Live migration enables the seamless transfer of virtual machines between physical hosts without downtime, ensuring continuous application availability. This process optimizes resource utilization and enhances load balancing across your data center, improving overall system performance. Explore the rest of the article to discover how live migration can transform your virtualization environment.
Table of Comparison
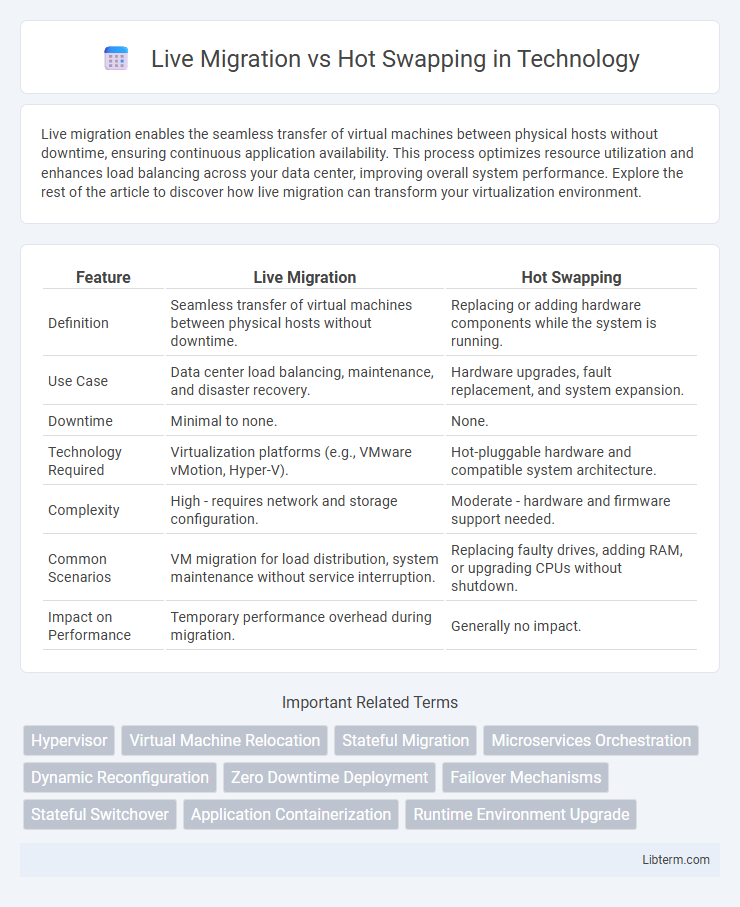
| Feature | Live Migration | Hot Swapping |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Seamless transfer of virtual machines between physical hosts without downtime. | Replacing or adding hardware components while the system is running. |
| Use Case | Data center load balancing, maintenance, and disaster recovery. | Hardware upgrades, fault replacement, and system expansion. |
| Downtime | Minimal to none. | None. |
| Technology Required | Virtualization platforms (e.g., VMware vMotion, Hyper-V). | Hot-pluggable hardware and compatible system architecture. |
| Complexity | High - requires network and storage configuration. | Moderate - hardware and firmware support needed. |
| Common Scenarios | VM migration for load distribution, system maintenance without service interruption. | Replacing faulty drives, adding RAM, or upgrading CPUs without shutdown. |
| Impact on Performance | Temporary performance overhead during migration. | Generally no impact. |
Introduction to Live Migration and Hot Swapping
Live Migration enables the seamless transfer of virtual machines between physical hosts with minimal downtime, optimizing resource allocation and maintaining workload continuity in data centers. Hot Swapping allows hardware components such as hard drives or network cards to be replaced or added without powering down the system, enhancing maintenance efficiency in enterprise environments. Both technologies play crucial roles in improving operational flexibility and minimizing service interruptions in IT infrastructure management.
Core Concepts: What is Live Migration?
Live Migration is the process of moving a running virtual machine or application instance from one physical host to another without downtime. It enables continuous availability by transferring the VM's active memory, storage, and network connections seamlessly. This technique is essential for load balancing, hardware maintenance, and minimizing service disruption in cloud computing and virtualization environments.
Core Concepts: What is Hot Swapping?
Hot swapping refers to the process of replacing or adding hardware components to a computer system without shutting down the system or interrupting its operation. This technique is commonly used in servers, storage devices, and network equipment to maintain uptime and minimize disruption during maintenance or upgrades. Unlike live migration, which involves moving virtual machines between hosts, hot swapping is specifically focused on physical hardware changes while the system remains active.
Key Differences Between Live Migration and Hot Swapping
Live migration transfers entire virtual machines or workloads between physical hosts without downtime, ensuring continuous operation and minimal impact on end users. Hot swapping refers to the replacement or addition of hardware components, such as drives or memory modules, while the system remains powered on, focusing on physical hardware flexibility rather than virtual machine mobility. The key difference lies in live migration's role in virtual environment management versus hot swapping's function in hardware maintenance and upgrades without interrupting system availability.
Use Cases: When to Use Live Migration
Live Migration is ideal for maintaining application availability during hardware maintenance or upgrades by moving virtual machines between physical hosts without downtime. It is frequently used in data centers requiring continuous service, such as cloud platforms and enterprise IT environments, ensuring workload mobility and minimizing disruption. Hot Swapping, in contrast, suits scenarios needing immediate hardware replacement without shutting down systems but does not address VM or workload relocation.
Use Cases: When to Choose Hot Swapping
Hot swapping is ideal for hardware components such as hard drives, network cards, and power supplies in environments requiring minimal downtime and immediate hardware replacement. Use cases include data centers needing high availability and systems with critical uptime demands, where physically removing or replacing parts without shutting down the system prevents service interruptions. When rapid hardware upgrades or fault recovery are necessary, hot swapping offers a direct solution without the complexities of live migration.
Performance Impact: Live Migration vs Hot Swapping
Live migration involves transferring a running virtual machine between hosts with minimal downtime, causing temporary CPU and network load spikes that can slightly degrade overall system performance. Hot swapping enables the replacement or addition of hardware components without shutting down the system, maintaining near-constant performance levels by avoiding resource-intensive data transfers. Performance impact during live migration is more pronounced due to continuous resource replication, whereas hot swapping's impact remains minimal and localized to hardware initialization processes.
Security Considerations in Both Approaches
Live migration and hot swapping both require stringent security measures to prevent data breaches during hardware or virtual machine transitions. Live migration emphasizes secure data transfer protocols and encryption to protect in-transit data, especially in multi-tenant cloud environments where virtual machines move between hosts. Hot swapping prioritizes secure device authentication and access control to prevent unauthorized hardware replacements that could introduce vulnerabilities or compromise system integrity.
Pros and Cons: Live Migration vs Hot Swapping
Live migration enables seamless transfer of virtual machines between hosts with minimal downtime, preserving application uptime and system performance, but it can introduce network overhead and requires complex configurations. Hot swapping allows direct replacement or addition of hardware components without shutting down the system, enhancing hardware maintenance flexibility and reducing downtime, yet it is limited to specific hardware types and can risk system stability if not properly managed. Each method balances operational continuity and risk, with live migration excelling in virtualized environments and hot swapping optimized for physical hardware maintenance.
Future Trends in System Maintenance Technologies
Live migration and hot swapping are evolving with advancements in AI-driven automation and edge computing, enabling faster, more efficient system maintenance without downtime. Future trends emphasize seamless integration of predictive analytics and real-time monitoring to anticipate hardware failures and optimize resource allocation during live migration or component replacement. Enhanced virtualization and containerization technologies are set to further reduce latency and improve system resilience in dynamic IT environments.
Live Migration Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com