Hardware Security Modules (HSMs) provide robust, tamper-resistant environments for generating, storing, and managing cryptographic keys, essential for securing sensitive data and supporting compliance requirements across industries. These devices deliver high-performance cryptographic operations, safeguarding your digital assets from unauthorized access and cyber threats. Explore the full article to understand how HSMs can enhance your organization's security infrastructure effectively.
Table of Comparison
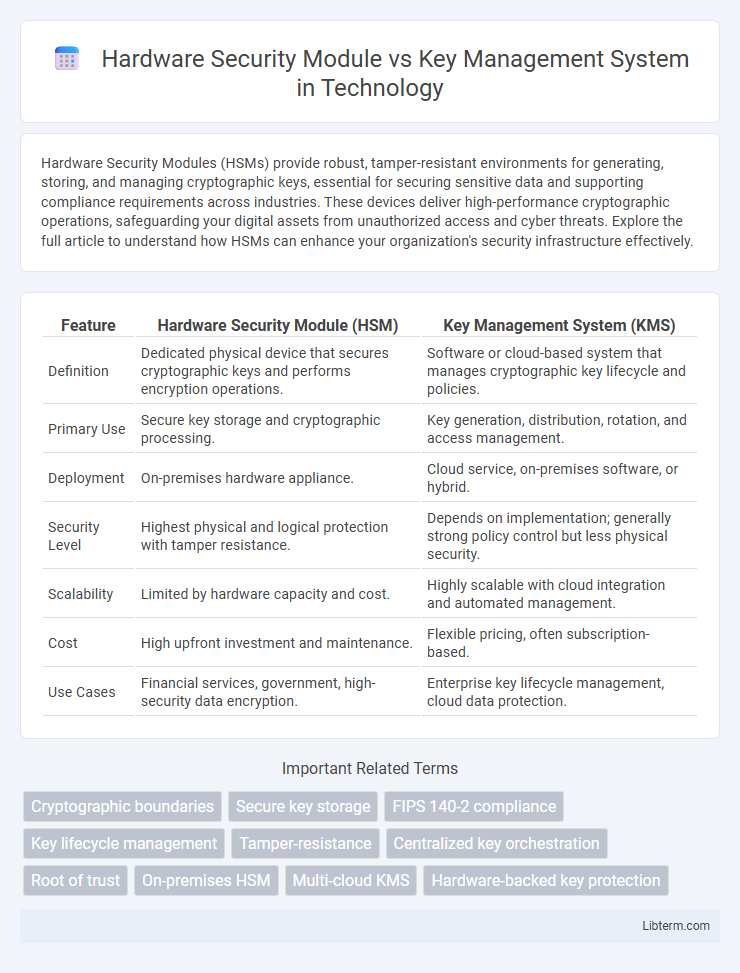
| Feature | Hardware Security Module (HSM) | Key Management System (KMS) |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Dedicated physical device that secures cryptographic keys and performs encryption operations. | Software or cloud-based system that manages cryptographic key lifecycle and policies. |
| Primary Use | Secure key storage and cryptographic processing. | Key generation, distribution, rotation, and access management. |
| Deployment | On-premises hardware appliance. | Cloud service, on-premises software, or hybrid. |
| Security Level | Highest physical and logical protection with tamper resistance. | Depends on implementation; generally strong policy control but less physical security. |
| Scalability | Limited by hardware capacity and cost. | Highly scalable with cloud integration and automated management. |
| Cost | High upfront investment and maintenance. | Flexible pricing, often subscription-based. |
| Use Cases | Financial services, government, high-security data encryption. | Enterprise key lifecycle management, cloud data protection. |
Introduction to Hardware Security Modules (HSM) and Key Management Systems (KMS)
Hardware Security Modules (HSM) are dedicated physical devices designed to securely generate, store, and manage cryptographic keys, providing tamper-resistant protection and high-assurance encryption operations. Key Management Systems (KMS) offer centralized software solutions for managing cryptographic keys across diverse applications, enabling automated key lifecycle management including creation, rotation, and deletion. While HSMs focus on hardware-based security for key storage and cryptographic functions, KMS platforms provide comprehensive key administration and policy enforcement often integrated with cloud and enterprise infrastructures.
Defining HSM: Core Functions and Capabilities
A Hardware Security Module (HSM) is a physical computing device designed to safeguard and manage digital keys for strong authentication and encryption, offering secure key generation, storage, and cryptographic processing. Core functions of HSMs include tamper-resistant hardware security, high-performance encryption and decryption, and secure key lifecycle management to prevent unauthorized access and ensure data integrity. Compared to Key Management Systems (KMS), HSMs provide dedicated hardware-based protection, making them essential for compliance with stringent security standards like FIPS 140-2 and GDPR.
