Batch processing efficiently handles large volumes of data by executing tasks in groups without manual intervention, optimizing system resource use and reducing processing time. It is essential for industries requiring repetitive data operations, like banking, manufacturing, and data analytics, ensuring accuracy and consistency across extensive datasets. Explore the full article to understand how batch processing can transform Your workflow and enhance productivity.
Table of Comparison
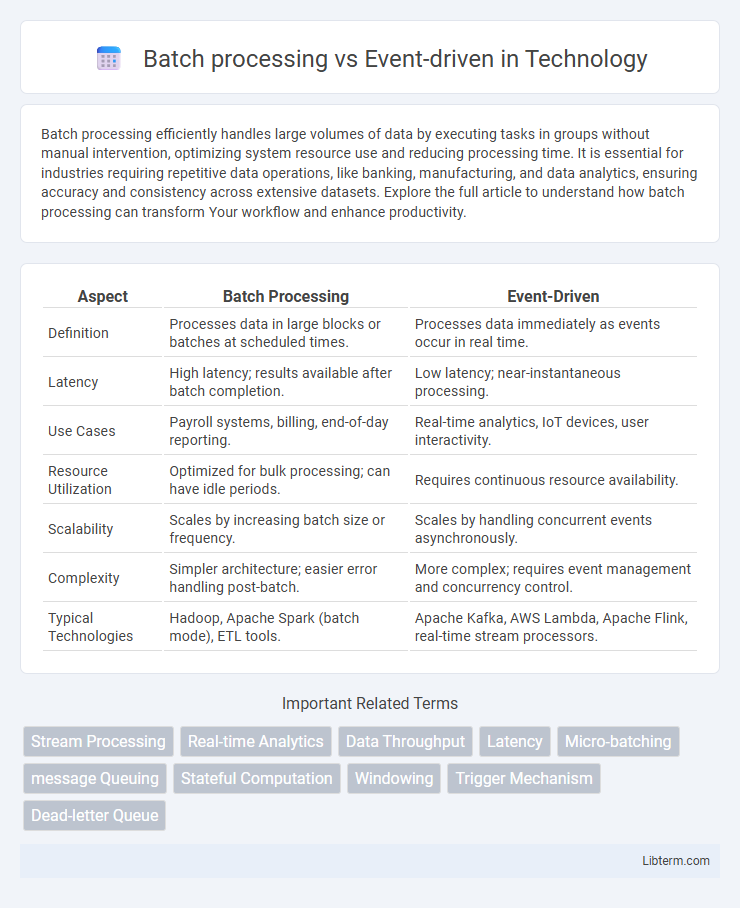
| Aspect | Batch Processing | Event-Driven |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Processes data in large blocks or batches at scheduled times. | Processes data immediately as events occur in real time. |
| Latency | High latency; results available after batch completion. | Low latency; near-instantaneous processing. |
| Use Cases | Payroll systems, billing, end-of-day reporting. | Real-time analytics, IoT devices, user interactivity. |
| Resource Utilization | Optimized for bulk processing; can have idle periods. | Requires continuous resource availability. |
| Scalability | Scales by increasing batch size or frequency. | Scales by handling concurrent events asynchronously. |
| Complexity | Simpler architecture; easier error handling post-batch. | More complex; requires event management and concurrency control. |
| Typical Technologies | Hadoop, Apache Spark (batch mode), ETL tools. | Apache Kafka, AWS Lambda, Apache Flink, real-time stream processors. |
Introduction to Batch Processing vs Event-driven
Batch processing involves executing a series of tasks or data jobs collected over a period in a single, efficient run, optimizing resource use for large volumes of data. Event-driven processing responds in real-time to specific events or changes, enabling immediate processing and dynamic system reactions. Understanding these two models is crucial for selecting the right approach based on workload timing, system design, and responsiveness requirements.
Core Concepts of Batch Processing
Batch processing involves executing a series of tasks or jobs collectively at scheduled times, optimizing system resource usage and throughput. It processes large volumes of data in groups, making it suitable for non-time-sensitive operations such as payroll, data aggregation, and report generation. Core concepts include job scheduling, sequential execution, and fault tolerance to ensure reliable and efficient completion of batch jobs.
Key Principles of Event-driven Architecture
Event-driven architecture prioritizes the production, detection, and reaction to events, enabling systems to respond to real-time changes with minimal latency. Key principles include decoupling of event producers and consumers, asynchronous communication, and scalable event handling through event brokers or message queues. This design enhances system flexibility, responsiveness, and scalability compared to batch processing, which executes tasks in scheduled bulk operations.
Advantages of Batch Processing
Batch processing excels in handling large volumes of data efficiently by processing tasks in groups, minimizing system overhead and maximizing resource utilization. It enables predictable scheduling, allowing organizations to allocate computing resources during off-peak hours, reducing operational costs. This method also ensures consistency and reliability by executing complex transactions in a controlled environment, which reduces the risk of errors compared to real-time event-driven systems.
Benefits of Event-driven Systems
Event-driven systems offer real-time processing capabilities that enable immediate response to data changes, improving system responsiveness and user experience. They enhance scalability by efficiently handling varying loads through asynchronous event handling, reducing bottlenecks common in batch processing. These systems also support better resource utilization and fault tolerance by decoupling event producers and consumers, leading to more flexible and resilient architectures.
Limitations of Batch Processing
Batch processing often suffers from latency issues, as it processes large volumes of data at scheduled intervals rather than in real-time. This delay can hinder time-sensitive decision-making and reduce system responsiveness in dynamic environments. Scalability challenges also arise due to the resource-intensive nature of handling massive batches simultaneously, leading to potential system bottlenecks.
Challenges in Event-driven Implementation
Event-driven implementation faces challenges such as handling unpredictable event loads, ensuring real-time data consistency, and managing complex event orchestration across distributed systems. Developers must design resilient architectures to address issues like event ordering, duplication, and fault tolerance in asynchronous environments. Scalability concerns also arise due to the dynamic nature of events, requiring robust messaging frameworks and monitoring tools to maintain system performance.
Use Cases for Batch Processing
Batch processing excels in handling large volumes of data where tasks can be executed at scheduled intervals, such as payroll processing, end-of-day financial reporting, and bulk data migration. It suits scenarios requiring efficient, cost-effective management of repetitive tasks that do not need real-time updates. Industries like banking, telecommunications, and retail benefit from batch processing to automate routine operations and ensure data consistency across systems.
Scenarios Favoring Event-driven Architecture
Event-driven architecture excels in scenarios requiring real-time responsiveness, such as fraud detection, IoT data processing, and dynamic user interactions in web applications. This model enables immediate reaction to events, supporting systems with fluctuating workloads and complex event chains where latency minimization is critical. Enterprises leveraging microservices also benefit from event-driven designs to enhance scalability and decoupling between services.
Choosing the Right Approach for Your Business
Batch processing excels in handling large volumes of data efficiently during off-peak hours, making it ideal for businesses with predictable, non-time-sensitive workloads such as payroll or end-of-day reports. Event-driven architecture suits real-time decision-making scenarios, offering immediate response capabilities for customer interactions, fraud detection, or inventory updates. Evaluating your business's latency tolerance, data volume, and processing complexity helps determine whether batch or event-driven systems align best with your operational goals and customer experience expectations.
Batch processing Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com