Task queues improve your system's efficiency by organizing and prioritizing workloads for streamlined processing. These queues enable asynchronous task execution, reducing bottlenecks and enhancing overall performance. Discover how implementing a task queue can transform your operations by reading the full article.
Table of Comparison
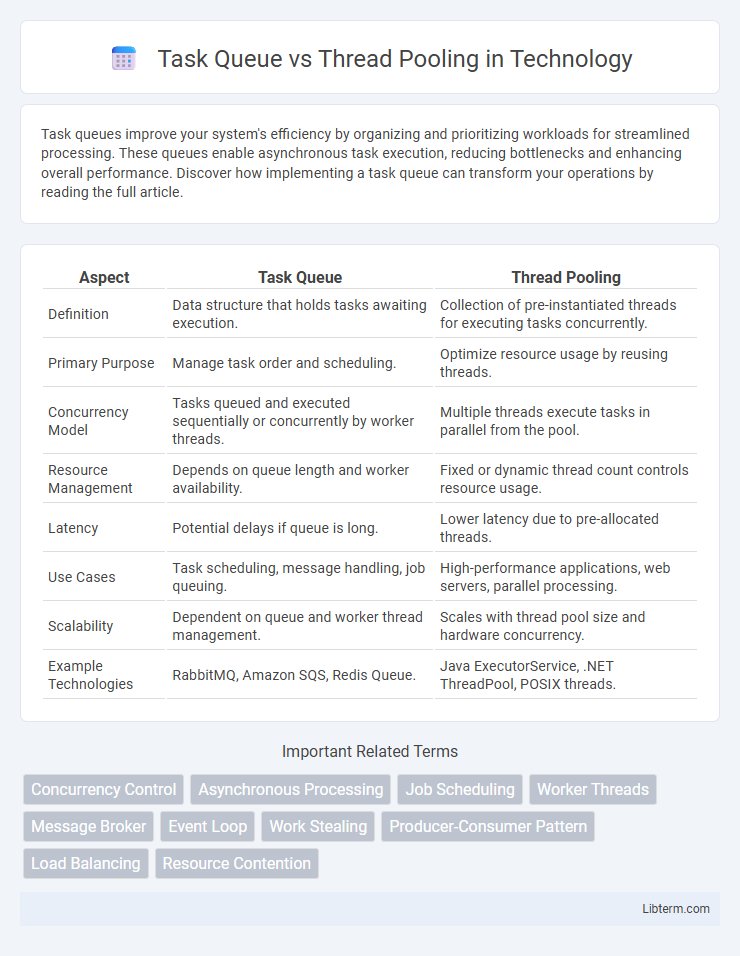
| Aspect | Task Queue | Thread Pooling |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Data structure that holds tasks awaiting execution. | Collection of pre-instantiated threads for executing tasks concurrently. |
| Primary Purpose | Manage task order and scheduling. | Optimize resource usage by reusing threads. |
| Concurrency Model | Tasks queued and executed sequentially or concurrently by worker threads. | Multiple threads execute tasks in parallel from the pool. |
| Resource Management | Depends on queue length and worker availability. | Fixed or dynamic thread count controls resource usage. |
| Latency | Potential delays if queue is long. | Lower latency due to pre-allocated threads. |
| Use Cases | Task scheduling, message handling, job queuing. | High-performance applications, web servers, parallel processing. |
| Scalability | Dependent on queue and worker thread management. | Scales with thread pool size and hardware concurrency. |
| Example Technologies | RabbitMQ, Amazon SQS, Redis Queue. | Java ExecutorService, .NET ThreadPool, POSIX threads. |
Introduction to Task Queue and Thread Pooling
Task queues organize tasks to be executed sequentially or concurrently, managing workload distribution efficiently across resources. Thread pooling maintains a set of reusable threads to execute multiple tasks, reducing the overhead of thread creation and destruction. Both mechanisms improve application performance by optimizing task scheduling and resource utilization in parallel processing environments.
