Efficient database storage ensures rapid access, optimized performance, and scalability for your data management needs. Modern storage solutions integrate advanced indexing, compression, and caching methods to maximize capacity and speed. Explore the rest of this article to discover how to enhance your database storage strategy effectively.
Table of Comparison
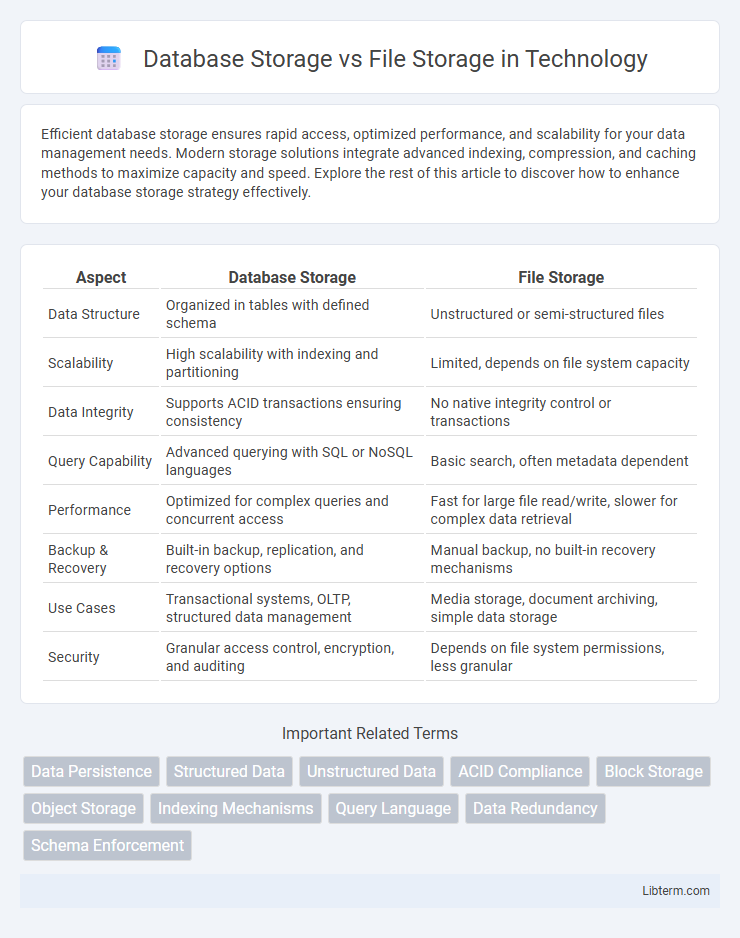
| Aspect | Database Storage | File Storage |
|---|---|---|
| Data Structure | Organized in tables with defined schema | Unstructured or semi-structured files |
| Scalability | High scalability with indexing and partitioning | Limited, depends on file system capacity |
| Data Integrity | Supports ACID transactions ensuring consistency | No native integrity control or transactions |
| Query Capability | Advanced querying with SQL or NoSQL languages | Basic search, often metadata dependent |
| Performance | Optimized for complex queries and concurrent access | Fast for large file read/write, slower for complex data retrieval |
| Backup & Recovery | Built-in backup, replication, and recovery options | Manual backup, no built-in recovery mechanisms |
| Use Cases | Transactional systems, OLTP, structured data management | Media storage, document archiving, simple data storage |
| Security | Granular access control, encryption, and auditing | Depends on file system permissions, less granular |
Introduction to Database Storage and File Storage
Database storage organizes data using structured schemas within tables and indexes, enabling efficient querying, retrieval, and management through relational or NoSQL models. File storage saves data as discrete files in a hierarchical directory system, ideal for unstructured data like documents, images, and media but lacks inherent data relationships or schema validation. Understanding the differences between database storage and file storage is crucial for selecting the appropriate method based on data complexity, access patterns, and scalability requirements.
Core Differences Between Database Storage and File Storage
Database storage organizes data into structured tables with defined schema, enabling efficient indexing, querying, and relational data handling, whereas file storage manages data as discrete files in a hierarchical folder system without inherent structure. Databases support transactions, data integrity, and concurrent access control, which file storage lacks, making databases ideal for complex data manipulation and consistency. File storage offers simplicity and direct access for unstructured data like documents and media, while databases excel in scalability and data retrieval optimizations.
Data Structure and Organization
Database storage organizes data using structured tables with defined schemas, enabling complex queries, relationships, and indexing for efficient retrieval and modification. File storage relies on a hierarchical system of directories and files, where data is stored as discrete files without inherent relationships or schema constraints. This fundamental difference impacts data access speed, consistency, and the ability to handle large-scale, interconnected datasets.
Performance and Scalability Comparison
Database storage offers superior performance for structured data queries due to optimized indexing, transaction management, and concurrent access handling, enabling faster retrieval times compared to file storage systems. Scalability in database storage is enhanced through sharding, replication, and distributed architectures, allowing seamless expansion as data volume and user load increase. File storage systems typically experience performance degradation at scale, lacking advanced metadata indexing and parallel processing capabilities inherent in modern databases.
Use Case Scenarios for Database Storage
Database storage excels in use cases requiring complex query capabilities, structured data organization, and transactional integrity, such as e-commerce platforms managing product inventories and customer orders. It is ideal for applications needing real-time updates and multi-user concurrency, including banking systems and enterprise resource planning (ERP) software. Unlike file storage, databases ensure data consistency and support advanced indexing, facilitating efficient retrieval and analytics in CRM and content management systems.
Use Case Scenarios for File Storage
File storage excels in scenarios requiring unstructured data management, such as multimedia files, documents, and backups, due to its straightforward hierarchical organization. Its compatibility with common operating system file interfaces benefits collaborative projects where multiple users need simultaneous access to shared files. Ideal for content management systems and archival purposes, file storage supports scalable and accessible data retention without the complexity of database query language.
Security and Data Integrity Considerations
Database storage provides robust security features such as encryption, access controls, and transaction logging that ensure data integrity and minimize unauthorized access risks. File storage often lacks granular permission settings and version control, making it more vulnerable to data corruption and accidental modifications. Ensuring compliance with data protection standards is more straightforward with database systems due to their built-in auditing and rollback capabilities.
Cost and Maintenance Factors
Database storage typically incurs higher initial setup costs due to complex infrastructure requirements but offers streamlined maintenance through automated backups, indexing, and data integrity management. File storage often presents lower upfront expenses and simpler management but may lead to increased long-term costs from manual maintenance, limited scalability, and potential data redundancy issues. Evaluating factors such as data access frequency, growth projections, and required security levels is essential to optimize total cost of ownership in storage solutions.
Pros and Cons of Database Storage vs File Storage
Database storage offers structured data management, enabling complex queries and transactions with high data integrity, but it requires more resources and sophisticated setup compared to file storage. File storage provides simplicity and ease of access for unstructured data, making it ideal for large media files and backups, though it lacks efficient indexing and querying capabilities. Choosing between database and file storage depends on the need for data structure, scalability, and access patterns in the application.
Choosing the Right Storage Solution for Your Needs
Database storage offers structured data management, enabling efficient querying and indexing, ideal for dynamic applications requiring complex transactions and relationships. File storage provides easy handling of unstructured data such as documents, images, and videos, benefiting systems with simple, hierarchical file access needs. Selecting the right storage involves assessing data complexity, access patterns, scalability requirements, and performance expectations to balance flexibility and cost-effectiveness.
Database Storage Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com