Data replication ensures the continuous availability and reliability of information by creating exact copies of data across multiple storage systems or locations. This process enhances disaster recovery, load balancing, and data accessibility, critical for maintaining seamless business operations. Discover how data replication can elevate your data management strategy by exploring the rest of this article.
Table of Comparison
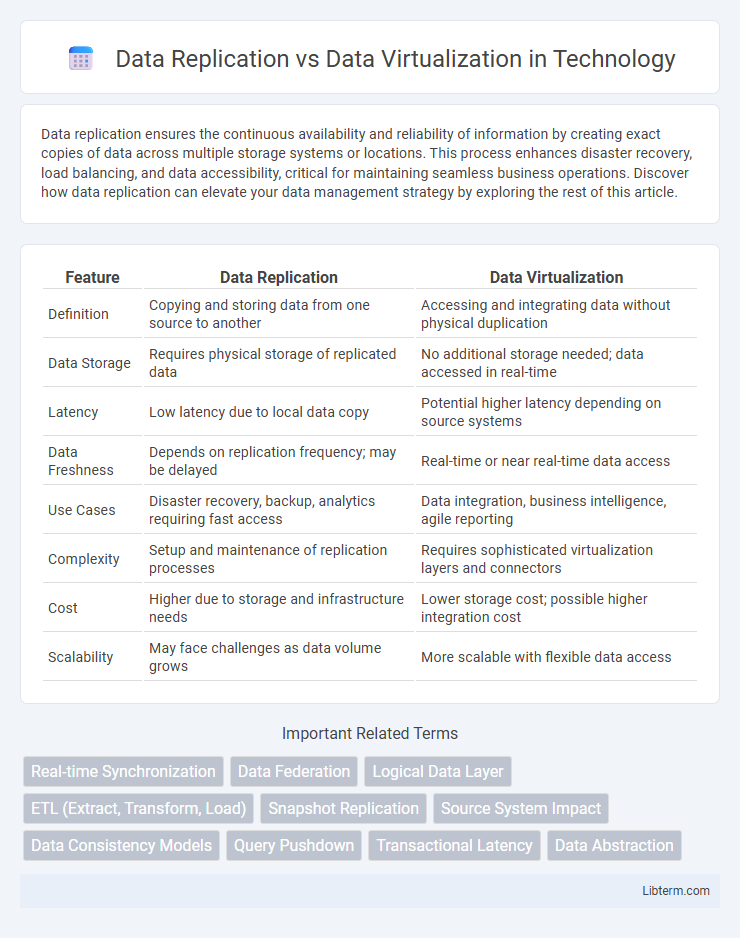
| Feature | Data Replication | Data Virtualization |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Copying and storing data from one source to another | Accessing and integrating data without physical duplication |
| Data Storage | Requires physical storage of replicated data | No additional storage needed; data accessed in real-time |
| Latency | Low latency due to local data copy | Potential higher latency depending on source systems |
| Data Freshness | Depends on replication frequency; may be delayed | Real-time or near real-time data access |
| Use Cases | Disaster recovery, backup, analytics requiring fast access | Data integration, business intelligence, agile reporting |
| Complexity | Setup and maintenance of replication processes | Requires sophisticated virtualization layers and connectors |
| Cost | Higher due to storage and infrastructure needs | Lower storage cost; possible higher integration cost |
| Scalability | May face challenges as data volume grows | More scalable with flexible data access |
Introduction to Data Replication and Data Virtualization
Data replication involves creating and maintaining copies of data across multiple systems or locations to ensure high availability, fault tolerance, and improved access speed. Data virtualization provides a unified, real-time view of data from disparate sources without physically moving or copying the data, enabling seamless data integration and faster decision-making. Both technologies play crucial roles in modern data management strategies, optimizing data accessibility and operational efficiency.
Core Concepts: What is Data Replication?
Data replication is the process of copying and maintaining database objects, such as tables or entire databases, across multiple servers or locations to ensure data consistency and availability. This technique enhances data redundancy, supports disaster recovery, and improves system performance by providing localized data access. Data replication involves synchronization mechanisms that keep the replicated data updated in near real-time or at scheduled intervals.
Understanding Data Virtualization: Key Principles
Data virtualization enables real-time data integration by creating a unified, virtual view of data from multiple sources without physically moving it. It relies on key principles such as abstraction, to hide data complexity; federation, to combine disparate data sources; and real-time access, ensuring up-to-date information delivery. This approach contrasts with data replication, which copies data to a separate repository, requiring synchronization and storage overhead.
Technical Architecture Comparison
Data replication involves copying and storing data from one system to another, creating physical duplicates that ensure high availability and disaster recovery through synchronized updates. In contrast, data virtualization provides a real-time unified view of data across multiple sources without physical movement by leveraging a virtual data layer that queries data in place, minimizing storage costs and latency. Architecturally, data replication relies on ETL/ELT pipelines and storage infrastructure, while data virtualization depends on a metadata-driven abstraction layer and query federation engines to integrate disparate data sources dynamically.
Use Cases for Data Replication
Data replication is essential for use cases requiring high availability, disaster recovery, and real-time analytics, ensuring consistent data across multiple systems. It supports operational workloads by providing local copies of data to reduce latency and improve application performance. Enterprises leverage data replication to maintain data integrity during system migrations and to enable seamless business continuity in distributed environments.
Use Cases for Data Virtualization
Data virtualization excels in use cases requiring real-time data access and integration across disparate sources without physical data movement, such as business intelligence dashboards, self-service analytics, and agile data integration for cloud migration. It supports scenarios where up-to-date insights are critical, enabling users to query live data from multiple systems like ERP, CRM, and data lakes through a unified virtual layer. Enterprises leverage data virtualization to reduce data latency, improve data governance, and enable rapid decision-making without the overhead of traditional ETL processes.
Performance and Scalability Considerations
Data replication enhances performance by creating physical copies of data closer to the user, reducing latency and enabling faster query responses, especially in high-transaction environments. In scalability, replication can handle increased loads by distributing data across multiple nodes but may introduce synchronization challenges and storage overhead. Data virtualization offers real-time data access without copying, which simplifies scalability and supports diverse data sources, yet it may suffer from lower performance due to query processing over multiple systems and network dependencies.
Data Consistency, Security, and Governance
Data replication ensures data consistency by creating exact copies across multiple locations, minimizing latency but increasing storage overhead and synchronization complexity. Data virtualization provides real-time access to data without duplication, enhancing security through centralized access control and reducing compliance risks by maintaining a single source of truth. Both approaches require robust governance frameworks, but data virtualization offers greater agility in enforcing policies due to its unified data abstraction layer.
Choosing the Right Approach: Factors to Consider
Choosing between data replication and data virtualization hinges on factors such as data freshness requirements, system performance, and storage capacity. Data replication ensures high availability and faster query response by creating physical copies, ideal for real-time analytics and disaster recovery scenarios. Data virtualization offers agile access to live data without duplication, reducing storage costs and simplifying data integration across diverse sources for dynamic business intelligence.
Future Trends in Data Management Technologies
Data replication continues to evolve with enhanced automation, real-time synchronization, and multi-cloud support, enabling more resilient and scalable data architectures. Data virtualization is advancing through AI-driven data integration, providing seamless access to distributed datasets without physical duplication, thereby accelerating decision-making processes. Emerging hybrid models combine both technologies to optimize data agility, reduce latency, and improve governance in complex, large-scale enterprise environments.
Data Replication Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com