Authoritative DNS servers hold the definitive records for domain names, ensuring accurate and reliable translation of URLs into IP addresses. These servers play a critical role in the domain name system hierarchy, providing the final answer to DNS queries. Explore the rest of this article to understand how authoritative DNS impacts your website's performance and security.
Table of Comparison
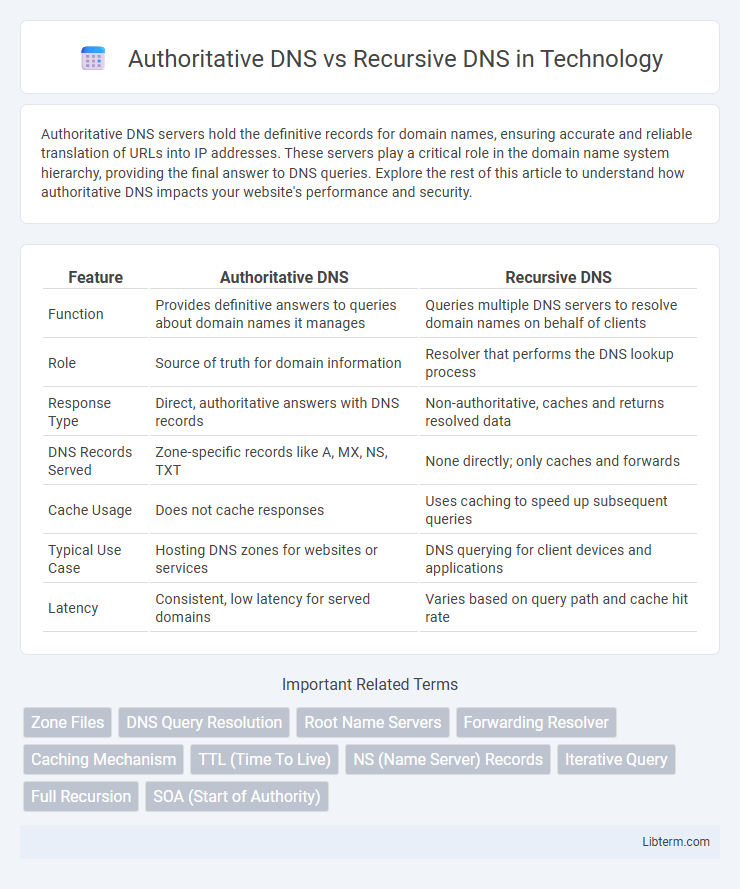
| Feature | Authoritative DNS | Recursive DNS |
|---|---|---|
| Function | Provides definitive answers to queries about domain names it manages | Queries multiple DNS servers to resolve domain names on behalf of clients |
| Role | Source of truth for domain information | Resolver that performs the DNS lookup process |
| Response Type | Direct, authoritative answers with DNS records | Non-authoritative, caches and returns resolved data |
| DNS Records Served | Zone-specific records like A, MX, NS, TXT | None directly; only caches and forwards |
| Cache Usage | Does not cache responses | Uses caching to speed up subsequent queries |
| Typical Use Case | Hosting DNS zones for websites or services | DNS querying for client devices and applications |
| Latency | Consistent, low latency for served domains | Varies based on query path and cache hit rate |
Understanding DNS: Authoritative vs Recursive
Authoritative DNS servers store the definitive records for domain names, providing precise answers about which IP addresses correspond to domain names. Recursive DNS servers act as intermediaries, querying multiple authoritative servers on behalf of clients to resolve domain names into IP addresses. Understanding the distinction between authoritative and recursive DNS is essential for optimizing DNS performance, security, and reliability.
What is an Authoritative DNS Server?
An Authoritative DNS server holds definitive records for a domain, providing responses to DNS queries with the source data for that zone. It stores DNS zone files and answers requests with authoritative information, such as IP addresses for domain names or mail exchange servers. Unlike recursive DNS servers that query other DNS servers to resolve names, authoritative servers give final, reliable answers directly related to the domains they manage.
