Authentication ensures that only authorized users can access sensitive information or systems by verifying their identity through passwords, biometrics, or security tokens. Effective authentication methods protect your data from unauthorized access and cyber threats. Explore the rest of the article to learn about various authentication techniques and best practices for securing your digital identity.
Table of Comparison
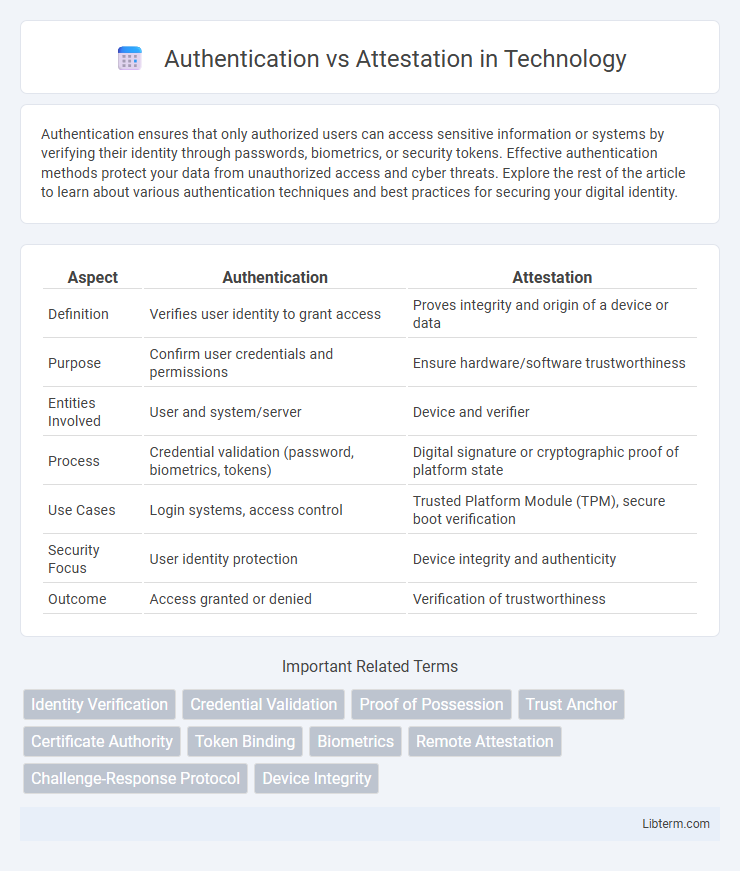
| Aspect | Authentication | Attestation |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Verifies user identity to grant access | Proves integrity and origin of a device or data |
| Purpose | Confirm user credentials and permissions | Ensure hardware/software trustworthiness |
| Entities Involved | User and system/server | Device and verifier |
| Process | Credential validation (password, biometrics, tokens) | Digital signature or cryptographic proof of platform state |
| Use Cases | Login systems, access control | Trusted Platform Module (TPM), secure boot verification |
| Security Focus | User identity protection | Device integrity and authenticity |
| Outcome | Access granted or denied | Verification of trustworthiness |
Introduction to Authentication and Attestation
Authentication verifies the identity of a user, device, or system by validating credentials such as passwords, biometrics, or tokens. Attestation provides proof that a device or system's hardware and software are in a trusted, unaltered state, often using cryptographic techniques. Both processes are crucial for ensuring security in digital interactions by confirming identity and system integrity.
Defining Authentication: Purpose and Methods
Authentication verifies a user's identity to grant access to systems, services, or data, utilizing methods such as passwords, biometrics, two-factor authentication (2FA), and digital certificates. The purpose of authentication is to prevent unauthorized access by confirming that the claimed identity is genuine. Effective authentication strengthens security protocols, protecting sensitive information from cyber threats and ensuring compliance with regulations like GDPR and HIPAA.
What is Attestation? Concepts and Applications
Attestation is the process of verifying and validating the integrity and authenticity of a device, software, or data using cryptographic proofs, ensuring it has not been tampered with. It involves generating a trusted report, often through a Trusted Platform Module (TPM) or secure enclave, which can be remotely verified by a third party to establish trust. Applications of attestation include secure boot validation, software integrity checks, and enabling trustworthy interactions in cloud computing and Internet of Things (IoT) environments.
Key Differences Between Authentication and Attestation
Authentication verifies the identity of a user or system through credentials like passwords, biometrics, or tokens, ensuring access control. Attestation validates the integrity and trustworthiness of a device or software by providing cryptographic proof that it meets specific security standards. The key difference lies in authentication confirming identity, while attestation confirms the device's or software's authenticity and security posture.
Use Cases: When to Choose Authentication vs Attestation
Authentication is ideal for verifying user identity in secure login systems, access control, and online transactions to prevent unauthorized access and fraud. Attestation is best suited for proving device integrity, software authenticity, and compliance in environments requiring trustworthy hardware or software states, such as IoT security and enterprise endpoint validation. Choosing authentication prioritizes identity validation, while attestation focuses on trustworthiness of the platform or environment.
Security Implications of Authentication and Attestation
Authentication verifies the identity of users or devices, serving as the first line of defense against unauthorized access and reducing the risk of identity theft and data breaches. Attestation ensures the integrity and trustworthiness of a device or software by validating its state before granting access, preventing compromised systems from interacting within a network. Together, authentication and attestation strengthen security by combining identity verification with device integrity assurance, minimizing vulnerabilities in IT environments.
Technologies Powering Authentication Systems
Authentication systems leverage technologies such as biometrics, multi-factor authentication (MFA), and public key infrastructure (PKI) to verify user identities reliably. Attestation mechanisms utilize cryptographic proofs and hardware-based trusted platform modules (TPMs) to confirm the integrity and origin of devices or software. These technologies combine to enhance security by ensuring both user authenticity and system trustworthiness.
Attestation Protocols in Modern Infrastructure
Attestation protocols in modern infrastructure provide a critical layer of security by enabling systems to verify the integrity and authenticity of hardware and software components before granting access. These protocols, such as TPM-based attestation and Intel SGX, ensure that devices meet predefined security policies, preventing unauthorized code execution and mitigating risks in cloud environments and IoT networks. Unlike authentication, which verifies user identity, attestation focuses on the trustworthiness of the device state, making it essential for zero-trust architectures and secure firmware updates.
Common Challenges and Solutions in Both Processes
Authentication and attestation face common challenges such as identity spoofing, data integrity breaches, and lack of user trust. Solutions include implementing multi-factor authentication (MFA), leveraging cryptographic techniques like digital signatures, and employing decentralized identity frameworks to enhance verification reliability. Continuous monitoring and adaptive risk assessment also improve security and user experience in both processes.
Future Trends: The Evolving Landscape of Authentication and Attestation
Future trends in authentication and attestation emphasize the integration of biometric technologies, decentralized identity frameworks, and continuous authentication methods. Advancements in blockchain enable secure, tamper-proof attestation of identity claims, while artificial intelligence enhances risk-based authentication by analyzing behavioral patterns in real-time. The evolving landscape prioritizes seamless user experiences combined with robust security measures to address increasingly sophisticated cyber threats.
Authentication Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com