Encryption secures your data by converting it into unreadable code, protecting sensitive information from unauthorized access. It is essential for safeguarding personal details, financial transactions, and confidential communications in the digital age. Discover how encryption works and why it's crucial for your online privacy in the full article.
Table of Comparison
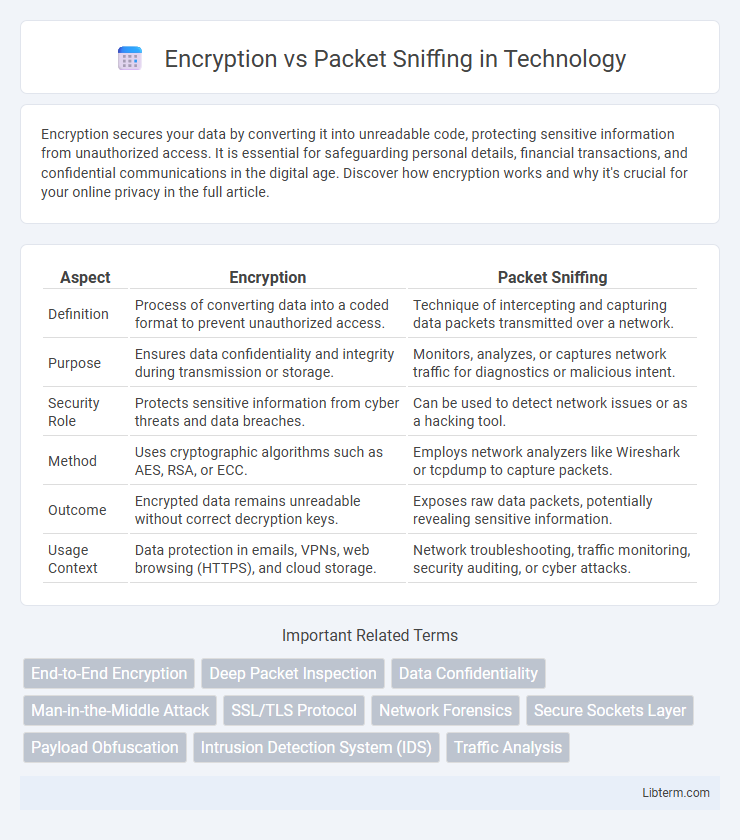
| Aspect | Encryption | Packet Sniffing |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Process of converting data into a coded format to prevent unauthorized access. | Technique of intercepting and capturing data packets transmitted over a network. |
| Purpose | Ensures data confidentiality and integrity during transmission or storage. | Monitors, analyzes, or captures network traffic for diagnostics or malicious intent. |
| Security Role | Protects sensitive information from cyber threats and data breaches. | Can be used to detect network issues or as a hacking tool. |
| Method | Uses cryptographic algorithms such as AES, RSA, or ECC. | Employs network analyzers like Wireshark or tcpdump to capture packets. |
| Outcome | Encrypted data remains unreadable without correct decryption keys. | Exposes raw data packets, potentially revealing sensitive information. |
| Usage Context | Data protection in emails, VPNs, web browsing (HTTPS), and cloud storage. | Network troubleshooting, traffic monitoring, security auditing, or cyber attacks. |
Understanding Encryption: A Brief Overview
Encryption transforms data into a coded format using algorithms and keys, making it unreadable to unauthorized users. It ensures confidentiality and integrity by securing sensitive information during transmission and storage. Common encryption methods include symmetric encryption (AES) and asymmetric encryption (RSA), both vital for protecting data against packet sniffing attacks.
What is Packet Sniffing?
Packet sniffing is a network analysis technique where data packets traveling across a network are intercepted and captured for inspection. It allows attackers or network administrators to monitor, analyze, and potentially manipulate data transmitted between devices. Unlike encryption, which secures data by encoding it, packet sniffing exploits unencrypted traffic to access sensitive information such as passwords, emails, and other private communications.
