Dedicated hosting provides your website with an entire server exclusively for its use, ensuring maximum performance, security, and control. This type of hosting is ideal for businesses and projects with high traffic volumes or resource-intensive applications. Explore the full article to understand how dedicated hosting can elevate your online presence.
Table of Comparison
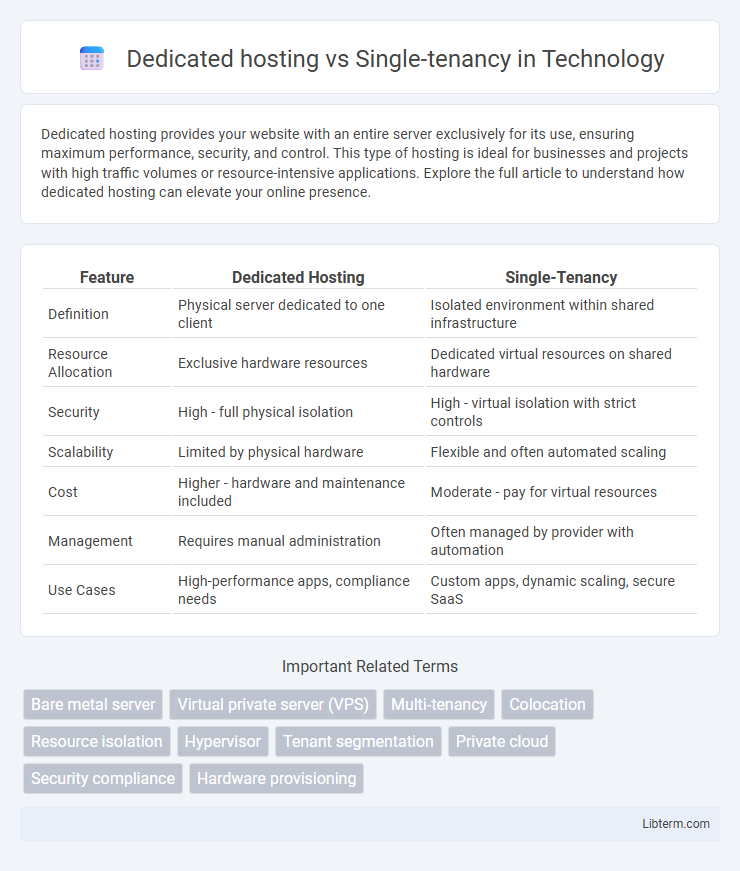
| Feature | Dedicated Hosting | Single-Tenancy |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Physical server dedicated to one client | Isolated environment within shared infrastructure |
| Resource Allocation | Exclusive hardware resources | Dedicated virtual resources on shared hardware |
| Security | High - full physical isolation | High - virtual isolation with strict controls |
| Scalability | Limited by physical hardware | Flexible and often automated scaling |
| Cost | Higher - hardware and maintenance included | Moderate - pay for virtual resources |
| Management | Requires manual administration | Often managed by provider with automation |
| Use Cases | High-performance apps, compliance needs | Custom apps, dynamic scaling, secure SaaS |
Understanding Dedicated Hosting: A Brief Overview
Dedicated hosting provides exclusive access to a physical server, ensuring optimal performance, enhanced security, and full control over server configurations. It contrasts with single-tenancy environments where resources are isolated within shared infrastructure but not necessarily tied to dedicated hardware. Understanding dedicated hosting involves recognizing its role in delivering predictable performance for resource-intensive applications by eliminating the variability inherent in multi-tenant systems.
What is Single-Tenancy in Web Hosting?
Single-tenancy in web hosting refers to an architecture where a single client exclusively uses an entire server, ensuring complete isolation from other users, enhancing security, performance, and customization. Unlike dedicated hosting, which often implies a physical server solely for one client, single-tenancy emphasizes the software and virtualization aspect, providing a dedicated environment within shared infrastructure. This model is ideal for businesses requiring strict data privacy, compliance, and tailored resource management.
