Physical delete refers to the complete removal of data from a storage device, ensuring it cannot be recovered by any means. This process involves overwriting or destroying the physical media, making your sensitive information irretrievable and enhancing data security. Explore the rest of the article to understand the methods and importance of physical deletion for protecting your digital privacy.
Table of Comparison
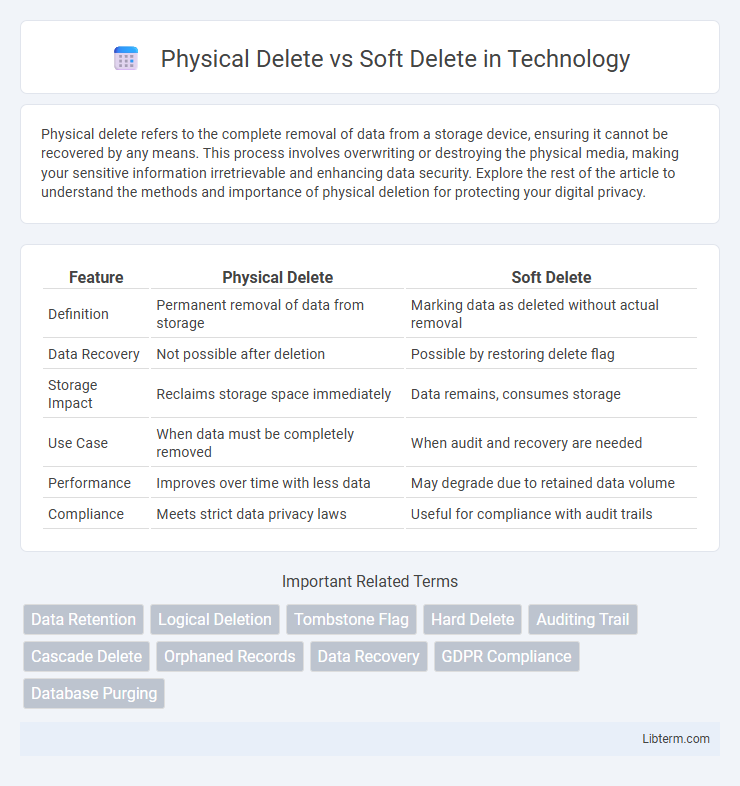
| Feature | Physical Delete | Soft Delete |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Permanent removal of data from storage | Marking data as deleted without actual removal |
| Data Recovery | Not possible after deletion | Possible by restoring delete flag |
| Storage Impact | Reclaims storage space immediately | Data remains, consumes storage |
| Use Case | When data must be completely removed | When audit and recovery are needed |
| Performance | Improves over time with less data | May degrade due to retained data volume |
| Compliance | Meets strict data privacy laws | Useful for compliance with audit trails |
Introduction to Data Deletion Methods
Physical delete permanently removes data from storage, ensuring it cannot be recovered, which is essential for compliance with strict data retention policies. Soft delete marks data as deleted without actual removal, preserving it for potential recovery or audit purposes, commonly used in applications requiring historical tracking. Understanding these data deletion methods helps balance security, recovery options, and storage management in database administration.
What is Physical Delete?
Physical delete permanently removes data from a database or storage system, eliminating all traces of the information and freeing up storage space immediately. This process ensures that the deleted records cannot be recovered or restored through normal means, enhancing data security when permanent removal is necessary. Physical delete is often used in systems requiring strict data retention policies or when data must be erased to comply with privacy regulations such as GDPR or HIPAA.
What is Soft Delete?
Soft delete is a data management technique where records are marked as deleted without being permanently removed from the database, enabling easy recovery and auditing. This method typically involves a boolean flag or status field indicating deletion, preserving data integrity and historical information. Soft delete is crucial in systems requiring compliance, data retention, and rollback capabilities, contrasting with physical delete where data is permanently erased.
Key Differences Between Physical and Soft Delete
Physical delete permanently removes data from the storage system, making recovery impossible, while soft delete flags data as deleted without actual removal, allowing for recovery and auditing. Key differences include data recovery capability, where soft delete supports retrieval through status flags, and physical delete results in complete data erasure. Soft delete often consumes more storage due to retained data, whereas physical delete optimizes storage by eliminating deleted entries.
Pros and Cons of Physical Delete
Physical delete permanently removes data from the database, freeing up storage space and improving query performance by reducing table size. However, it eliminates any possibility of data recovery or auditing, which can be detrimental for compliance and troubleshooting purposes. The irreversible nature of physical delete requires careful handling to avoid accidental data loss.
Pros and Cons of Soft Delete
Soft delete preserves data by marking records as deleted without removing them from the database, allowing for easy recovery and audit trails. However, it can lead to data bloat and requires additional query filtering to exclude deleted records from active results. Performance may degrade over time due to the accumulation of logically deleted entries, necessitating periodic data cleanup or archiving strategies.
Use Cases for Physical Delete
Physical delete is ideal for use cases requiring permanent removal of data, such as compliance with data privacy regulations like GDPR that mandate erasing personal information upon request. It is also preferred in scenarios where storage optimization is critical, enabling the system to reclaim disk space by completely deleting unnecessary records. Additionally, physical delete is suitable for sensitive data management, ensuring that deleted information is irrecoverable to maintain security and prevent unauthorized access.
Use Cases for Soft Delete
Soft delete is ideal for applications requiring data recovery and audit trails, such as user management systems and e-commerce platforms where accidental deletion must be reversible. It supports compliance with regulations by preserving historical records while marking items as inactive without permanent removal. Soft delete also enables safer data modifications in collaborative environments by preventing immediate data loss and allowing easy restoration.
Security and Compliance Considerations
Physical delete permanently removes data from storage, reducing the risk of unauthorized recovery but complicating audit trails and compliance with data retention regulations like GDPR and HIPAA. Soft delete retains data in a hidden or inaccessible state, allowing easier recovery and audit logging but requires robust access controls and encryption to mitigate risks of data breaches and unauthorized access. Organizations must balance security needs and regulatory requirements by implementing strict policies and monitoring mechanisms for both deletion methods.
Best Practices for Implementing Delete Strategies
Implementing delete strategies requires balancing data integrity and recovery needs; physical deletes permanently remove records from the database, ideal for sensitive data compliance but risky without backups. Soft deletes mark records as inactive or deleted using flags, preserving data for audit trails and restoring capabilities, making them a best practice in systems requiring historical data tracking. Best practices recommend using soft deletes by default, combined with scheduled physical deletions based on retention policies to optimize storage and maintain compliance.
Physical Delete Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com