Public cloud offers scalable and cost-effective computing resources managed by third-party providers, allowing businesses to access virtual servers, storage, and applications over the internet. Security, compliance, and performance are key considerations when selecting a public cloud service to ensure your data remains protected. Explore the rest of the article to understand how to leverage public cloud solutions for your organization's growth.
Table of Comparison
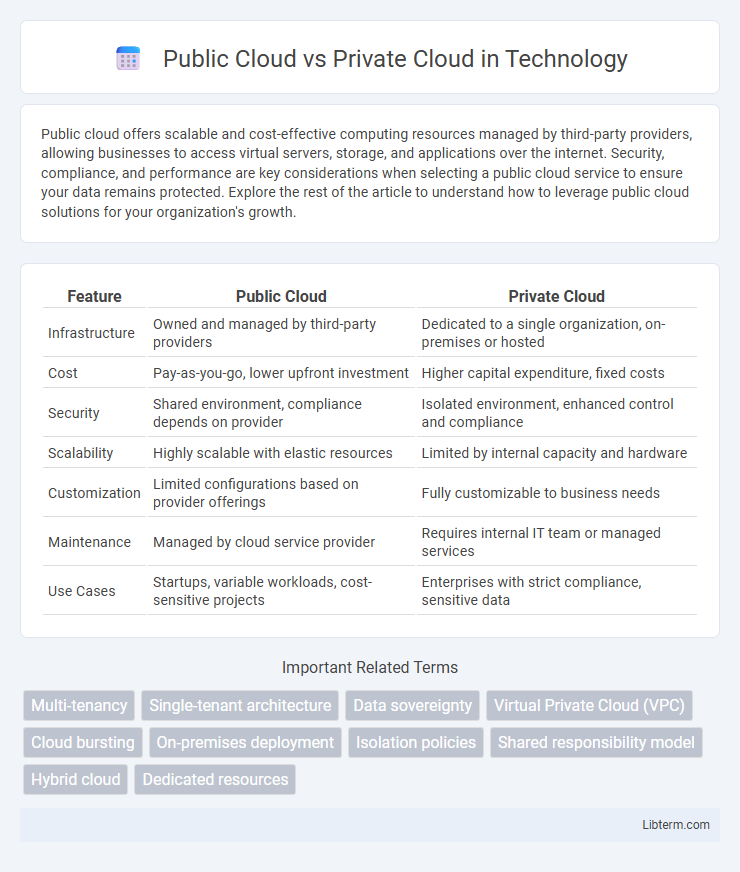
| Feature | Public Cloud | Private Cloud |
|---|---|---|
| Infrastructure | Owned and managed by third-party providers | Dedicated to a single organization, on-premises or hosted |
| Cost | Pay-as-you-go, lower upfront investment | Higher capital expenditure, fixed costs |
| Security | Shared environment, compliance depends on provider | Isolated environment, enhanced control and compliance |
| Scalability | Highly scalable with elastic resources | Limited by internal capacity and hardware |
| Customization | Limited configurations based on provider offerings | Fully customizable to business needs |
| Maintenance | Managed by cloud service provider | Requires internal IT team or managed services |
| Use Cases | Startups, variable workloads, cost-sensitive projects | Enterprises with strict compliance, sensitive data |
Introduction to Cloud Computing
Public cloud offers scalable resources provided by third-party vendors over the internet, enabling businesses to access computing power and storage without investing in physical infrastructure. Private cloud delivers dedicated cloud environments exclusively for one organization, enhancing security, control, and compliance. Cloud computing integrates public and private clouds to optimize resource allocation, cost efficiency, and operational agility across diverse IT workloads.
Defining Public Cloud
Public Cloud refers to cloud computing services offered by third-party providers over the public internet, making resources like servers, storage, and applications accessible to multiple organizations on a shared infrastructure. These services provide scalable, pay-as-you-go models that eliminate the need for businesses to invest in physical hardware. Examples of leading Public Cloud providers include Amazon Web Services (AWS), Microsoft Azure, and Google Cloud Platform (GCP).
Defining Private Cloud
Private cloud refers to a cloud computing environment dedicated exclusively to a single organization, providing enhanced security, control, and customization compared to public cloud services. It operates on a private network, either on-premises or hosted by third-party providers, ensuring compliance with industry regulations and sensitive data protection. Enterprises leverage private clouds to optimize performance, reduce latency, and maintain complete governance over their IT infrastructure.
Key Differences Between Public and Private Cloud
Public cloud services offer scalable resources hosted by third-party providers accessible over the internet, enabling cost efficiency and rapid deployment. Private cloud infrastructure is dedicated to a single organization, providing enhanced security, control, and customization tailored to specific business needs. Key differences include ownership, with public clouds shared among multiple tenants and private clouds maintained internally or by a third party for exclusive use, impacting compliance, security, and performance.
Cost Considerations: Public vs Private Cloud
Public cloud solutions typically offer lower upfront costs with a pay-as-you-go pricing model, which reduces capital expenditure and provides scalability without large investments in hardware. Private cloud requires higher initial capital investment for dedicated infrastructure, but may lower long-term operating expenses through optimized resource utilization and enhanced security control. Organizations must assess workload demands, compliance requirements, and total cost of ownership to determine the most cost-effective cloud deployment.
Security and Compliance in Cloud Environments
Public cloud environments offer scalable infrastructure but pose greater security risks due to multi-tenancy and potential exposure to external threats. Private clouds provide enhanced security controls and compliance adherence by isolating data and workloads within dedicated infrastructure, minimizing vulnerabilities. Enterprises handling sensitive data prioritize private clouds to meet stringent regulatory requirements such as HIPAA, GDPR, and PCI-DSS.
Scalability and Performance Comparison
Public cloud platforms offer unparalleled scalability by leveraging vast shared resources, enabling rapid expansion and dynamic workload management. Private clouds provide optimized performance through dedicated infrastructure, reducing latency and enhancing security for mission-critical applications. Scalability in private clouds is limited by physical hardware, whereas public clouds deliver virtually limitless resources on-demand, impacting cost-efficiency and operational agility.
Use Cases for Public Cloud
Public cloud environments excel in handling variable workloads, supporting large-scale web applications, and enabling rapid deployment for startups and enterprises. They provide cost-effective, scalable solutions for disaster recovery, big data analytics, and content delivery networks due to their vast global infrastructure. Public cloud platforms like AWS, Microsoft Azure, and Google Cloud offer extensive services that cater to development testing, machine learning projects, and global collaboration needs.
Use Cases for Private Cloud
Private cloud environments are ideal for organizations requiring enhanced data security, regulatory compliance, and customization, such as financial institutions, healthcare providers, and government agencies. They enable sensitive workloads to be managed within dedicated infrastructure, ensuring strict access control and data sovereignty. Private clouds also support specialized applications needing low latency and predictable performance that public cloud services may not consistently guarantee.
Choosing the Right Cloud Model for Your Business
Choosing the right cloud model for your business depends on factors such as data security requirements, budget constraints, and scalability needs. Public cloud services offer cost-effective, scalable solutions ideal for businesses with variable workloads and limited infrastructure management resources. Private cloud provides enhanced security and control, making it suitable for enterprises handling sensitive data or requiring compliance with strict regulatory standards.
Public Cloud Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com