JWT (JSON Web Token) is a compact, secure way to transmit information between parties as a JSON object, commonly used for authentication and authorization. This token is digitally signed, ensuring the integrity and authenticity of the data it carries, making it a reliable choice for securing API communication. Discover how JWT can enhance your application's security and streamline user authentication in the rest of this article.
Table of Comparison
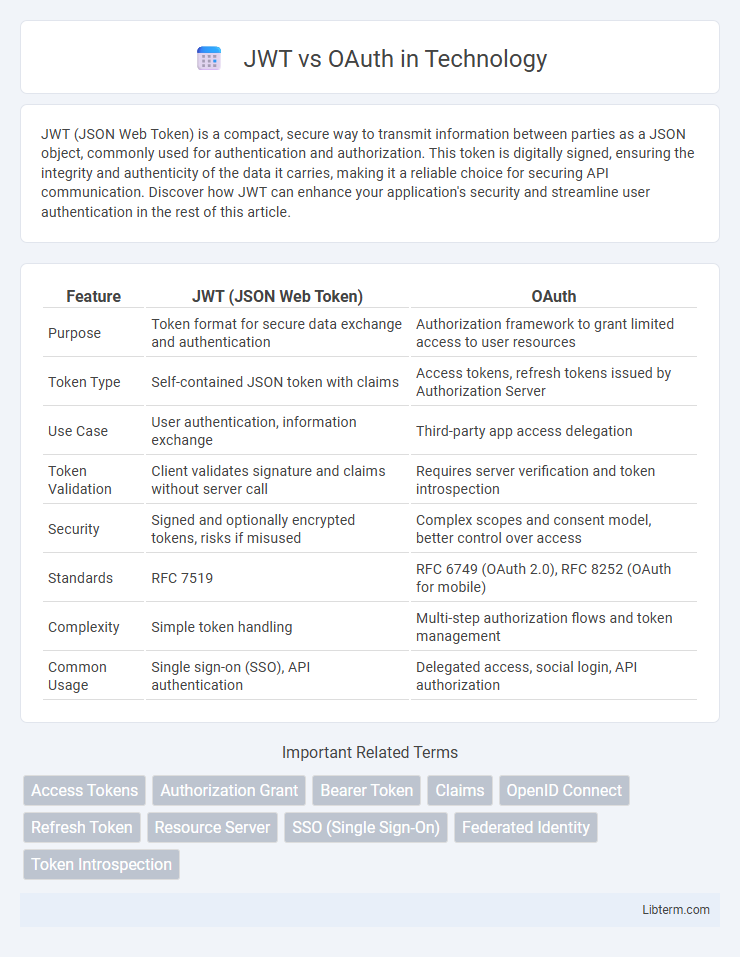
| Feature | JWT (JSON Web Token) | OAuth |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Token format for secure data exchange and authentication | Authorization framework to grant limited access to user resources |
| Token Type | Self-contained JSON token with claims | Access tokens, refresh tokens issued by Authorization Server |
| Use Case | User authentication, information exchange | Third-party app access delegation |
| Token Validation | Client validates signature and claims without server call | Requires server verification and token introspection |
| Security | Signed and optionally encrypted tokens, risks if misused | Complex scopes and consent model, better control over access |
| Standards | RFC 7519 | RFC 6749 (OAuth 2.0), RFC 8252 (OAuth for mobile) |
| Complexity | Simple token handling | Multi-step authorization flows and token management |
| Common Usage | Single sign-on (SSO), API authentication | Delegated access, social login, API authorization |
Introduction to JWT and OAuth
JWT (JSON Web Token) is a compact, URL-safe token format used for securely transmitting information between parties as a JSON object, commonly for authentication and information exchange. OAuth is an authorization framework enabling third-party applications to access user resources on a server without exposing user credentials by issuing scoped access tokens. Both JWT and OAuth play critical roles in modern secure authentication and authorization mechanisms, with JWT often used as the token format within OAuth workflows.
What is JWT?
JWT (JSON Web Token) is a compact, URL-safe token format used to securely transmit information between parties as a JSON object, often employed in authentication and authorization processes. It consists of three parts: a header, payload, and signature, enabling verification of the token's authenticity and integrity. JWTs are stateless, allowing servers to validate user credentials without maintaining session state, improving scalability in distributed systems.
What is OAuth?
OAuth is an open standard authorization framework that enables third-party applications to obtain limited access to user resources without exposing user credentials. It works by issuing access tokens that grant specific permissions, enhancing security and user control over data sharing. OAuth is widely used for secure delegated access in web, mobile, and cloud applications.
Key Differences Between JWT and OAuth
JWT (JSON Web Token) is a compact, self-contained token format used primarily for securely transmitting information between parties as a JSON object, while OAuth is an authorization framework that permits third-party applications to access user resources without sharing credentials. JWT serves as a token format often employed within OAuth for access and ID tokens, enabling stateless authentication and authorization. OAuth defines the protocols and mechanisms for token issuance and validation, focusing on delegated access control and secure API interactions.
How JWT Works in Authentication
JWT (JSON Web Token) is a compact, URL-safe token used in authentication to securely transmit information between parties as a JSON object. During authentication, the server generates a JWT containing user claims and signs it with a secret key, enabling the client to include the token in subsequent requests for stateless verification without querying the database. The server validates the JWT's signature and expiration, ensuring secure access control and session management.
How OAuth Operates in Authorization
OAuth operates in authorization by granting third-party applications limited access to user resources without sharing credentials, relying on access tokens issued by an authorization server. These tokens represent specific scopes and permissions for resource access, enhancing security and user control. OAuth's delegation mechanism enables fine-grained authorization through bearer tokens that communicate client authorization to resource servers.
Use Cases: When to Use JWT
JWT (JSON Web Token) is ideal for stateless authentication in distributed systems, enabling secure transmission of user information between parties with minimal overhead. It excels in single sign-on (SSO) scenarios, API authorization, and mobile app authentication where scalability and performance are critical. Use JWT when session state management is not required on the server, and security relies on token expiration and signature verification.
Use Cases: When to Use OAuth
OAuth is ideal for delegating access in scenarios where third-party applications require limited permissions to a user's resources without exposing credentials, such as enabling social media logins or granting payment app permissions. It excels in protecting resources with token-based authorization, especially in API security for services like Google Drive or GitHub integrations. OAuth's use of access tokens with specific scopes ensures fine-grained control over resource access in multi-application environments.
Security Considerations for JWT and OAuth
JWT (JSON Web Token) security revolves around the importance of secure key management and token expiration to prevent token theft and replay attacks. OAuth enhances security by delegating access with scoped permissions and using refresh tokens to minimize exposure but depends heavily on secure authorization server implementation. Both require robust encryption, HTTPS enforcement, and regular vulnerability assessments to mitigate risks such as token interception and misuse.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Solution
Choosing between JWT and OAuth depends on the specific security needs of your application; JWT is ideal for stateless authentication where token payloads store user information securely, while OAuth excels in delegated access scenarios requiring token-based authorization across third-party services. Implement JWT for efficient, scalable user session management without server-side state, and select OAuth when enabling secure resource access delegation with robust scope and permission controls. Analyzing factors like token lifespan, complexity of the authentication flow, and integration requirements helps determine the optimal approach.
JWT Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com