How Encryption Protects Your Data
Encryption transforms sensitive data into an unreadable format using complex algorithms and cryptographic keys, ensuring information remains inaccessible to unauthorized entities during transmission. This process safeguards data integrity and confidentiality against packet sniffing techniques, which intercept and analyze network traffic to extract valuable information. By implementing strong encryption protocols such as AES and TLS, organizations prevent cybercriminals from deciphering captured packets, thereby protecting personal and business data from breaches.
Methods and Tools Used in Packet Sniffing
Packet sniffing involves capturing data packets transmitted over a network using tools like Wireshark, tcpdump, and Ettercap, which analyze packet headers and payloads for network monitoring or malicious interception. Encryption methods such as AES, RSA, and TLS secure data by encoding it, preventing unauthorized access during transmission, rendering intercepted packets unreadable. While packet sniffers rely on passive data capture and interpretation, encryption employs cryptographic algorithms to ensure confidentiality and integrity of network communications.
Encryption Algorithms: Types and Uses
Encryption algorithms such as AES (Advanced Encryption Standard), RSA (Rivest-Shamir-Adleman), and ECC (Elliptic Curve Cryptography) are critical for securing data against packet sniffing attacks by converting plaintext into unreadable ciphertext. AES is widely used for symmetric key encryption due to its efficiency and strength in protecting data in transit, while RSA and ECC provide asymmetric encryption for secure key exchange and digital signatures. These algorithms are implemented across various applications, including VPNs, SSL/TLS protocols, and encrypted messaging, ensuring data confidentiality and integrity from unauthorized interceptors monitoring network traffic.
Real-World Examples of Packet Sniffing Attacks
Packet sniffing attacks demonstrate the critical need for robust encryption, as attackers intercept sensitive data transmitted over unsecured networks. High-profile incidents like the 2013 Target data breach exploited weak network security, where attackers captured unencrypted customer information via packet sniffing tools. Encryption protocols such as TLS and WPA3 effectively prevent packet sniffers from accessing readable data, protecting personal and financial details in real-time communications.
Encryption vs Packet Sniffing: Key Differences
Encryption secures data by converting it into an unreadable format using algorithms like AES or RSA, ensuring confidentiality even if intercepted during transmission. Packet sniffing involves capturing network packets to analyze data flow, often used for troubleshooting or maliciously intercepting unencrypted information. The key difference lies in encryption's role in protecting data integrity and privacy, while packet sniffing focuses on data capture and analysis without inherently providing security.
How Packet Sniffers Bypass Weak Encryption
Packet sniffers exploit vulnerabilities in weak encryption protocols such as WEP and outdated WPA versions by capturing and analyzing encrypted data packets to reveal keys through known algorithm weaknesses or brute-force attacks. Techniques like replay attacks and statistical analysis enable packet sniffers to crack poorly implemented encryption, compromising sensitive information transmitted over networks. Strong encryption standards like WPA3 with robust key management and forward secrecy prevent packet sniffers from easily decrypting intercepted data.
Best Practices to Defend Against Packet Sniffing
Encryption protocols such as TLS and AES secure data by encoding packets, making intercepted information unreadable to packet sniffers, which capture raw network traffic. Implementing strong encryption standards, regularly updating cryptographic keys, and enforcing the use of secure communication channels like VPNs effectively mitigate the risk of data breaches through packet sniffing. Network segmentation, intrusion detection systems, and proper access controls further enhance defenses by limiting unauthorized traffic monitoring and ensuring only legitimate packet analysis occurs.
The Future of Encryption in Network Security
The future of encryption in network security hinges on advanced algorithms like quantum-resistant cryptography to counter emerging threats from quantum computing. Enhanced encryption protocols such as TLS 1.3 and end-to-end encryption frameworks are becoming essential to protect data from sophisticated packet sniffing techniques. Continued innovation in cryptographic standards ensures robust defense mechanisms against unauthorized data interception and maintains privacy in increasingly complex network environments.
Encryption Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com