Indexing enhances database performance by allowing faster data retrieval, significantly reducing query response times. Partitioning divides large tables into smaller, manageable segments, improving maintenance efficiency and query optimization. Discover how indexing and partitioning can optimize your database in the following article.
Table of Comparison
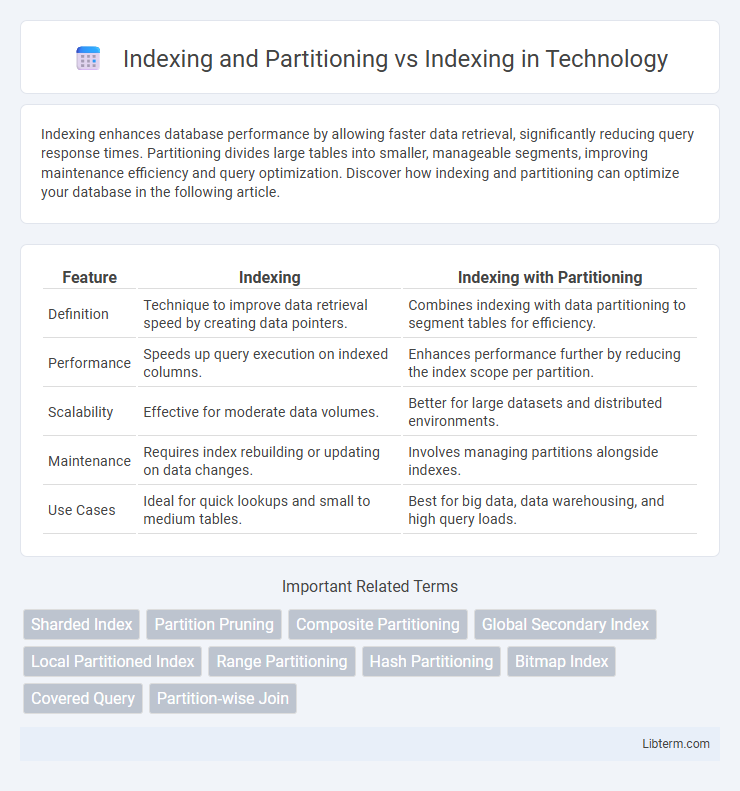
| Feature | Indexing | Indexing with Partitioning |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Technique to improve data retrieval speed by creating data pointers. | Combines indexing with data partitioning to segment tables for efficiency. |
| Performance | Speeds up query execution on indexed columns. | Enhances performance further by reducing the index scope per partition. |
| Scalability | Effective for moderate data volumes. | Better for large datasets and distributed environments. |
| Maintenance | Requires index rebuilding or updating on data changes. | Involves managing partitions alongside indexes. |
| Use Cases | Ideal for quick lookups and small to medium tables. | Best for big data, data warehousing, and high query loads. |
Understanding Database Indexing
Database indexing improves query performance by creating data structures that allow rapid data retrieval, while partitioning divides large tables into smaller, manageable segments to enhance query efficiency and maintenance. Combining indexing with partitioning leverages both fast data access and optimized data distribution, reducing query response times significantly. Understanding the balance between using indexes alone and integrating partitioning is crucial for designing scalable, high-performance databases.
The Fundamentals of Partitioning
Partitioning enhances database performance by dividing large tables into smaller, manageable segments based on specific criteria like range, list, or hash, allowing faster query execution and maintenance. Unlike traditional indexing, which improves data retrieval speed by creating data pointers, partitioning physically organizes data, reducing I/O and improving parallel processing. Understanding partitioning fundamentals involves grasping partition types, strategies for data distribution, and how partition pruning optimizes access to relevant data slices.
Indexing: Core Principles and Benefits
Indexing improves database query performance by creating data structures that allow rapid data retrieval without scanning entire tables. Indexes reduce I/O operations and enhance search efficiency through mechanisms such as B-trees, hash indexes, or bitmap indexes. Proper indexing significantly decreases query execution time, supporting faster analytics and transaction processing in complex databases.
How Partitioning Enhances Data Management
Partitioning divides large datasets into smaller, manageable segments that improve query performance and simplify maintenance tasks compared to indexing alone. By distributing data based on partition keys, partitioning reduces I/O load and enables efficient data pruning during searches. This approach enhances data management scalability and accelerates backup, recovery, and archiving processes in database systems.
Combining Indexing with Partitioning
Combining indexing with partitioning significantly improves query performance by dividing large tables into manageable segments while maintaining fast data retrieval through indexes. Partitioning reduces the amount of data scanned during queries, and indexes on each partition further optimize access paths, enabling efficient search within segmented data sets. This hybrid approach is essential for scaling databases and handling large volumes of data with minimal latency.
Indexing Alone: Advantages and Limitations
Indexing alone improves query performance by enabling faster data retrieval through structured data access paths, significantly reducing search time in large databases. However, it may lead to increased storage overhead and slower write operations due to index maintenance during data modifications. Additionally, indexing without partitioning can struggle with scalability and performance issues when handling extremely large datasets, as all data remains in a single partition.
Performance Comparison: Indexing vs Indexing with Partitioning
Indexing with partitioning significantly enhances query performance by reducing the volume of data scanned during searches, as partitions allow the database to target specific data subsets. Traditional indexing improves data retrieval speed by creating data structures like B-trees or hash indexes, but when combined with partitioning, operations like range queries and large dataset scans become more efficient due to minimized I/O overhead. Benchmark tests show that indexing with partitioning can reduce query execution time by up to 70% compared to indexing alone, especially in large-scale databases with high transaction volumes.
Use Cases: When to Use Indexing Only
Indexing only is ideal for small to medium-sized tables where quick search and retrieval of data are priorities without the complexity of data management overhead. It suits scenarios requiring frequent read operations with minimal writes, such as lookup tables, static reference data, or query optimization in OLTP systems. Indexing alone enhances performance in use cases involving selective queries on non-partitioned datasets with predictable and uniform access patterns.
Best Practices for Indexing and Partitioning
Effective indexing and partitioning strategies significantly enhance database performance by reducing query response times and improving data manageability. Best practices include selecting appropriate partition keys to evenly distribute data across partitions, creating indexes on frequently queried columns, and using composite indexes to optimize multi-column searches while avoiding over-indexing that leads to maintenance overhead. Regularly monitoring query performance and updating statistics ensures indexes and partitions remain efficient as data evolves.
Conclusion: Optimizing Databases with Indexing and Partitioning
Indexing and partitioning together significantly enhance database performance by reducing query response times and improving data management efficiency. Indexing accelerates data retrieval by creating fast-access pathways, while partitioning divides large tables into manageable segments, facilitating parallel processing and maintenance. Optimizing databases with both techniques ensures scalable, high-performance systems capable of handling growing data volumes and complex queries effectively.
Indexing and Partitioning Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com