Packet loss occurs when data packets traveling across a network fail to reach their destination, often causing disruptions in online activities like streaming and gaming. Network congestion, hardware issues, or poor signal quality can contribute to this problem, impacting your connection's performance and reliability. Explore the rest of the article to learn how to identify and troubleshoot packet loss effectively.
Table of Comparison
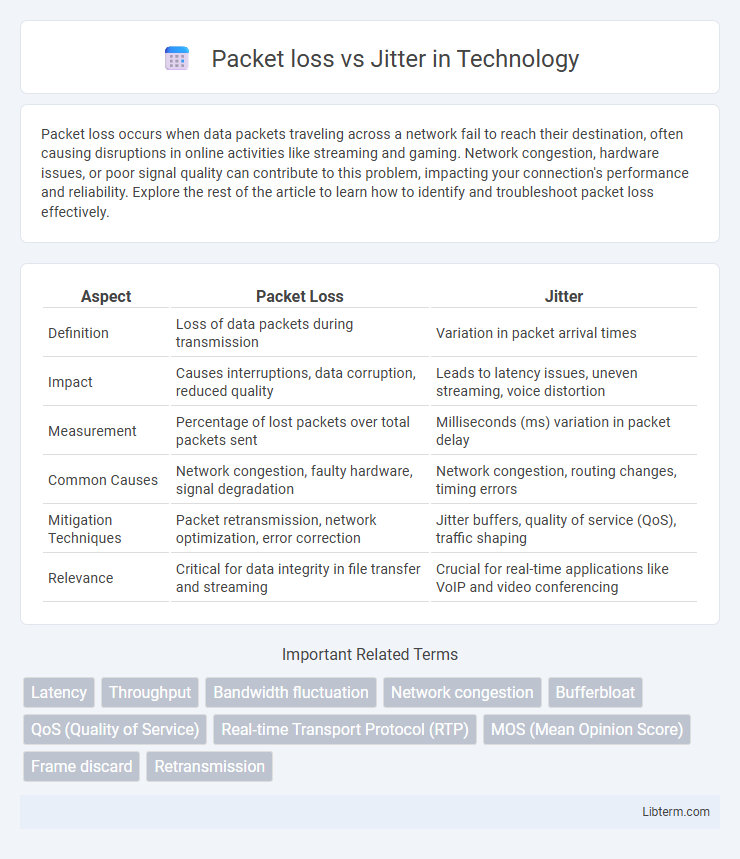
| Aspect | Packet Loss | Jitter |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Loss of data packets during transmission | Variation in packet arrival times |
| Impact | Causes interruptions, data corruption, reduced quality | Leads to latency issues, uneven streaming, voice distortion |
| Measurement | Percentage of lost packets over total packets sent | Milliseconds (ms) variation in packet delay |
| Common Causes | Network congestion, faulty hardware, signal degradation | Network congestion, routing changes, timing errors |
| Mitigation Techniques | Packet retransmission, network optimization, error correction | Jitter buffers, quality of service (QoS), traffic shaping |
| Relevance | Critical for data integrity in file transfer and streaming | Crucial for real-time applications like VoIP and video conferencing |
Understanding Packet Loss: Definition and Causes
Packet loss refers to the failure of data packets reaching their destination during transmission over a network, often caused by network congestion, faulty hardware, or poor signal quality. It disrupts the continuity of data streams, leading to degraded performance in applications like VoIP, online gaming, and video streaming. Understanding the causes of packet loss is essential for diagnosing network issues and optimizing connectivity to ensure reliable communication.
What is Jitter? A Complete Overview
Jitter refers to the variation in packet arrival time during data transmission, causing packets to arrive out of order or with inconsistent delays, significantly impacting real-time communications like VoIP and video streaming. Unlike packet loss, which involves missing packets, jitter affects the timing of packet delivery, leading to distorted audio, video glitches, or choppy calls. Effective jitter management involves using jitter buffers and Quality of Service (QoS) mechanisms to ensure smooth and reliable network performance.
Packet Loss vs Jitter: Key Differences
Packet loss refers to the failure of data packets to reach their destination, causing interruptions and reduced quality in network communications, especially in real-time applications like VoIP and video streaming. Jitter measures the variability in packet arrival times, leading to uneven data flow and potential distortion or delays in audio and video transmission. While packet loss results in missing information, jitter affects the timing and smoothness of data delivery, both critically impacting overall network performance and user experience.
Impact of Packet Loss on Network Performance
Packet loss significantly degrades network performance by causing data retransmissions, increased latency, and reduced throughput, leading to disrupted real-time communications such as VoIP and video conferencing. High packet loss rates result in choppy audio, video stuttering, and poor user experience in online gaming and streaming services. Network infrastructure issues, congestion, and faulty hardware are common causes that exacerbate packet loss, emphasizing the need for robust error correction and quality of service (QoS) mechanisms.
How Jitter Affects Real-Time Communications
Jitter causes variations in packet arrival times, disrupting the smooth flow of real-time communications like VoIP and video conferencing. This irregular delay impacts audio clarity and video synchronization, leading to choppy sound and blurred images. Minimizing jitter is crucial for maintaining quality of service (QoS) in latency-sensitive applications.
Common Causes of Packet Loss and Jitter
Packet loss commonly occurs due to network congestion, faulty hardware, or poor signal quality, resulting in missing data packets during transmission. Jitter is primarily caused by inconsistent latency variations in packet delivery, often triggered by network congestion, route changes, or network interference. Both packet loss and jitter degrade real-time application performance, especially in VoIP and streaming services.
Measuring Packet Loss and Jitter: Tools and Techniques
Measuring packet loss involves tools like Wireshark and Ping, which analyze packet transmission and identify dropped packets by comparing sent versus received data. Jitter measurement uses software such as iPerf and NetScout to assess the variation in packet arrival times, providing insights into network stability and performance fluctuations. Combining these techniques with real-time monitoring systems ensures accurate detection and troubleshooting of network issues affecting voice and video communications.
Strategies to Reduce Packet Loss
Effective strategies to reduce packet loss include implementing Quality of Service (QoS) protocols to prioritize critical data traffic and reduce congestion on the network. Utilizing wired connections over wireless ones can minimize interference and signal degradation, which often contribute to packet loss. Regularly updating network hardware and firmware ensures optimal performance and helps prevent packet drops caused by device malfunctions.
Solutions for Minimizing Jitter
Minimizing jitter involves implementing Quality of Service (QoS) protocols that prioritize real-time traffic, such as VoIP and video streaming, to ensure consistent packet delivery times. Network administrators can also deploy jitter buffers at receivers to smooth out packet arrival times and maintain audio and video quality. Regularly monitoring network performance with tools like ping tests and protocol analyzers aids in identifying and resolving congestion or hardware issues that contribute to jitter.
Packet Loss or Jitter: Which is Worse for VoIP and Streaming?
Packet loss severely impacts VoIP and streaming by causing gaps in audio and video, leading to choppy calls and interrupted playback, while jitter causes variations in packet arrival time that disrupts smooth data flow, resulting in delays and buffering. In real-time communications like VoIP, packet loss often degrades call quality more noticeably than jitter because missing packets cannot be recovered, whereas jitter can be partially mitigated with jitter buffers. For streaming, packet loss causes visible artifacts and stream interruptions, making it generally more detrimental than jitter to user experience.
Packet loss Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com