Cloud Load Balancing distributes network traffic across multiple servers to ensure optimal resource use, reduce latency, and prevent service downtime. It adapts dynamically to fluctuating demand, enhancing application performance and reliability in various cloud environments. Discover how implementing cloud load balancing can improve your infrastructure's efficiency and resilience by reading the full article.
Table of Comparison
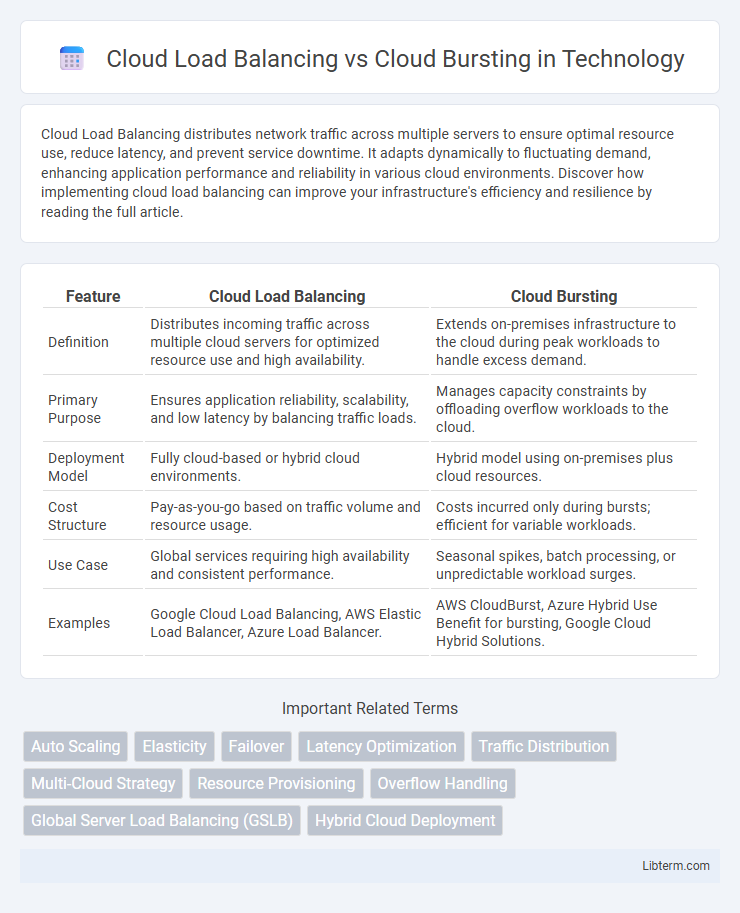
| Feature | Cloud Load Balancing | Cloud Bursting |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Distributes incoming traffic across multiple cloud servers for optimized resource use and high availability. | Extends on-premises infrastructure to the cloud during peak workloads to handle excess demand. |
| Primary Purpose | Ensures application reliability, scalability, and low latency by balancing traffic loads. | Manages capacity constraints by offloading overflow workloads to the cloud. |
| Deployment Model | Fully cloud-based or hybrid cloud environments. | Hybrid model using on-premises plus cloud resources. |
| Cost Structure | Pay-as-you-go based on traffic volume and resource usage. | Costs incurred only during bursts; efficient for variable workloads. |
| Use Case | Global services requiring high availability and consistent performance. | Seasonal spikes, batch processing, or unpredictable workload surges. |
| Examples | Google Cloud Load Balancing, AWS Elastic Load Balancer, Azure Load Balancer. | AWS CloudBurst, Azure Hybrid Use Benefit for bursting, Google Cloud Hybrid Solutions. |
Introduction to Cloud Load Balancing and Cloud Bursting
Cloud Load Balancing distributes incoming network traffic across multiple servers to ensure high availability and reliability, optimizing resource use and minimizing response time. Cloud Bursting enables applications to dynamically extend into public cloud resources during peak demand, providing seamless scalability without permanent infrastructure expansion. Both technologies enhance cloud computing efficiency but address different challenges: load balancing optimizes resource distribution, while bursting manages workload spikes.
