Headless CMS separates content management from the presentation layer, enabling developers to deliver content across multiple platforms with ease and flexibility. This approach improves scalability, enhances performance, and streamlines content updates without dependency on a specific front-end framework. Explore the rest of the article to discover how a Headless CMS can revolutionize your content strategy and digital experience.
Table of Comparison
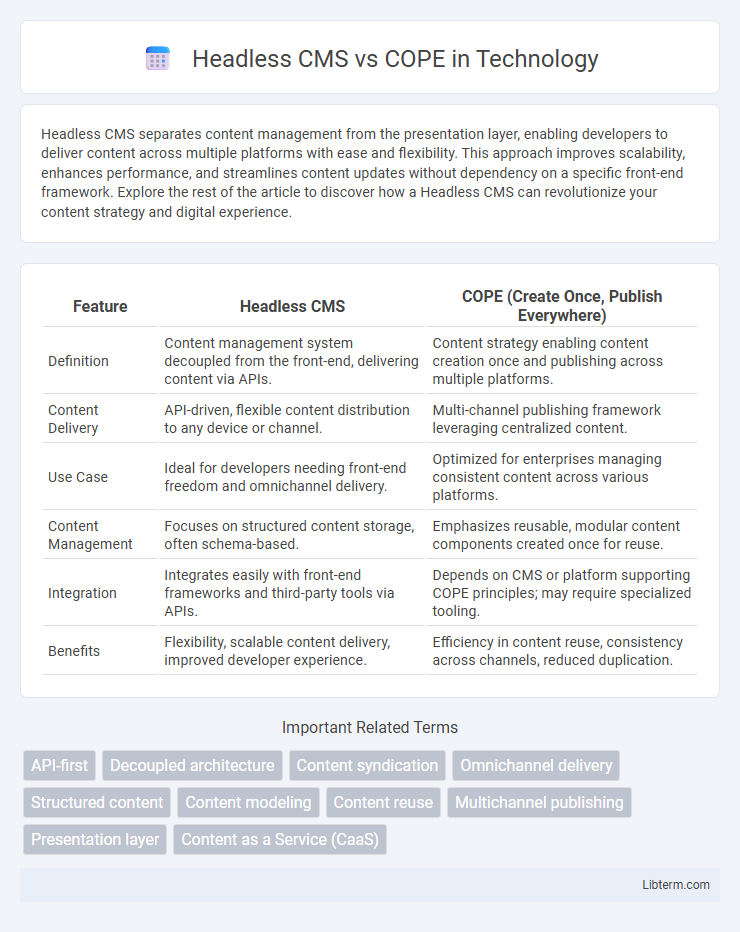
| Feature | Headless CMS | COPE (Create Once, Publish Everywhere) |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Content management system decoupled from the front-end, delivering content via APIs. | Content strategy enabling content creation once and publishing across multiple platforms. |
| Content Delivery | API-driven, flexible content distribution to any device or channel. | Multi-channel publishing framework leveraging centralized content. |
| Use Case | Ideal for developers needing front-end freedom and omnichannel delivery. | Optimized for enterprises managing consistent content across various platforms. |
| Content Management | Focuses on structured content storage, often schema-based. | Emphasizes reusable, modular content components created once for reuse. |
| Integration | Integrates easily with front-end frameworks and third-party tools via APIs. | Depends on CMS or platform supporting COPE principles; may require specialized tooling. |
| Benefits | Flexibility, scalable content delivery, improved developer experience. | Efficiency in content reuse, consistency across channels, reduced duplication. |
Introduction to Headless CMS and COPE
Headless CMS separates content management from presentation, allowing developers to deliver content via APIs to any device or platform, enhancing flexibility and scalability. COPE (Create Once, Publish Everywhere) is a content strategy emphasizing content reuse across multiple channels, reducing duplication and ensuring consistency. Both approaches streamline content distribution but differ in focus: Headless CMS is a technical architecture for content delivery, while COPE is a content management philosophy promoting efficiency in multi-channel publishing.
