The data plane is responsible for forwarding packets based on rules set by the control plane, ensuring efficient and fast data transmission within a network. It plays a crucial role in network devices such as routers and switches by handling traffic directly and maintaining high throughput. Explore this article to understand how the data plane impacts your network performance and security.
Table of Comparison
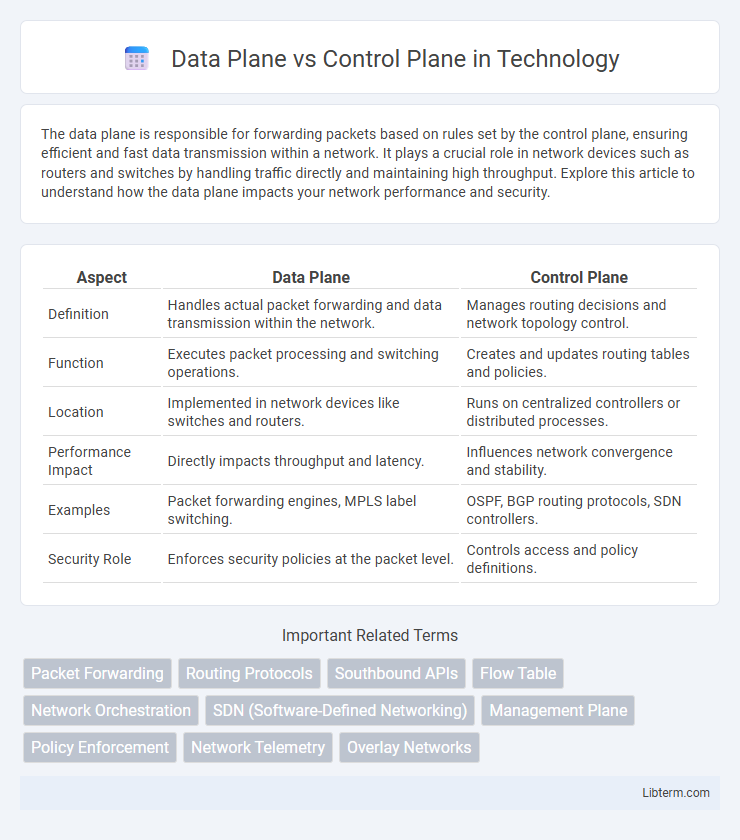
| Aspect | Data Plane | Control Plane |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Handles actual packet forwarding and data transmission within the network. | Manages routing decisions and network topology control. |
| Function | Executes packet processing and switching operations. | Creates and updates routing tables and policies. |
| Location | Implemented in network devices like switches and routers. | Runs on centralized controllers or distributed processes. |
| Performance Impact | Directly impacts throughput and latency. | Influences network convergence and stability. |
| Examples | Packet forwarding engines, MPLS label switching. | OSPF, BGP routing protocols, SDN controllers. |
| Security Role | Enforces security policies at the packet level. | Controls access and policy definitions. |
Introduction to Data Plane and Control Plane
The data plane processes and forwards user traffic within a network, handling packet forwarding based on established rules. The control plane manages network routing decisions and policy enforcement by maintaining routing tables and network topology information. Together, these planes enable efficient communication and optimal network performance.
Core Functions of the Data Plane
The data plane is responsible for the core functions of packet forwarding, including packet encapsulation, switching, and routing based on destination addresses, ensuring efficient traffic delivery across the network. It processes user data in real-time, managing packet queuing, classification, and filtering to maintain optimal network performance and security. The data plane operates independently from the control plane, executing forwarding decisions conveyed by routing protocols and policies established by the control plane.
Key Responsibilities of the Control Plane
The control plane is responsible for network routing decisions, traffic management, and maintaining the overall network topology by exchanging routing information via protocols such as OSPF, BGP, and RIP. It dynamically updates routing tables, manages policy enforcement, and controls signaling to ensure efficient data forwarding. Key functions include path computation, network resource allocation, and network state monitoring to provide centralized control and optimize network performance.
Architectural Differences Between Data and Control Plane
The data plane is responsible for the actual forwarding of packets based on predetermined rules, operating at high speed to process user traffic efficiently. In contrast, the control plane manages the network routing decisions, signaling, and protocol exchanges to establish and maintain the forwarding tables used by the data plane. Architecturally, the data plane is embedded within network devices such as switches and routers to handle packet-level processing, while the control plane runs on centralized or distributed controllers that execute network intelligence and policy logic.
How Data Plane Affects Network Performance
The data plane directly impacts network performance by handling the forwarding of data packets between devices at high speeds, ensuring low latency and efficient throughput. Its efficiency in packet processing and switching determines the overall bandwidth utilization and responsiveness of the network infrastructure. Optimizing the data plane reduces bottlenecks, minimizes packet loss, and enhances real-time data delivery critical for applications like video streaming and VoIP.
Control Plane’s Role in Network Management
The control plane is responsible for network management by making decisions about routing, signaling, and network topology. It maintains the routing tables, manages network traffic policies, and orchestrates dynamic adjustments to optimize data flow across the network. Effective control plane functions enable seamless communication between devices, ensuring network stability, scalability, and efficient bandwidth utilization.
Communication Between Data Plane and Control Plane
The communication between the data plane and control plane occurs through secure, low-latency channels to ensure efficient network management and packet forwarding. Control plane protocols such as OpenFlow, NETCONF, and REST APIs facilitate real-time updates and configuration commands from the control plane to the data plane, enabling dynamic routing and policy enforcement. This interaction is crucial for maintaining synchronization between network state information held by the control plane and operational packet processing performed by the data plane.
Security Implications: Data Plane vs Control Plane
The Data Plane processes user traffic and enforces security policies at line rate, making it a critical target for attacks like data exfiltration and DDoS. The Control Plane manages routing and signaling, with vulnerabilities potentially leading to network misconfigurations or unauthorized access. Securing the Control Plane requires robust authentication and access controls, while protecting the Data Plane demands real-time monitoring and threat detection to prevent service disruption.
Real-World Use Cases and Applications
The Data Plane handles packet forwarding and traffic management in high-speed networks like routers and switches, enabling efficient delivery of data in real-time applications such as video streaming and VoIP communications. The Control Plane manages routing protocols and network topology decisions, essential for dynamic path selection in large-scale environments like Internet Service Providers and enterprise SD-WAN deployments. In software-defined networking (SDN), the separation of Data Plane and Control Plane facilitates centralized network control and automation, optimizing resource allocation and improving security in cloud data centers and IoT infrastructures.
Choosing the Right Balance: Data Plane and Control Plane
Choosing the right balance between the data plane and control plane is essential for optimizing network performance and scalability. The data plane manages packet forwarding and traffic handling at high speeds, while the control plane focuses on routing decisions and network topology updates. Efficient separation and coordination between these planes enable improved network reliability, faster response times, and flexible management in software-defined networking (SDN) environments.
Data Plane Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com