Lean methodology streamlines processes by eliminating waste and focusing on value creation to boost efficiency and quality. Implementing Lean principles helps your organization reduce costs, improve customer satisfaction, and foster continuous improvement. Explore the rest of the article to discover practical steps for adopting Lean in your workflow.
Table of Comparison
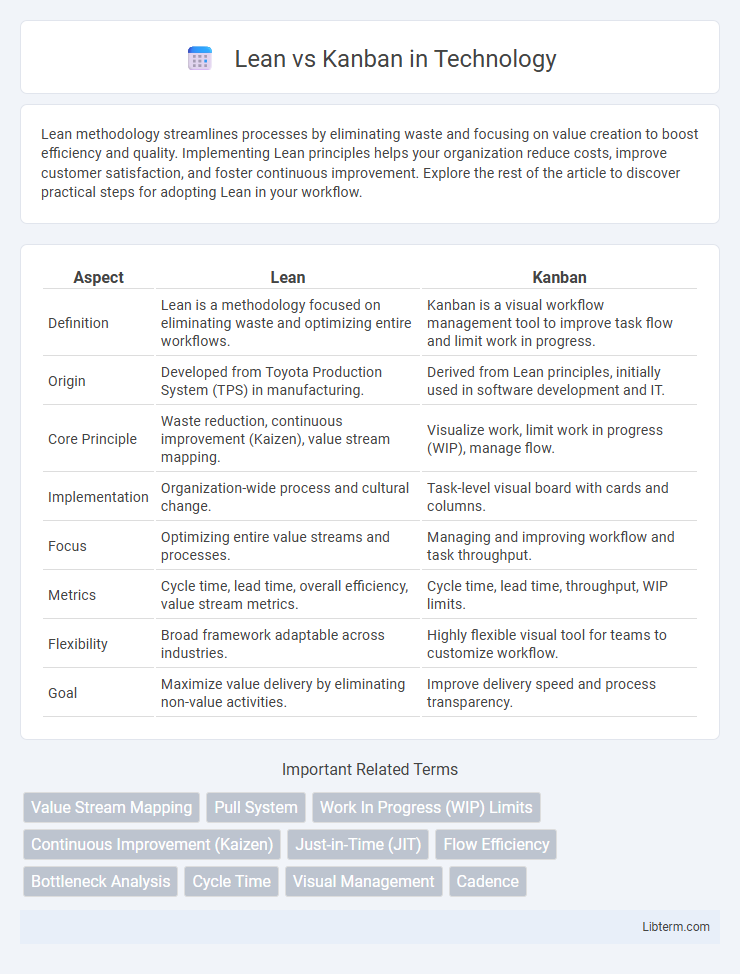
| Aspect | Lean | Kanban |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Lean is a methodology focused on eliminating waste and optimizing entire workflows. | Kanban is a visual workflow management tool to improve task flow and limit work in progress. |
| Origin | Developed from Toyota Production System (TPS) in manufacturing. | Derived from Lean principles, initially used in software development and IT. |
| Core Principle | Waste reduction, continuous improvement (Kaizen), value stream mapping. | Visualize work, limit work in progress (WIP), manage flow. |
| Implementation | Organization-wide process and cultural change. | Task-level visual board with cards and columns. |
| Focus | Optimizing entire value streams and processes. | Managing and improving workflow and task throughput. |
| Metrics | Cycle time, lead time, overall efficiency, value stream metrics. | Cycle time, lead time, throughput, WIP limits. |
| Flexibility | Broad framework adaptable across industries. | Highly flexible visual tool for teams to customize workflow. |
| Goal | Maximize value delivery by eliminating non-value activities. | Improve delivery speed and process transparency. |
Introduction to Lean and Kanban
Lean is a systematic methodology focused on minimizing waste and maximizing value by optimizing workflows, often applied in manufacturing and software development. Kanban is a visual workflow management tool within Lean principles that uses boards and cards to represent work items and their progress, enhancing transparency and continuous delivery. Both Lean and Kanban aim to improve efficiency, reduce cycle times, and promote incremental improvements in processes.
Core Principles of Lean
Lean centers on eliminating waste, continuous improvement, and delivering maximum value to customers by optimizing processes and resources. Its core principles include defining value from the customer's perspective, mapping the value stream to identify inefficiencies, creating flow to ensure smooth production, establishing pull systems to reduce overproduction, and pursuing perfection through iterative improvements. These principles create a foundation for efficient operations that minimize delays and enhance product quality.
Core Principles of Kanban
Kanban centers on visualizing workflow, limiting work in progress, and managing flow to improve efficiency and identify bottlenecks. Its core principles include starting with existing processes, encouraging evolutionary change, and fostering collaborative leadership at every level. Emphasizing transparency and continuous delivery, Kanban aims to optimize process adaptability without radical overhauls.
Key Differences Between Lean and Kanban
Lean is a comprehensive management philosophy aimed at maximizing value by eliminating waste and optimizing processes across an organization, while Kanban is a specific visual workflow management method used to implement Lean principles, focusing on work-in-progress limits and continuous delivery. Lean emphasizes broad organizational change through value stream mapping and process improvement, whereas Kanban targets workflow visualization and real-time capacity management within teams. The key difference lies in Lean's holistic approach to system-wide efficiency versus Kanban's tactical approach to managing and improving individual workflows.
When to Choose Lean
Choose Lean methodology when your organization seeks to eliminate waste, improve overall process efficiency, and foster a culture of continuous improvement across multiple departments. Lean is ideal for complex projects requiring systemic evaluation of value streams and long-term operational excellence, emphasizing principles like just-in-time production and respect for people. It works best in environments where reducing cycle time and optimizing resource flow are critical to meeting customer demands and business goals.
When to Use Kanban
Kanban is ideal for teams aiming to improve workflow efficiency and manage work-in-progress limits without overhauling existing processes. It excels in environments with continuous delivery and unpredictable workloads, allowing for real-time prioritization and flexibility. Use Kanban when visualizing tasks and minimizing bottlenecks are critical to maintaining steady productivity and transparency.
Lean and Kanban Implementation Steps
Lean implementation steps begin with defining value from the customer's perspective, mapping the value stream to identify waste, and creating a flow by eliminating non-value-added activities. Kanban implementation involves visualizing workflow on a Kanban board, limiting work in progress (WIP) to enhance focus, and managing flow by continuously reviewing and adjusting work items. Both methodologies emphasize continuous improvement and employee involvement to optimize processes and increase efficiency.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Lean
Lean methodology enhances efficiency by minimizing waste and optimizing processes, resulting in faster delivery and reduced costs. Its emphasis on continuous improvement fosters adaptability but may require significant cultural change and employee training. Lean can struggle in environments with highly variable demand, as strict waste reduction may limit flexibility.
Pros and Cons of Kanban
Kanban offers visual workflow management that enhances transparency and identifies bottlenecks quickly, improving overall efficiency. Its flexibility allows teams to adapt to changing priorities without disrupting ongoing work, but it can lead to task accumulation if WIP (work in progress) limits are not strictly enforced. However, Kanban may lack clear deadlines, making it less suitable for projects requiring strict time constraints or predictable delivery schedules.
Combining Lean and Kanban for Optimal Results
Combining Lean and Kanban integrates Lean's waste-reduction principles with Kanban's visual workflow management to enhance productivity and efficiency. This approach leverages continuous improvement cycles and real-time task visualization, enabling faster response to bottlenecks and smoother process flow. Organizations adopting this synergy achieve reduced lead times, improved quality, and higher customer satisfaction through data-driven decision-making and optimized resource allocation.
Lean Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com