Core Concepts: What is a Task Queue?
A Task Queue is a data structure that holds tasks waiting to be executed by available worker threads, enabling asynchronous processing and efficient workload management. It decouples task submission from execution, allowing multiple producers to enqueue tasks while a pool of consumer threads processes them concurrently. Task Queues optimize resource utilization and improve system responsiveness by managing task scheduling and execution order.
Core Concepts: What is Thread Pooling?
Thread pooling is a concurrency management technique where a fixed number of threads are created and maintained to execute multiple tasks, reducing the overhead of thread creation and destruction. It improves application performance by reusing existing threads from the pool to handle incoming tasks, ensuring efficient CPU utilization. This approach is essential in environments with high-frequency task execution, minimizing latency and resource consumption compared to creating a new thread for each task.
Task Queue Architecture Explained
Task queue architecture manages workloads by organizing tasks into a queue that worker threads process asynchronously, enhancing scalability and system efficiency. This design decouples task submission from execution, allowing for better load balancing and improved resource utilization. Task queues are essential in distributed systems to handle high concurrency and ensure reliable task management, contrasting with thread pooling which pre-allocates a fixed number of threads for task execution.
Thread Pooling Architecture Explained
Thread pooling architecture manages a collection of reusable threads to perform multiple tasks concurrently, reducing the overhead of thread creation and destruction. It typically involves a pool manager that assigns tasks from a queue to available threads, maintaining optimal resource utilization and improving application performance. By controlling the number of active threads, thread pooling ensures efficient CPU usage and minimizes context switching in multi-threaded environments.
Key Differences between Task Queues and Thread Pools
Task queues manage the scheduling and execution order of tasks by holding them until threads are available, while thread pools consist of a fixed number of pre-created threads that execute tasks concurrently to optimize resource usage. Task queues improve task organization and allow for asynchronous processing by decoupling task submission from execution, whereas thread pools focus on reusing threads to reduce overhead and enhance performance during multi-threading operations. The key difference lies in task queues serving as a buffer to manage workload distribution, contrasted with thread pools providing the actual execution context for running those tasks.
Performance Comparison: Task Queue vs Thread Pooling
Task queues and thread pooling both enhance concurrency but differ in performance metrics; task queues excel in managing large-scale asynchronous workloads by decoupling task submission from execution, reducing overhead during peak loads. Thread pools optimize CPU utilization by reusing fixed numbers of threads, minimizing context switching and thread creation costs, which improves latency and throughput for CPU-bound tasks. Overall, thread pooling delivers superior performance for compute-intensive operations, while task queues offer better scalability and flexibility in distributed or I/O-bound environments.
Use Cases: When to Use Task Queue or Thread Pooling
Task queues excel in managing distributed systems and workloads requiring asynchronous processing, such as background job execution and load balancing across multiple servers. Thread pooling is ideal for applications needing efficient resource management and concurrency within a single process, like handling multiple client requests in web servers or parallelizing CPU-bound tasks. Use task queues for scalability across systems and thread pools for optimized multitasking in localized environments.
Scalability and Resource Management Considerations
Task queue systems improve scalability by decoupling task submission from execution, enabling efficient load distribution across multiple workers and preventing resource contention. Thread pooling optimizes resource management by reusing a fixed number of threads, reducing the overhead of thread creation while controlling concurrency to avoid thread exhaustion. Both approaches enhance system responsiveness, but task queues excel in distributed environments, whereas thread pools are ideal for managing limited resources within a single process.
Best Practices for Implementing Task Queues and Thread Pools
Implementing task queues and thread pools efficiently requires aligning queue size and thread count with system capabilities to prevent resource exhaustion and maximize throughput. Task queues benefit from smooth backpressure management and prioritization strategies for critical jobs, while thread pools demand configuring thread lifetimes and handling deadlocks carefully to ensure robustness. Monitoring runtime metrics such as queue length, task wait time, and thread utilization enables dynamic adjustments that uphold optimal concurrency and responsiveness.
Task Queue Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com