WebSockets enable real-time, bidirectional communication between your browser and servers, significantly improving the responsiveness of web applications. This protocol reduces latency by maintaining a persistent connection, allowing instant data exchange without repeated HTTP requests. Explore the rest of the article to understand how WebSockets can transform your web experience.
Table of Comparison
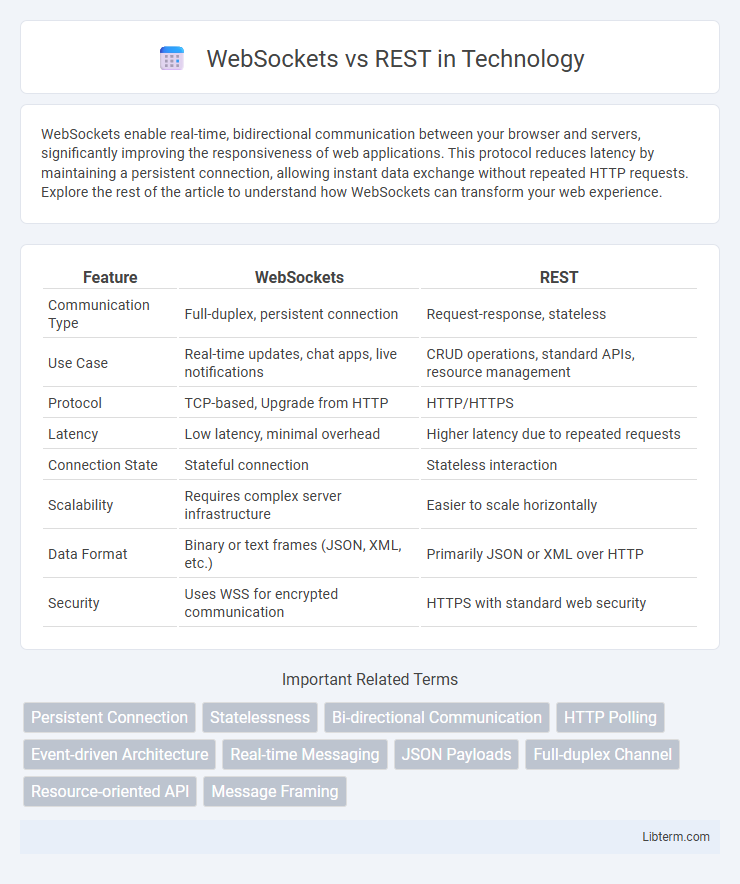
| Feature | WebSockets | REST |
|---|---|---|
| Communication Type | Full-duplex, persistent connection | Request-response, stateless |
| Use Case | Real-time updates, chat apps, live notifications | CRUD operations, standard APIs, resource management |
| Protocol | TCP-based, Upgrade from HTTP | HTTP/HTTPS |
| Latency | Low latency, minimal overhead | Higher latency due to repeated requests |
| Connection State | Stateful connection | Stateless interaction |
| Scalability | Requires complex server infrastructure | Easier to scale horizontally |
| Data Format | Binary or text frames (JSON, XML, etc.) | Primarily JSON or XML over HTTP |
| Security | Uses WSS for encrypted communication | HTTPS with standard web security |
Introduction to WebSockets and REST
WebSockets enable full-duplex communication channels over a single TCP connection, facilitating real-time data exchange between clients and servers. REST (Representational State Transfer) operates on stateless HTTP protocols, focusing on resource-based interactions using standard methods like GET, POST, PUT, and DELETE. WebSockets suit applications requiring continuous data streams, while REST excels in request-response scenarios and reflects a stateless, cacheable communication style.
How WebSockets Work
WebSockets establish a persistent, full-duplex communication channel over a single TCP connection, enabling real-time data exchange between client and server without the overhead of repeated HTTP requests. The WebSocket protocol begins with an HTTP handshake that upgrades the connection, then continuously transmits messages in both directions with low latency. This differs from REST's request-response model, making WebSockets ideal for applications requiring instant updates like chat systems, live gaming, and financial tickers.
How REST APIs Operate
REST APIs operate using stateless HTTP requests where each client-server interaction is independent, relying on standard methods like GET, POST, PUT, and DELETE to perform operations on resources identified by URLs. These APIs utilize JSON or XML to exchange data formats, enabling interoperability between diverse systems and platforms. The statelessness of REST ensures scalability and simplicity but limits real-time communication, as each request requires a new connection.
Key Differences Between WebSockets and REST
WebSockets enable full-duplex communication channels over a single TCP connection, providing real-time, low-latency data exchange, whereas REST operates on a stateless request-response model typically over HTTP. WebSockets maintain persistent connections allowing servers to push data instantly, contrasting with REST which requires clients to initiate each call and receive discrete responses. WebSockets excel in applications demanding continuous data flow such as live chat or gaming, while REST suits CRUD operations and stateless web services.
Performance Comparison: WebSockets vs REST
WebSockets provide superior performance for real-time, bidirectional communication by maintaining a persistent connection, reducing latency and overhead compared to REST's stateless request-response model. REST APIs involve repeated HTTP requests and responses, which increase network traffic and latency, particularly in scenarios requiring frequent data updates. WebSockets excel in applications like gaming, chat, and live data feeds where low latency and efficient resource usage are critical.
Use Cases for WebSockets
WebSockets excel in real-time applications such as online gaming, live chat, and financial trading platforms where continuous, bidirectional communication is essential. Unlike REST, which follows a request-response model ideal for CRUD operations and stateless interactions, WebSockets maintain an open connection enabling instant data exchange with minimal latency. This makes WebSockets the preferred protocol for use cases requiring rapid updates, event-driven notifications, and persistent connections.
Use Cases for REST
REST APIs excel in scenarios requiring stateless communication and a clear separation between client and server, making them ideal for CRUD operations in web applications. They are widely used for public APIs, allowing easy integration with third-party services and supporting caching mechanisms to improve performance. REST is also preferred for applications with low-frequency data updates where scalability and simplicity are critical.
Security Considerations
WebSockets establish persistent, full-duplex communication channels, requiring robust measures such as TLS encryption (wss://) to prevent eavesdropping and man-in-the-middle attacks, while REST relies on stateless HTTP requests secured by HTTPS. WebSocket implementations must enforce strict origin validation and authentication to mitigate risks like cross-site WebSocket hijacking, whereas REST APIs typically benefit from mature, well-understood security models including OAuth and token-based authentication. Rate-limiting and input validation remain critical for both, but the continuous connection nature of WebSockets demands vigilant monitoring for abnormal traffic patterns to prevent resource exhaustion and denial-of-service attacks.
Scalability and Maintenance
WebSockets offer superior scalability for real-time applications by maintaining persistent connections, reducing overhead from repeated HTTP requests, and enabling efficient bidirectional communication. REST APIs, built on stateless HTTP protocols, scale easily across distributed systems but can incur higher latency and resource use under heavy concurrent connection loads. Maintenance for WebSockets requires managing connection states and handling more complex error recovery, while REST benefits from simpler stateless design, making it easier to test, cache, and integrate with existing infrastructure.
Choosing Between WebSockets and REST
Choosing between WebSockets and REST depends on the real-time communication needs of your application; WebSockets provide persistent, full-duplex communication ideal for instant updates and low-latency interactions, such as live chat or gaming. REST, based on stateless HTTP requests, excels in CRUD operations and scalability, making it suitable for standard web services and applications with intermittent data exchange. Evaluating factors like connection persistence, data transfer frequency, and complexity will guide the optimal protocol choice for your system architecture.
WebSockets Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com