A centralized data center consolidates an organization's IT resources, enabling efficient management, enhanced security, and reduced operational costs. It streamlines data storage and processing by housing servers and networking equipment in a single, secure location. Explore this article to discover how a centralized data center can optimize your business infrastructure.
Table of Comparison
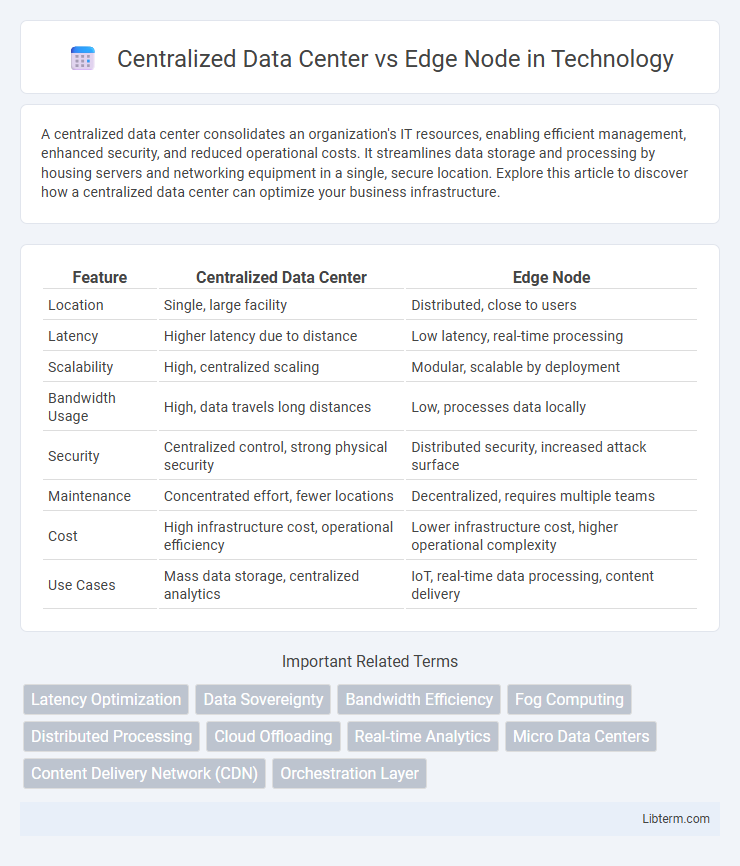
| Feature | Centralized Data Center | Edge Node |
|---|---|---|
| Location | Single, large facility | Distributed, close to users |
| Latency | Higher latency due to distance | Low latency, real-time processing |
| Scalability | High, centralized scaling | Modular, scalable by deployment |
| Bandwidth Usage | High, data travels long distances | Low, processes data locally |
| Security | Centralized control, strong physical security | Distributed security, increased attack surface |
| Maintenance | Concentrated effort, fewer locations | Decentralized, requires multiple teams |
| Cost | High infrastructure cost, operational efficiency | Lower infrastructure cost, higher operational complexity |
| Use Cases | Mass data storage, centralized analytics | IoT, real-time data processing, content delivery |
Introduction to Centralized Data Centers and Edge Nodes
Centralized data centers are large-scale facilities that consolidate computing resources, storage, and networking infrastructure to provide scalable and reliable services from a central location. Edge nodes, on the other hand, are decentralized computing points positioned closer to data sources and end-users, enabling low-latency processing and real-time analytics. The contrast between centralized data centers and edge nodes highlights trade-offs in latency, bandwidth usage, and data processing distribution essential for modern IT architectures.
Core Differences Between Centralized and Edge Computing
Centralized data centers consolidate computing resources in a single or few locations, offering high processing power and streamlined management but often facing latency and bandwidth constraints. Edge nodes distribute computing closer to data sources, reducing latency and enabling real-time data processing by handling tasks locally. This fundamental difference impacts performance, scalability, and security, with centralized systems excelling in large-scale data handling and edge computing optimizing responsiveness for time-sensitive applications.
