Mesh topology creates a network where each device connects directly to every other device, ensuring robust communication and high fault tolerance. This design minimizes the risk of network failure as data can travel along multiple paths, enhancing reliability and speed for your connections. Explore the rest of the article to discover how mesh topology can optimize your network infrastructure.
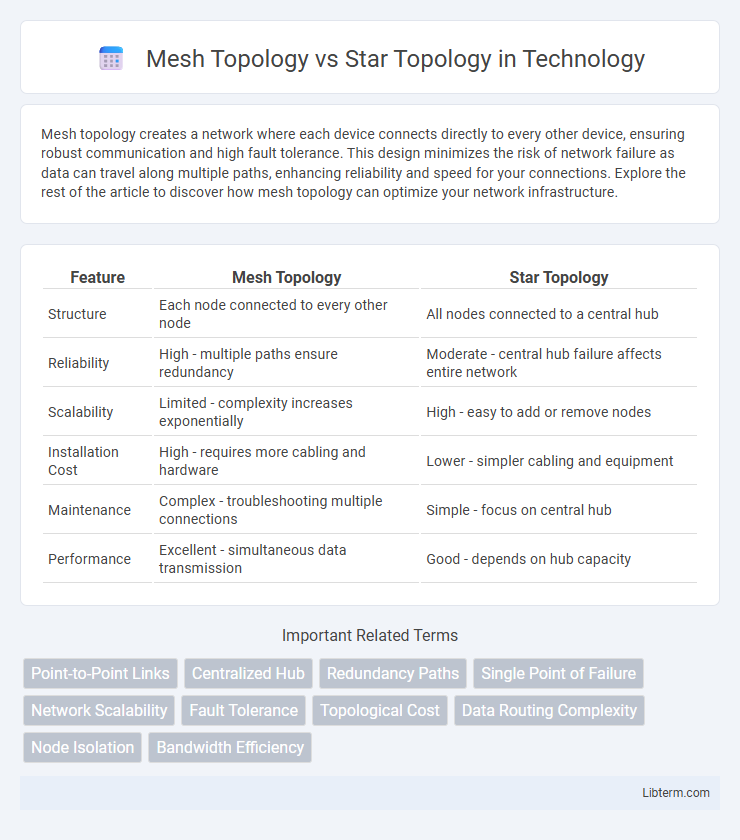
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Mesh Topology | Star Topology |
|---|---|---|
| Structure | Each node connected to every other node | All nodes connected to a central hub |
| Reliability | High - multiple paths ensure redundancy | Moderate - central hub failure affects entire network |
| Scalability | Limited - complexity increases exponentially | High - easy to add or remove nodes |
| Installation Cost | High - requires more cabling and hardware | Lower - simpler cabling and equipment |
| Maintenance | Complex - troubleshooting multiple connections | Simple - focus on central hub |
| Performance | Excellent - simultaneous data transmission | Good - depends on hub capacity |
Introduction to Network Topologies
Mesh topology features a network design where each device interconnects directly with every other device, ensuring high redundancy and fault tolerance for critical communication systems. Star topology centralizes connections through a single hub or switch, simplifying network management but creating a potential single point of failure. Understanding these fundamental network topologies is essential for optimizing network performance, scalability, and reliability in various IT infrastructures.
What is Mesh Topology?
Mesh topology is a network configuration where each device connects directly to every other device, ensuring high redundancy and reliability. This setup allows data to be transmitted along multiple paths, reducing the risk of network failure and optimizing communication efficiency. Mesh topology is especially beneficial in critical networks requiring consistent uptime and robust fault tolerance.
What is Star Topology?
Star topology is a network configuration where all devices connect to a central hub or switch, enabling efficient data transmission and easy management. Each node independently communicates with the central device, minimizing the impact of individual device failures on the entire network. This topology is widely used in local area networks (LANs) due to its scalability and straightforward troubleshooting advantages compared to mesh topology.
Key Differences Between Mesh and Star Topologies
Mesh topology features direct connections between all nodes, ensuring high redundancy and fault tolerance, which contrasts with star topology's centralized hub that manages all network traffic. Mesh networks excel in reliability and data routing efficiency, while star topology simplifies network management and reduces cable complexity. Key differences include mesh's robust fault tolerance versus star's ease of maintenance and scalability, impacting network performance and design choices.
Advantages of Mesh Topology
Mesh topology offers superior fault tolerance by ensuring each device is connected to multiple nodes, minimizing network downtime during failures. It provides enhanced security through direct connections, reducing the risk of data interception and unauthorized access. High reliability and efficient data routing make mesh topology ideal for critical applications requiring uninterrupted and robust communication.
Advantages of Star Topology
Star topology offers centralized management where each node connects independently to a central hub, simplifying network troubleshooting and maintenance. It provides robust performance with minimal impact on the entire system when a single node fails, enhancing network reliability. Scalability is straightforward, allowing easy addition or removal of devices without disrupting overall network functionality.
Disadvantages of Mesh Topology
Mesh topology faces significant disadvantages such as higher implementation costs and increased complexity due to the extensive cabling and numerous connections required for each device. Troubleshooting and maintenance become difficult because a fault in one connection can disrupt the entire network, making system management cumbersome. Scalability is limited as adding new nodes exponentially increases the number of connections, impacting network performance and reliability.
Disadvantages of Star Topology
Star topology experiences a significant drawback due to its reliance on a central hub or switch, creating a single point of failure that can disrupt the entire network if the hub malfunctions. Scalability issues arise as the network grows, requiring more ports and cabling that increase complexity and costs. Performance bottlenecks occur at the central device, limiting overall network efficiency and increasing latency during high traffic volumes.
Mesh Topology vs Star Topology: Use Cases
Mesh topology excels in environments requiring high redundancy and fault tolerance, such as military communication systems and data center networks, due to its decentralized connectivity. Star topology is preferred in home networks and office settings where simplicity, ease of management, and cost-effectiveness are critical, as all devices connect through a central hub or switch. Mesh topology supports high bandwidth and real-time data transmission essential for IoT applications, while star topology is ideal for structured cabling and limited device connectivity scenarios.
Choosing the Right Topology for Your Network
Choosing the right network topology involves evaluating factors such as scalability, fault tolerance, and cost. Mesh topology offers high redundancy and reliability by connecting each device directly to others, making it ideal for critical systems requiring continuous uptime. Star topology simplifies network management and is cost-effective for smaller setups by centralizing connections through a hub or switch.
Mesh Topology Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com