What is a Recursive DNS Server?
A Recursive DNS server acts as an intermediary that processes DNS queries by recursively searching through multiple DNS servers until it retrieves the requested domain's IP address. It receives requests from client devices and queries authoritative DNS servers on behalf of the client, ensuring efficient resolution of domain names. Recursive DNS servers often employ caching mechanisms to speed up subsequent requests for the same domain, enhancing internet browsing performance.
Core Functions: Authoritative vs Recursive DNS
Authoritative DNS servers store and provide definitive answers for domain names within their specific zones, ensuring accurate and up-to-date DNS records are served directly from the source. Recursive DNS servers act as intermediaries that query multiple authoritative servers on behalf of clients to resolve domain names, caching responses to improve lookup efficiency and reduce latency. The core function of authoritative DNS is to maintain and deliver DNS zone data, while recursive DNS focuses on resolving queries by traversing the DNS hierarchy and optimizing the resolution process through caching.
Data Handling Differences in DNS Servers
Authoritative DNS servers store and manage definitive DNS records for specific domains, responding to queries with original, accurate data directly from the zone files they maintain. Recursive DNS servers act as intermediaries that query multiple authoritative servers on behalf of clients, caching responses temporarily to improve speed and reduce network traffic. The primary data handling difference lies in authoritative servers providing original data, while recursive servers resolve, aggregate, and cache data from across the DNS infrastructure.
Security Implications: Authoritative vs Recursive
Authoritative DNS servers store and provide definitive answers for domain name queries, making them prime targets for DDoS attacks and cache poisoning attempts that can disrupt domain resolution integrity. Recursive DNS servers, responsible for querying multiple authoritative servers to resolve domain names for clients, are vulnerable to cache poisoning, which can redirect users to malicious sites, and amplification attacks that exploit DNS responses to overwhelm networks. Implementing DNSSEC and rate limiting across both authoritative and recursive servers enhances security by ensuring data authenticity and reducing the risk of DNS-based attacks.
Performance Impact: Query Resolution Speed
Authoritative DNS servers store definitive domain information, enabling faster response times for queries within their zones, reducing latency. Recursive DNS servers perform iterative lookups, which may increase query resolution time due to multiple external requests before providing the final answer. Performance impact favors authoritative DNS for direct queries, while recursive DNS speed depends on caching efficiency and network conditions.
Real-World Use Cases for Each DNS Type
Authoritative DNS servers provide definitive responses for domain names by hosting the original zone files, essential for managing domain ownership and ensuring accurate global DNS resolution. Recursive DNS servers act as intermediaries that query authoritative servers on behalf of clients, optimizing web browsing speed and improving security through caching and filtering. In real-world use, authoritative DNS is critical for domain registries and enterprises maintaining their own domains, while recursive DNS is widely used by ISPs, enterprise networks, and public DNS providers like Google Public DNS and Cloudflare for faster, reliable user queries.
Choosing the Right DNS Server for Your Needs
Authoritative DNS servers provide definitive answers for domain queries by storing DNS records for specific domains, making them essential for website owners hosting their own domains. Recursive DNS servers handle user queries by fetching data from authoritative servers, offering fast lookup services and caching results to improve performance and reduce latency. Choosing the right DNS server depends on whether you need to manage domain records directly (authoritative) or prioritize query resolution speed and efficiency for end-users (recursive).
Authoritative and Recursive DNS: Key Takeaways
Authoritative DNS servers store and provide definitive answers for domain names they are responsible for, ensuring domain name resolution accuracy by holding original DNS records. Recursive DNS servers act as intermediaries, querying multiple authoritative servers on behalf of the user to resolve domain names completely. Understanding the roles of authoritative and recursive DNS is crucial for optimizing DNS performance, security, and troubleshooting domain resolution issues effectively.
Authoritative DNS Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com