Architectural Overview: Centralized Data Centers
Centralized data centers feature a core architecture where all computing resources, storage, and processing power are housed in a single, large facility, optimized for scalability and centralized management. This architecture enables efficient resource allocation, high security with controlled access, and consolidated data handling, but may introduce latency due to physical distance from end-users. Key components include high-performance servers, extensive cooling systems, redundant power supplies, and robust networking infrastructure to support large-scale, mission-critical applications.
Architectural Overview: Edge Node Infrastructure
Edge node infrastructure consists of distributed computing resources located closer to data sources, minimizing latency and bandwidth usage compared to centralized data centers. These nodes typically include micro data centers or edge servers equipped with processing power, storage, and networking capabilities to handle local data processing and analytics. By offloading tasks from centralized data centers, edge nodes enable faster response times and improved reliability for real-time applications such as IoT, autonomous vehicles, and smart cities.
Performance and Latency Considerations
Centralized data centers offer robust processing power and extensive storage but often face increased latency due to the greater physical distance from end-users. Edge nodes reduce latency significantly by processing data closer to the source, improving real-time performance for applications like IoT and autonomous vehicles. Balancing centralized data centers with strategically placed edge nodes optimizes overall system responsiveness and network efficiency.
Scalability and Flexibility: Data Center vs Edge
Centralized data centers offer high scalability by leveraging vast computing resources in a single location, enabling extensive data processing and storage capacity. Edge nodes provide enhanced flexibility by distributing data processing closer to the source, reducing latency and adapting quickly to local demand fluctuations. While data centers excel in managing large-scale operations, edge nodes deliver agile, real-time responsiveness essential for IoT and mobile applications.
Security Challenges and Solutions
Centralized data centers face significant security challenges such as single points of failure, large-scale cyber-attacks, and concentrated data breaches, demanding robust firewall protections, intrusion detection systems, and comprehensive access controls. Edge nodes, distributed closer to end-users, encounter unique security risks including physical tampering, limited computational resources for advanced encryption, and increased attack surfaces, requiring lightweight security protocols, device authentication, and real-time anomaly detection. Combining centralized oversight with decentralized edge security solutions enhances overall network resilience by balancing strong perimeter defense with localized threat detection and rapid response capabilities.
Use Cases: When to Choose Centralized vs Edge
Centralized data centers excel in handling large-scale data processing, complex analytics, and centralized storage needs, making them ideal for enterprise resource planning (ERP) and big data workloads. Edge nodes are preferred for low-latency applications such as real-time IoT data processing, autonomous vehicles, and augmented reality, where immediate data processing near the data source reduces latency and bandwidth usage. Choosing between centralized vs edge depends on factors like latency requirements, data volume, network bandwidth, and the need for real-time insights.
Cost Implications and Resource Management
Centralized data centers often incur higher capital expenditures due to large-scale infrastructure and cooling requirements, whereas edge nodes reduce latency costs by processing data closer to users but may increase operational expenses given the need for multiple distributed sites. Resource management in centralized centers benefits from economies of scale and consolidated maintenance, while edge nodes demand more complex management strategies to handle dispersed resources and ensure consistent performance. Balancing the cost implications involves analyzing workload distribution, the frequency of data processing, and network bandwidth usage to optimize both infrastructure investment and operational efficiency.
Future Trends in Data Center and Edge Node Integration
Future trends in data center and edge node integration emphasize decentralized computing architectures that optimize data processing closer to end-users, reducing latency and bandwidth demands. Hybrid models combining centralized data centers with distributed edge nodes enable scalable cloud services and real-time analytics for IoT, 5G, and AI applications. Advanced technologies like AI-driven orchestration and software-defined networking facilitate dynamic resource allocation, enhancing performance and energy efficiency across integrated infrastructures.
Centralized Data Center Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com