Key Differences Between Dedicated Hosting and Single-Tenancy
Dedicated hosting provides physical servers exclusively for one client, ensuring full control over hardware resources and customization options. Single-tenancy refers to a software architecture where each customer operates on an isolated instance of an application, enhancing data security and performance. While dedicated hosting emphasizes hardware isolation, single-tenancy focuses on application-level isolation within shared infrastructure.
Performance Comparison: Dedicated Hosting vs Single-Tenancy
Dedicated hosting offers exclusive server resources, ensuring high performance with minimal latency and consistent processing power, ideal for resource-heavy applications. Single-tenancy architecture provides isolated environments within shared infrastructure, delivering strong performance benefits by reducing noisy neighbor effects and improving security boundaries. Performance benchmarks typically show dedicated hosting excels in raw resource availability, while single-tenancy balances efficiency and scalability through virtualization technologies.
Security and Compliance: Evaluating Each Model
Dedicated hosting offers enhanced security by isolating resources on a single physical server, reducing risks associated with multi-tenant environments and allowing strict compliance with regulations like HIPAA and GDPR. Single-tenancy provides a tailored security framework where applications run on separate instances, minimizing data leakage risks and enabling granular compliance controls for standards such as PCI DSS. Evaluating security and compliance in both models depends on specific organizational requirements, with dedicated hosting excelling in hardware isolation and single-tenancy offering flexible software-level protections.
Customization and Control: Which Offers More Flexibility?
Dedicated hosting provides extensive customization and control over server configurations, allowing users to tailor hardware, software, and security settings to specific needs, resulting in high flexibility. Single-tenancy, while also offering isolated environments with dedicated resources, often comes with platform-managed options that can limit customization compared to full dedicated servers. For businesses prioritizing maximum control and customizable infrastructure, dedicated hosting typically offers more flexibility.
Cost Considerations in Dedicated Hosting and Single-Tenancy
Dedicated hosting typically involves a fixed monthly fee that covers exclusive use of physical servers, leading to higher upfront costs but predictable expenses. Single-tenancy architecture may increase costs due to the need for isolated resources and customized infrastructure, but it can reduce overhead by optimizing resource utilization per tenant. Businesses must evaluate server management, hardware maintenance, and scalability expenses to determine the most cost-effective solution between dedicated hosting and single-tenancy environments.
Scalability and Future-Proofing Your Infrastructure
Dedicated hosting offers limited scalability as resources are confined to a single physical server, making it less flexible for growing workloads. Single-tenancy solutions provide superior scalability by isolating resources for each client, enabling seamless upgrades and customization to accommodate increasing demands. Investing in single-tenancy infrastructure ensures future-proofing with enhanced security, performance, and the ability to integrate emerging technologies without disrupting existing operations.
Ideal Use Cases for Dedicated Hosting vs Single-Tenancy
Dedicated hosting is ideal for businesses requiring full control over server resources, high performance, and enhanced security without sharing infrastructure, making it suitable for e-commerce platforms, large enterprises, and heavy-duty applications. Single-tenancy is best for organizations seeking isolated software environments with customizable applications while leveraging cloud benefits, often used in SaaS deployments that demand data privacy and compliance. Both solutions cater to different scalability and management needs, with dedicated hosting focusing on hardware exclusivity and single-tenancy emphasizing software isolation.
Making the Right Choice: Factors to Consider
Choosing between dedicated hosting and single-tenancy involves evaluating factors such as security, control, and resource allocation. Dedicated hosting offers an entire physical server for exclusive use, enhancing performance for resource-heavy applications, while single-tenancy provides isolated environments within shared infrastructure, improving cost efficiency without compromising data segregation. Consider workload demands, compliance requirements, and budget constraints to determine which hosting model aligns best with business objectives.
Dedicated hosting Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com