Defining Cloud Load Balancing
Cloud Load Balancing distributes incoming network traffic across multiple cloud servers to ensure high availability, optimize resource utilization, and improve application responsiveness. It dynamically adjusts traffic to prevent server overload and maintain consistent performance. Unlike Cloud Bursting, which extends resources to a public cloud during peak demand, Cloud Load Balancing focuses on efficiently managing traffic within the cloud infrastructure.
What is Cloud Bursting?
Cloud bursting is a hybrid cloud computing strategy that allows an application to run in a private cloud or data center and "burst" into a public cloud when the local resources are insufficient to handle peak workloads. This approach enables organizations to maintain control over their primary infrastructure while leveraging the scalability and flexibility of public cloud resources to manage unexpected spikes in demand. Cloud bursting helps optimize costs by using on-premises resources for steady workloads and seamlessly expanding capacity to the cloud during high traffic periods.
Key Differences Between Cloud Load Balancing and Cloud Bursting
Cloud Load Balancing distributes incoming network traffic across multiple servers or resources to ensure high availability and reliability of applications, optimizing resource utilization and reducing latency. Cloud Bursting extends an on-premises application into the cloud during peak demand periods, providing additional computing capacity without permanent cloud deployment. The key difference lies in load balancing managing traffic distribution within existing resources, whereas cloud bursting dynamically scales infrastructure by offloading workloads to the cloud only when necessary.
Use Cases for Cloud Load Balancing
Cloud Load Balancing is ideal for distributing incoming traffic across multiple servers to enhance application availability and scalability in real-time, commonly used in web hosting, e-commerce platforms, and online gaming. It supports high availability by automatically rerouting traffic from unhealthy instances to healthy ones, ensuring seamless user experiences during peak traffic. Cloud Bursting, on the other hand, is best suited for handling unpredictable spikes in workload by dynamically extending private cloud resources into the public cloud, primarily for batch processing and large-scale data analysis.
Use Cases for Cloud Bursting
Cloud bursting is ideal for businesses experiencing sudden spikes in workload that exceed their private cloud capacity, such as e-commerce sites during holiday sales or financial firms processing end-of-day transactions. It enables seamless offloading of excess traffic to a public cloud, ensuring optimal application performance without the need for permanent infrastructure expansion. Use cases include disaster recovery, batch processing, and seasonal demand spikes where cost-effective scalability and resource optimization are critical.
Advantages of Cloud Load Balancing
Cloud Load Balancing enhances application performance by distributing traffic evenly across multiple servers, ensuring high availability and reduced latency during peak demand. It provides seamless scalability without downtime, automatically routing requests to healthy instances and preventing overload on any single server. This approach improves fault tolerance and optimizes resource utilization, making it ideal for dynamic and mission-critical cloud environments.
Benefits of Cloud Bursting
Cloud bursting enables enterprises to handle peak workloads efficiently by dynamically extending on-premises resources to the cloud, resulting in cost savings from avoiding over-provisioning. It provides enhanced scalability and flexibility, ensuring applications maintain performance during traffic spikes without permanent investment in additional infrastructure. This approach optimizes resource utilization and guarantees business continuity by seamlessly integrating private and public cloud environments.
Challenges and Limitations of Each Approach
Cloud Load Balancing faces challenges such as latency issues and uneven workload distribution when demand spikes unpredictably, potentially causing bottlenecks and increased operational costs. Cloud Bursting encounters limitations with data synchronization delays and security concerns, as extending private workloads to public clouds can expose sensitive information and complicate compliance. Both approaches require complex management and monitoring tools to maintain performance and ensure seamless integration across hybrid environments.
Choosing the Right Strategy for Your Business
Cloud Load Balancing distributes incoming network traffic across multiple servers to ensure high availability and reliability, making it ideal for businesses with consistent, heavy workloads requiring seamless scalability. Cloud Bursting enables on-demand resource expansion by offloading excess traffic to the cloud during peak periods, suitable for companies with variable workloads and cost-sensitive infrastructures. Selecting the right strategy depends on workload patterns, budget constraints, and the need for scalability and performance optimization.
Cloud Load Balancing Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com