Vault ensures the security of your sensitive information through robust secret management and encryption capabilities, while Consul excels in service discovery and dynamic configuration for distributed systems. Together, they provide a comprehensive solution for managing secrets and enabling seamless communication within cloud-native environments. Explore the article to understand how integrating Vault and Consul can enhance your infrastructure's security and reliability.
Table of Comparison
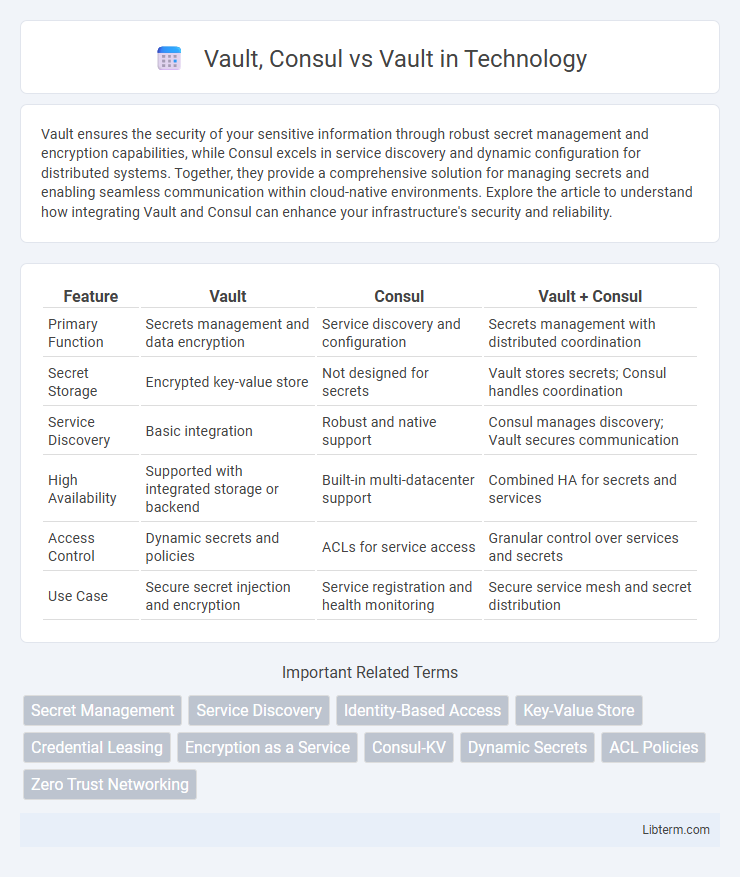
| Feature | Vault | Consul | Vault + Consul |
|---|---|---|---|
| Primary Function | Secrets management and data encryption | Service discovery and configuration | Secrets management with distributed coordination |
| Secret Storage | Encrypted key-value store | Not designed for secrets | Vault stores secrets; Consul handles coordination |
| Service Discovery | Basic integration | Robust and native support | Consul manages discovery; Vault secures communication |
| High Availability | Supported with integrated storage or backend | Built-in multi-datacenter support | Combined HA for secrets and services |
| Access Control | Dynamic secrets and policies | ACLs for service access | Granular control over services and secrets |
| Use Case | Secure secret injection and encryption | Service registration and health monitoring | Secure service mesh and secret distribution |
Introduction to Vault and Consul
Vault is a powerful tool by HashiCorp designed for secure secret management, enabling encryption, dynamic secrets, and access control across distributed systems. Consul, also from HashiCorp, focuses on service discovery, configuration, and network segmentation through a distributed key-value store and health checking capabilities. Together, Vault and Consul integrate to provide robust security and service management in cloud-native and microservices architectures.
What is HashiCorp Vault?
HashiCorp Vault is a powerful secrets management tool designed to securely store, access, and distribute sensitive data such as API keys, passwords, and certificates. Unlike Consul, which primarily focuses on service discovery and configuration, Vault specializes in encryption as a service, dynamic secrets, and access control policies. Vault provides robust auditing, lease mechanisms, and support for multiple authentication backends to enhance enterprise-grade security.
What is HashiCorp Consul?
HashiCorp Consul is a powerful service mesh and service discovery tool designed to automate network connectivity across distributed systems. It enables secure service-to-service communication, health monitoring, and configuration management within dynamic infrastructure environments. Unlike Vault, which focuses primarily on secrets management and data protection, Consul provides comprehensive service networking capabilities essential for microservices and cloud-native applications.
Core Features of Vault
Vault excels in secure secret management by providing robust data encryption, dynamic secrets, and detailed audit logging. Its core features include secure storage of tokens, passwords, certificates, and API keys, support for dynamic secrets with automatic expiration, and key rolling with encryption-as-a-service capabilities. Unlike Consul, which specializes in service discovery and health checking, Vault focuses on managing sensitive information and access control policies with granular permissions and secure introduction of credentials.
Core Features of Consul
Consul provides core features such as service discovery, health checking, key-value storage, and multi-datacenter support that enable seamless service networking and configuration management. Unlike Vault, which specializes in secrets management, Consul excels at maintaining a dynamic infrastructure by monitoring service health and enabling service segmentation with service mesh capabilities. Its robust DNS and HTTP interfaces facilitate automatic service registration and discovery across distributed systems.
Vault Use Cases and Benefits
Vault provides secrets management, encryption as a service, and dynamic secrets generation, enhancing application security by centrally controlling access to sensitive data like API keys, passwords, and certificates. It supports dynamic infrastructure, enabling secure, short-lived credentials and minimizing exposure risk through automatic credential rotation and revocation. Vault's integration with cloud platforms, DevOps pipelines, and identity providers streamlines secrets management and enforces robust access policies, making it ideal for securing microservices and multi-cloud environments.
Consul Use Cases and Benefits
Consul excels in service discovery, health checking, and multi-data center networking, providing dynamic service segmentation and secure service-to-service communication. Its key use cases include enabling service mesh architectures, managing distributed configuration, and facilitating automated failover across microservices. By integrating with Vault, Consul enhances secret management with real-time service authentication and authorization, bolstering overall infrastructure security and scalability.
Key Differences: Consul vs Vault
Consul focuses on service discovery, configuration, and segmentation, enabling seamless network connectivity and dynamic infrastructure management, while Vault specializes in secure secret management, encryption as a service, and access control. Consul provides capabilities like health checking, key-value storage, and multi-datacenter federation, whereas Vault delivers robust identity-based authentication, secrets leasing, and audit logging. The key difference lies in Consul managing infrastructure and service networking, whereas Vault secures sensitive information and enforces strong access policies.
Choosing Between Vault and Consul
Choosing between Vault and Consul depends on your specific security and infrastructure needs, as Vault specializes in secrets management, encryption, and identity-based access, while Consul primarily focuses on service discovery, configuration, and network segmentation. Vault provides robust features for securing sensitive data, such as dynamic secrets, encryption as a service, and detailed audit logs, ideal for managing application secrets and credentials. Consul's strengths lie in enabling service mesh capabilities and health monitoring, making it suitable for distributed systems requiring resilient service communication and scalability.
Conclusion: Which Is Right for You?
Vault excels in centralized secrets management, providing robust encryption, dynamic secrets, and access control crucial for securing sensitive data across complex environments. Consul specializes in service discovery, configuration management, and network segmentation, offering strong support for distributed systems and real-time updates. Choosing Vault is ideal for organizations prioritizing secret storage and cryptographic operations, while Consul is better suited for managing service connectivity and configuration in microservices architectures.
Vault, Consul Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com