Single-tenancy refers to a software architecture where a single instance of an application serves one customer or tenant exclusively, ensuring dedicated resources and enhanced security. This model is ideal for businesses requiring custom configurations and strict data isolation, improving performance and compliance. Explore the rest of the article to understand how single-tenancy can benefit your organization's IT strategy.
Table of Comparison
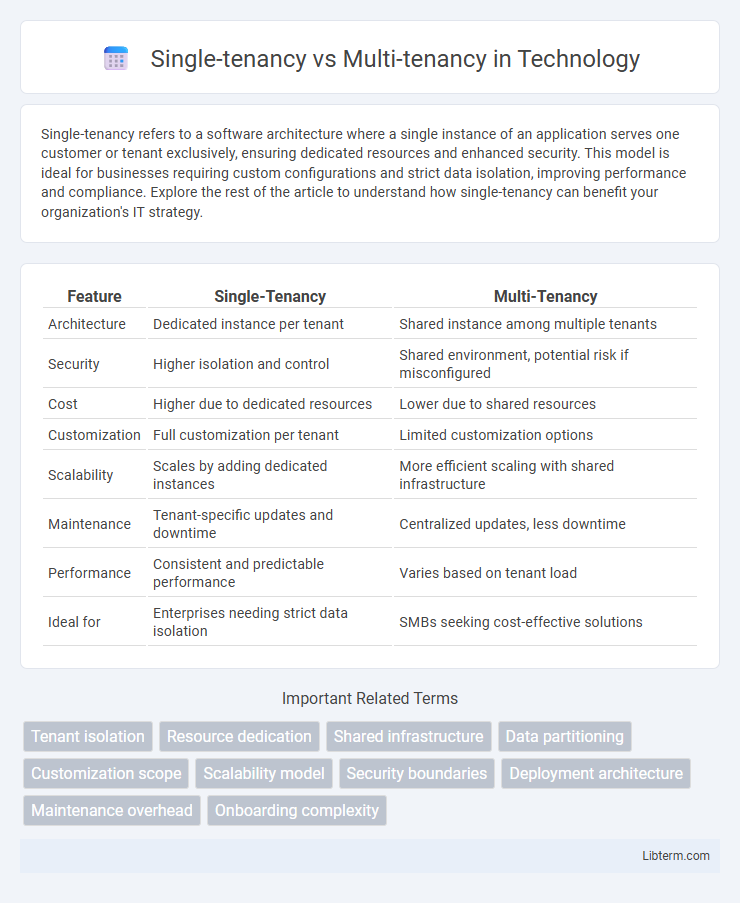
| Feature | Single-Tenancy | Multi-Tenancy |
|---|---|---|
| Architecture | Dedicated instance per tenant | Shared instance among multiple tenants |
| Security | Higher isolation and control | Shared environment, potential risk if misconfigured |
| Cost | Higher due to dedicated resources | Lower due to shared resources |
| Customization | Full customization per tenant | Limited customization options |
| Scalability | Scales by adding dedicated instances | More efficient scaling with shared infrastructure |
| Maintenance | Tenant-specific updates and downtime | Centralized updates, less downtime |
| Performance | Consistent and predictable performance | Varies based on tenant load |
| Ideal for | Enterprises needing strict data isolation | SMBs seeking cost-effective solutions |
Introduction to Single-Tenancy and Multi-Tenancy
Single-tenancy architecture dedicates one instance of software and its supporting infrastructure per customer, ensuring enhanced data isolation and customizable environments. Multi-tenancy enables multiple customers to share a single software instance and infrastructure, optimizing resource utilization and reducing costs. Understanding these models is critical for businesses aiming to balance security, scalability, and cost-effectiveness in cloud computing and SaaS deployments.
Core Definitions: What is Single-Tenancy?
Single-tenancy is a software architecture where each customer or tenant has a separate, dedicated instance of an application or infrastructure, ensuring exclusive access to resources and data. This model enhances security and customization by isolating environments, reducing the risk of data breaches or performance interference from other tenants. Single-tenancy is often preferred in industries with strict compliance requirements or when tailored user experiences are critical.
Understanding Multi-Tenancy Architecture
Multi-tenancy architecture enables multiple independent users or organizations, known as tenants, to share a single software instance while keeping their data isolated and secure. This design optimizes resource utilization by centralizing hardware, maintenance, and updates, leading to reduced operational costs and improved scalability. Understanding data partitioning methods such as database-level, schema-level, or application-level multi-tenancy is essential for ensuring tenant data privacy and system performance.
Key Differences Between Single-Tenancy and Multi-Tenancy
Single-tenancy hosts a single customer per instance, providing dedicated resources, enhanced control, and higher security, while multi-tenancy serves multiple customers on a shared instance, optimizing resource utilization and reducing costs. Single-tenancy offers easier customization and data isolation, whereas multi-tenancy excels in scalability and streamlined maintenance through shared updates. The choice depends on factors such as security requirements, cost sensitivity, and the need for personalized configurations.
Security Considerations in Both Models
Single-tenancy offers enhanced security by isolating each tenant's data and resources, minimizing risks of data breaches between clients. Multi-tenancy, while efficient in resource utilization, requires robust access controls, encryption, and strict tenant isolation mechanisms to prevent cross-tenant data exposure. Security best practices in multi-tenant environments include continuous monitoring, regular vulnerability assessments, and implementing role-based access control (RBAC) to safeguard sensitive information.
Scalability and Performance Comparison
Single-tenancy architecture offers dedicated resources per user, resulting in predictable performance and easier customization but potentially higher costs and limited scalability. Multi-tenancy supports many users on shared infrastructure, enabling rapid scaling and cost efficiency, though performance can vary due to resource contention. For enterprises requiring consistent high performance and isolation, single-tenancy is optimal, while multi-tenancy suits applications prioritizing flexible scalability and cost-effective resource management.
Cost Implications: Single vs Multi-Tenancy
Single-tenancy typically incurs higher costs due to dedicated hardware and individualized maintenance, resulting in increased operational expenses. Multi-tenancy reduces overall costs by sharing resources across multiple users, thereby optimizing server utilization and lowering infrastructure investments. Companies prioritize multi-tenancy for scalable, cost-efficient cloud solutions that maximize resource allocation and minimize overhead.
Customization and Flexibility
Single-tenancy offers greater customization and flexibility by providing dedicated resources that can be tailored to specific business requirements, allowing extensive control over software configurations and updates. Multi-tenancy, while more cost-efficient, restricts customization due to shared infrastructure, limiting flexibility as all tenants must operate within a unified environment. Enterprises prioritizing bespoke solutions and unique workflows often choose single-tenancy to maximize adaptability and personalized user experiences.
Use Cases: When to Choose Each Model
Single-tenancy is ideal for businesses requiring enhanced data security, customization, and dedicated resources, such as healthcare providers and financial institutions handling sensitive information. Multi-tenancy suits scalable SaaS applications, startups, and enterprises looking to optimize costs and simplify maintenance across multiple users sharing the same infrastructure. Choosing between models depends on priorities like data isolation, compliance requirements, cost efficiency, and the level of customization needed.
Conclusion: Making the Right Choice for Your Business
Choosing between single-tenancy and multi-tenancy depends on your business's security needs, scalability goals, and budget constraints. Single-tenancy offers enhanced data isolation and customization at a higher cost, ideal for enterprises requiring strict compliance. Multi-tenancy provides cost efficiency and easier maintenance suited for startups and businesses prioritizing rapid growth.
Single-tenancy Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com