Understanding Key Management Systems: Features and Benefits
Key Management Systems (KMS) provide centralized control for cryptographic keys, enabling secure generation, storage, distribution, and lifecycle management of keys across diverse applications. Unlike Hardware Security Modules (HSMs) that focus on physical key protection and cryptographic operations, KMS emphasizes integration with cloud environments, automated key rotation, and granular access controls to enhance operational efficiency and compliance. The benefits of KMS include simplified key governance, improved auditability, and scalability in managing encryption keys across hybrid and multi-cloud infrastructures.
Key Differences Between HSM and KMS
Hardware Security Modules (HSMs) physically protect cryptographic keys using tamper-resistant hardware, ensuring high-security key storage and cryptographic operations. Key Management Systems (KMS) primarily provide software-based key lifecycle management, including key generation, rotation, and access control across cloud and enterprise environments. HSMs emphasize hardware-level security and compliance, while KMS solutions prioritize centralized key administration and integration with various applications and services.
Security Architecture: Hardware Security vs Software-Based Management
Hardware Security Modules (HSMs) provide robust physical protection for cryptographic keys by utilizing tamper-resistant hardware and secure key storage, ensuring keys never leave the device in unencrypted form. Key Management Systems (KMS) rely primarily on software-based management, offering flexibility and scalability but depending heavily on platform security controls and network defenses. The security architecture of HSMs delivers higher assurance against physical and logical attacks, while KMS solutions emphasize centralized key lifecycle management integrated with cloud or enterprise environments.
Use Cases for HSM and KMS in Enterprise Environments
Hardware Security Modules (HSMs) provide tamper-resistant, dedicated cryptographic processing ideal for securing sensitive keys in high-assurance environments such as payment processing, certificate authority management, and hardware-based encryption key storage. Key Management Systems (KMS) streamline encryption key lifecycle management across cloud services, databases, and application infrastructures, enabling centralized key provisioning, rotation, and policy enforcement to maintain regulatory compliance and data protection. Enterprises leverage HSMs for physical security and cryptographic operations requiring certification (e.g., FIPS 140-2), while KMS solutions handle scalable, automated key workflows critical for modern hybrid and multi-cloud environments.
Performance and Scalability Considerations
Hardware Security Modules (HSMs) deliver high performance by providing dedicated cryptographic processing, ensuring low latency and rapid key operations essential for real-time applications. Key Management Systems (KMS) emphasize scalability with cloud-based architectures that support dynamic key lifecycle management across distributed environments, enabling seamless integration and flexible resource allocation. Balancing HSM's robust, hardware-accelerated security with KMS's scalable, software-driven key administration is crucial for optimizing both performance and scalability in enterprise cryptographic infrastructures.
Integration and Compatibility with Existing Infrastructure
Hardware Security Modules (HSMs) offer robust cryptographic processing with seamless integration into existing IT infrastructures through standardized APIs such as PKCS#11, KMIP, and JCE. Key Management Systems (KMS) provide centralized key lifecycle management and are designed for compatibility with diverse cloud platforms, applications, and on-premises environments via RESTful APIs and SDKs. Both solutions emphasize interoperability, but HSMs prioritize hardware-level security integration, while KMS focuses on flexible software-driven key management within hybrid infrastructures.
Regulatory Compliance and Industry Standards
Hardware Security Modules (HSMs) provide physical and tamper-resistant protection for cryptographic keys, ensuring compliance with industry standards like FIPS 140-2/3 and PCI DSS, critical for regulated sectors such as finance and healthcare. Key Management Systems (KMS) offer centralized control over key lifecycle management, supporting compliance with standards including GDPR, HIPAA, and SOC 2 by enforcing policies for key rotation, usage, and access auditing. Combining HSMs with KMS enhances regulatory compliance by securing key storage and providing robust administrative controls aligned with global cybersecurity frameworks.
Choosing the Right Solution: HSM or KMS for Your Organization
Selecting the right solution between a Hardware Security Module (HSM) and a Key Management System (KMS) depends on your organization's security requirements and infrastructure. HSMs provide tamper-resistant hardware for generating, storing, and managing cryptographic keys with high assurance, ideal for environments requiring stringent physical security and compliance standards like FIPS 140-2/3. KMS offers scalable software-based key lifecycle management with flexible integration options, suitable for cloud-native applications and organizations prioritizing centralized, automated key administration.
Hardware Security Module Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com