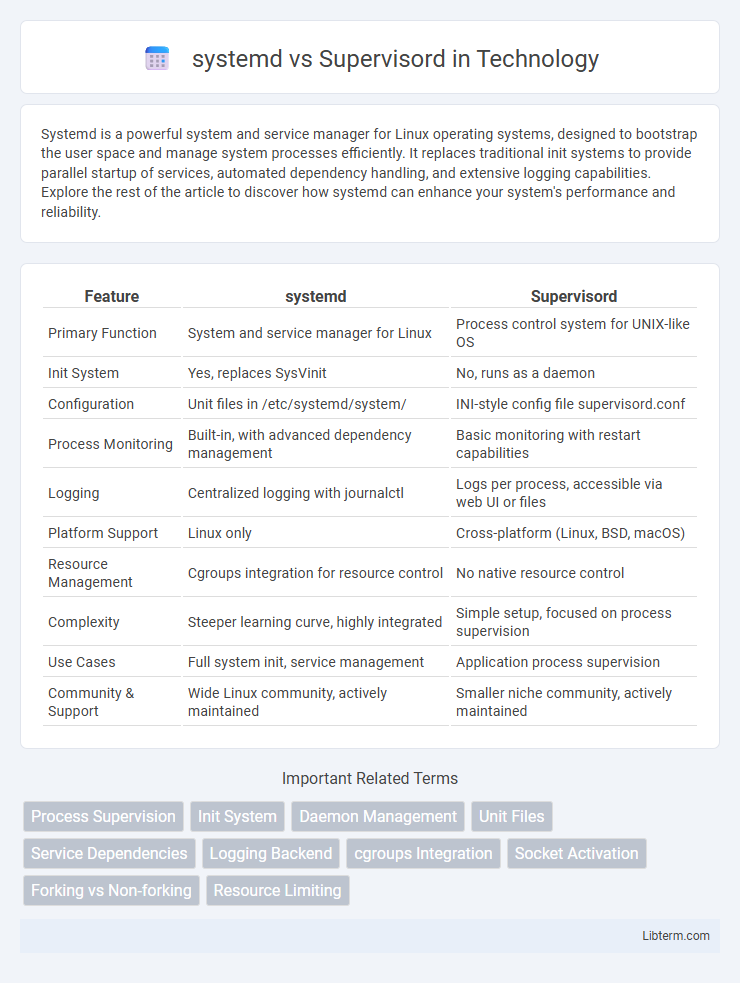
| Feature | systemd | Supervisord |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Function | System and service manager for Linux | Process control system for UNIX-like OS |
| Init System | Yes, replaces SysVinit | No, runs as a daemon |
| Configuration | Unit files in /etc/systemd/system/ | INI-style config file supervisord.conf |
| Process Monitoring | Built-in, with advanced dependency management | Basic monitoring with restart capabilities |
| Logging | Centralized logging with journalctl | Logs per process, accessible via web UI or files |
| Platform Support | Linux only | Cross-platform (Linux, BSD, macOS) |
| Resource Management | Cgroups integration for resource control | No native resource control |
| Complexity | Steeper learning curve, highly integrated | Simple setup, focused on process supervision |
| Use Cases | Full system init, service management | Application process supervision |
| Community & Support | Wide Linux community, actively maintained | Smaller niche community, actively maintained |
Introduction to Process Management Tools
Systemd and Supervisord are prominent process management tools used for initializing and controlling system services and background processes. Systemd integrates deeply with Linux systems, offering advanced features like parallel service startup, dependency management, and detailed logging through journalctl. Supervisord provides a simpler, Python-based approach to process monitoring and controlling, ideal for managing multiple processes in application environments without complex system integration.
What is systemd?
Systemd is a powerful init system and service manager designed for Linux operating systems to bootstrap user space and manage system processes after booting. It offers parallelized startup of services, dependency-based service control, and integrates logging through the journal, enhancing system performance and reliability. Systemd replaces traditional init systems by providing advanced features such as socket activation, on-demand starting of daemons, and comprehensive resource control via cgroups.
What is Supervisord?
Supervisord is an open-source process control system designed to manage and monitor multiple long-running applications and services on Unix-like operating systems. It provides a simple configuration format and a web-based or command-line interface to start, stop, and restart processes automatically, ensuring high availability. Supervisord is often favored for lightweight environments and development setups where minimal overhead and straightforward process management are priorities.
Architecture Comparison: systemd vs Supervisord
Systemd operates as a low-level init system with tight integration into the Linux kernel, managing system and service initialization through unit files and cgroups for resource control. Supervisord functions as a user-space process manager designed primarily for managing and monitoring processes, utilizing a configuration-driven approach with a centralized event-based architecture. Systemd's architecture supports parallel service startup and advanced dependency management, while Supervisord emphasizes simplicity and extensibility through XML-RPC API and flexible plugin support.
Installation and Configuration Differences
Systemd installs natively on most modern Linux distributions as part of the base system, requiring no separate download, while Supervisord must be installed via package managers like pip or apt. Configuration in systemd relies on declarative unit files located in /etc/systemd/system/, which use a structured syntax to define service dependencies and behaviors; Supervisord configurations employ an ini-style supervisord.conf file emphasizing simple process control and groupings. Systemd supports complex dependency management and advanced features like cgroups integration by default, contrasting with Supervisord's focus on straightforward process monitoring and automatic restarts.
Service Management Capabilities
Systemd offers advanced service management capabilities including parallelized startup, dependency tracking, and socket activation, optimizing system boot time and reliability. Supervisord focuses on process monitoring with automatic restarts and easy configuration for managing daemonized applications but lacks deep integration with system initialization and dependency handling. Systemd's comprehensive control over services provides enhanced resource management and logging through journald, making it suitable for complex system environments.
Monitoring and Logging Features
Systemd offers integrated monitoring through its built-in journald logging system, capturing detailed service logs with timestamping and structured data for seamless troubleshooting. Supervisord provides extensive real-time process monitoring and centralized logging features, with the ability to capture stdout and stderr streams, facilitating custom log file management. Both tools support alerting on process failures, but systemd's deep integration with Linux kernel features enables enhanced performance metrics and resource management monitoring.
Performance and Resource Usage
Systemd offers superior performance and lower resource usage compared to Supervisord due to its tight integration with the Linux kernel and efficient event-driven architecture. It manages services with minimal overhead, leveraging native cgroups for precise resource control and rapid process management. Supervisord, being a Python-based process control system, typically consumes more CPU and memory, making it less optimal for large-scale or resource-constrained environments.
Use Cases and Best Fit Scenarios
Systemd excels in managing background processes and system services on modern Linux distributions, making it ideal for system-level service management and boot-time initialization. Supervisord is better suited for controlling and monitoring long-running user-space applications, especially in development or lightweight server environments where process restarts and logs management are critical. Use systemd for comprehensive service dependency handling and Supervisord for simpler process control in isolated application contexts.
Conclusion: Choosing Between systemd and Supervisord
Systemd excels in managing system and service startup dependencies with deep integration into Linux operating systems, offering robust process supervision, logging, and resource control. Supervisord provides a simpler, language-agnostic solution focused on application-level process management, ideal for lightweight or containerized environments where ease of configuration is paramount. Selecting between systemd and Supervisord depends on the complexity of service requirements, operating system compatibility, and the need for advanced system-level features versus straightforward application process supervision.
systemd Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com