Defining Headless CMS: Key Features
Headless CMS is a content management system that decouples the content repository from the presentation layer, enabling seamless content delivery across multiple platforms via APIs. It features content accessibility through RESTful or GraphQL endpoints, flexible front-end integration, and enhanced scalability for omnichannel publishing. Unlike traditional CMS, Headless CMS prioritizes content as a service, allowing developers to use any technology stack for front-end development while managing content centrally.
What is COPE (Create Once, Publish Everywhere)?
COPE, standing for Create Once, Publish Everywhere, is a content management strategy designed to streamline content production by enabling creators to develop content a single time and distribute it seamlessly across multiple platforms and devices. This approach contrasts with traditional Headless CMS, which separates content from presentation but may require additional effort to adapt content for various channels. COPE emphasizes maximizing content reuse and consistency, ultimately enhancing efficiency and reducing duplication in multichannel publishing environments.
Core Principles: Headless CMS vs COPE
Headless CMS prioritizes decoupling the content repository from the presentation layer, enabling content delivery via APIs for flexible multi-channel publishing. COPE (Create Once, Publish Everywhere) emphasizes content reusability and syndication by structuring content into modular, atomic units that can be seamlessly published across diverse platforms. Both focus on content agility but COPE extends the Headless CMS principle by promoting content repurposing for broader cross-channel consistency and efficiency.
Content Workflow Comparison
Headless CMS enables flexible content delivery across multiple platforms by decoupling content creation from presentation, streamlining workflows through API-driven content management and real-time editing. COPE (Create Once, Publish Everywhere) emphasizes content reuse by centralizing content creation for seamless distribution to diverse channels, reducing duplication and accelerating time-to-market. Both systems improve content workflows, with Headless CMS offering granular control over content presentation while COPE optimizes consistency and efficiency in multi-channel publishing.
Flexibility and Scalability in Both Approaches
Headless CMS delivers exceptional flexibility by decoupling content creation from presentation, enabling developers to distribute content seamlessly across multiple platforms via APIs. COPE (Create Once, Publish Everywhere) emphasizes scalability, allowing organizations to manage and repurpose content efficiently across diverse channels without redundant efforts. Both approaches support dynamic content delivery, but Headless CMS excels in customization capabilities, whereas COPE offers streamlined workflows for consistent multi-channel publishing at scale.
Integration Capabilities: APIs and Beyond
Headless CMS platforms excel in integration capabilities by providing robust RESTful and GraphQL APIs, enabling seamless content delivery across multiple channels and devices. COPE (Create Once, Publish Everywhere) approaches leverage these APIs to centralize content creation and automate distribution workflows, enhancing consistency and scalability. Beyond APIs, advanced integration tools like webhooks, SDKs, and third-party connectors further empower developers to customize and extend content ecosystems efficiently.
Use Cases: When to Choose Headless CMS or COPE
Headless CMS is ideal for organizations seeking flexible content delivery across multiple digital channels, such as mobile apps, websites, and IoT devices, enabling seamless omnichannel experiences. COPE (Create Once, Publish Everywhere) suits publishers and media companies focused on content syndication and repurposing across various platforms while maintaining consistent editorial workflows. Choosing between Headless CMS and COPE depends on the need for multi-channel content management versus streamlined content distribution and reuse.
Pros and Cons: Headless CMS vs COPE
Headless CMS offers flexibility by decoupling content management from presentation layers, enabling seamless multi-channel delivery but may require more developer resources for front-end integration. COPE (Create Once, Publish Everywhere) streamlines content distribution across multiple platforms, increasing efficiency yet can limit customization due to its standardized publishing workflow. Choosing between Headless CMS and COPE depends on the need for agility in content presentation versus centralized, consistent content dissemination.
Future Trends in Digital Content Management
Headless CMS and COPE (Create Once, Publish Everywhere) represent pivotal trends shaping the future of digital content management by enabling seamless, multi-channel content distribution and enhanced scalability. The rise of AI-driven personalization and omnichannel strategies demands flexible content architectures like headless CMS, while COPE streamlines workflows by ensuring content consistency across platforms. Emerging integrations with IoT devices and voice-activated systems further highlight the need for adaptive content frameworks that support dynamic, context-aware user experiences.
Headless CMS Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com