Redacted data serves as a critical tool in protecting sensitive information by obscuring or removing specific details from documents or datasets. It prevents unauthorized access to confidential content while maintaining the overall context needed for analysis or review. Discover how redacted data plays a pivotal role in information security and compliance by reading the full article.
Table of Comparison
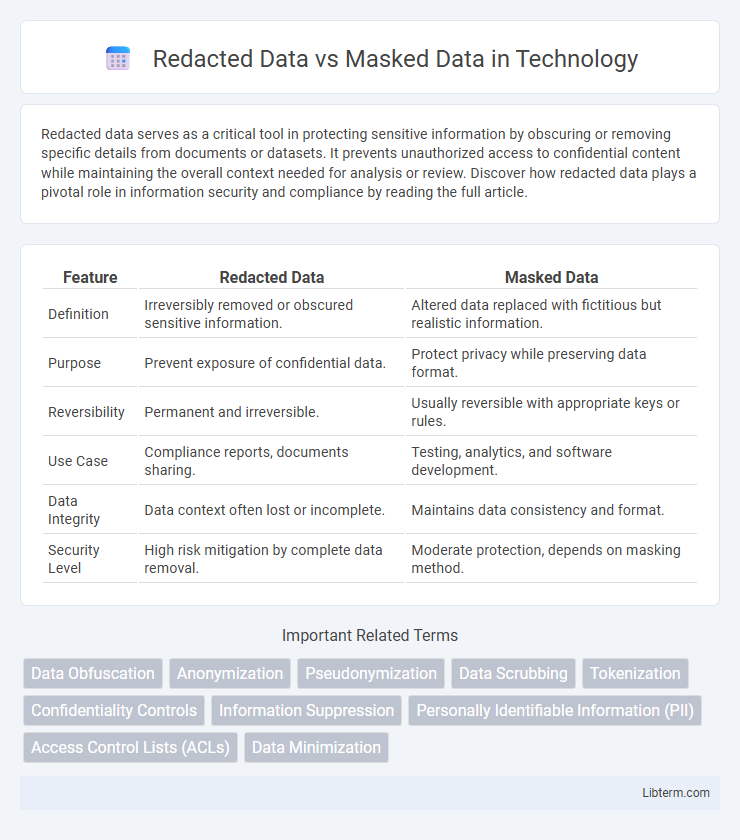
| Feature | Redacted Data | Masked Data |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Irreversibly removed or obscured sensitive information. | Altered data replaced with fictitious but realistic information. |
| Purpose | Prevent exposure of confidential data. | Protect privacy while preserving data format. |
| Reversibility | Permanent and irreversible. | Usually reversible with appropriate keys or rules. |
| Use Case | Compliance reports, documents sharing. | Testing, analytics, and software development. |
| Data Integrity | Data context often lost or incomplete. | Maintains data consistency and format. |
| Security Level | High risk mitigation by complete data removal. | Moderate protection, depends on masking method. |
Introduction to Redacted and Masked Data
Redacted data involves permanently removing or obscuring sensitive information to prevent unauthorized access, often used in legal and governmental documents to protect privacy. Masked data replaces original sensitive values with fictional but realistic substitutes, enabling data usability for testing and analysis without exposing real information. Both techniques are essential for maintaining data privacy compliance and minimizing security risks in data handling.
Defining Redacted Data
Redacted data refers to information that has been permanently removed or obscured to prevent disclosure of sensitive content, often used in legal, governmental, and corporate documents to protect privacy or confidential details. Unlike masked data, which substitutes original data with altered but structurally similar values for testing or analysis purposes, redacted data is irreversibly altered and cannot be recovered or reconstructed. The primary goal of redaction is to ensure compliance with data privacy regulations and safeguard sensitive information from unauthorized access.
Understanding Masked Data
Masked data involves transforming sensitive information by obscuring or replacing specific data elements to prevent unauthorized access while preserving data format and usability for testing or analysis purposes. Unlike redacted data, which permanently removes or blacks out information, masked data ensures confidentiality by allowing original data patterns to remain intact, enabling realistic data scenarios without exposure of actual values. Common masking techniques include substitution, shuffling, encryption, and character scrambling, ensuring compliance with data privacy regulations like GDPR and HIPAA.
Key Differences Between Redacted and Masked Data
Redacted data involves permanently removing or obscuring sensitive information from documents or datasets to prevent unauthorized access, typically replacing the content with black bars or deletion. Masked data, in contrast, substitutes original data with fictitious but realistic values, maintaining the format and usability of the dataset while protecting privacy. The key difference lies in redaction's irreversible deletion versus masking's reversible or reversible-like transformation aimed at preserving data utility for testing or analysis.
Common Use Cases for Data Redaction
Data redaction is commonly used in legal documents to permanently remove sensitive information such as social security numbers and confidential business details, ensuring privacy compliance. In healthcare, redacted data protects patient identities by concealing personal health information while enabling the sharing of medical records for research. Financial institutions use data redaction to safeguard customer account numbers and transaction details when producing reports or sharing data externally.
Typical Applications of Data Masking
Data masking is commonly applied in software testing, development environments, and user training to protect sensitive information while preserving data structure and usability. It is extensively used in industries such as healthcare, finance, and retail where compliance with regulations like HIPAA and GDPR is critical. Masking ensures that confidential data remains secure during analysis and sharing, unlike redacted data which is permanently removed or obscured.
Benefits and Limitations of Redacted Data
Redacted data offers the benefit of permanently removing sensitive information, ensuring compliance with privacy laws and reducing the risk of unauthorized data exposure. However, this process limits data usability, as redacted portions are irreversibly deleted, potentially hindering thorough analysis or context understanding. Organizations must balance the security advantages of redaction against the operational challenges of working with incomplete datasets.
Advantages and Challenges of Masked Data
Masked data offers enhanced security by obfuscating sensitive information while preserving data utility for testing and analysis, making it ideal for development environments. This approach reduces the risk of data breaches compared to redacted data, which often results in incomplete or unusable datasets. Challenges of masked data include maintaining consistent masking across systems and ensuring reversible masking methods when necessary for authorized access.
Compliance and Regulatory Considerations
Redacted data involves permanently removing or obscuring sensitive information to meet strict compliance requirements such as GDPR and HIPAA, ensuring that unauthorized individuals cannot access protected details. Masked data, on the other hand, replaces sensitive elements with fictional but realistic values, supporting regulatory needs for data security while enabling safe use in non-production environments like testing and analytics. Both techniques address privacy mandates, but redaction is favored for irreversible data concealment, whereas masking balances data utility and protection in compliance frameworks.
Choosing Between Redaction and Masking in Data Security
Choosing between redacted data and masked data depends on the specific data security requirements and use cases. Redaction permanently removes sensitive information, making it irreversible and ideal for compliance with strict privacy regulations, whereas masking replaces data with fictitious but realistic values, preserving data format for testing or development environments. Organizations must assess the level of data utility needed alongside confidentiality to determine whether redaction's irreversible obfuscation or masking's reversible, usable simulation better protects sensitive information while supporting operational needs.
Redacted Data Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com