Snowflake ID is a unique identifier system designed for distributed computing environments, providing scalable and collision-free IDs with high time precision. These IDs are commonly used in databases and messaging systems to efficiently track and reference data across multiple nodes without relying on centralized coordination. Explore the rest of the article to understand how Snowflake IDs can optimize your data management and system architecture.
Table of Comparison
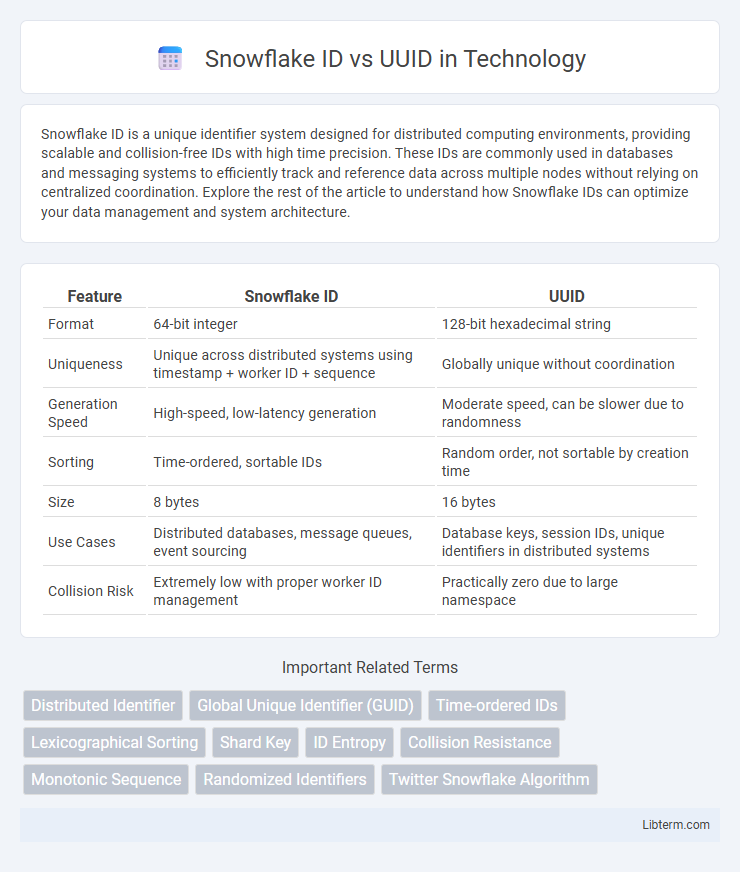
| Feature | Snowflake ID | UUID |
|---|---|---|
| Format | 64-bit integer | 128-bit hexadecimal string |
| Uniqueness | Unique across distributed systems using timestamp + worker ID + sequence | Globally unique without coordination |
| Generation Speed | High-speed, low-latency generation | Moderate speed, can be slower due to randomness |
| Sorting | Time-ordered, sortable IDs | Random order, not sortable by creation time |
| Size | 8 bytes | 16 bytes |
| Use Cases | Distributed databases, message queues, event sourcing | Database keys, session IDs, unique identifiers in distributed systems |
| Collision Risk | Extremely low with proper worker ID management | Practically zero due to large namespace |
Understanding Unique Identifiers: Snowflake ID vs UUID
Snowflake ID and UUID serve as unique identifiers but differ significantly in structure and use cases. Snowflake IDs are 64-bit numerical values generated using timestamp, machine ID, and sequence number, ensuring high scalability and chronological ordering ideal for distributed systems like Twitter. UUIDs are 128-bit identifiers, standardized for universal uniqueness across space and time, favored in scenarios requiring decentralized generation without coordination.
What Is a Snowflake ID?
A Snowflake ID is a unique identifier generated using a distributed system that encodes a timestamp, machine ID, and sequence number into a 64-bit integer, ensuring scalability and low latency in distributed environments. Unlike UUIDs (Universally Unique Identifiers), which are 128 bits and generally random or time-based with less emphasis on ordering, Snowflake IDs provide sortable and collision-free IDs optimized for distributed databases like Twitter's distributed platform. Snowflake IDs improve performance and indexing efficiency in large-scale systems by combining time-ordered uniqueness with compact size.
What Is a UUID?
A UUID (Universally Unique Identifier) is a 128-bit number used to uniquely identify information in computer systems, commonly represented as a 36-character string including hyphens. It provides a standardized method for generating unique keys across distributed systems without requiring central coordination. UUIDs are widely used in databases, networking protocols, and software development to ensure global uniqueness.
Structural Differences: Snowflake ID and UUID
Snowflake ID is a 64-bit integer composed of a timestamp, a worker node ID, and a sequence number, enabling ordered and scalable unique identifiers. UUID is a 128-bit value structured into fields such as time-low, time-mid, time-high-and-version, clock sequence, and node, designed for global uniqueness without centralized coordination. The compactness and timestamp-based hierarchy of Snowflake IDs contrast with the fixed-length, randomized or time-based components of UUIDs, impacting database indexing and system performance.
Generation Method: Snowflake ID vs UUID
Snowflake ID generates unique identifiers using a combination of timestamps, machine IDs, and sequence numbers, ensuring ordered and scalable ID creation across distributed systems. UUID generates 128-bit identifiers based on random or pseudo-random numbers, timestamps, or hardware information, prioritizing uniqueness without inherent order. Snowflake IDs are typically more efficient for database indexing due to their time-based structure, while UUIDs provide universal uniqueness without dependency on a central authority.
Performance Considerations
Snowflake IDs offer improved performance over UUIDs by generating sequential, time-ordered identifiers that enhance database indexing and reduce query latency. UUIDs, while globally unique, often cause index fragmentation due to their random nature, leading to slower insertions and lookups in large-scale databases. Systems requiring high throughput and efficient key sorting benefit from Snowflake's structured approach to ID generation, minimizing performance degradation in distributed environments.
Scalability in Distributed Systems
Snowflake IDs provide scalable and time-ordered unique identifiers by combining a timestamp, machine ID, and sequence number, ensuring low latency and collision-free generation in distributed systems. UUIDs, while globally unique, lack inherent ordering and can lead to increased storage and indexing overhead, potentially impacting performance at scale. Snowflake's structure optimizes scalability by enabling efficient sorting and partitioning, critical for high-throughput distributed architectures.
Storage and Efficiency Comparison
Snowflake IDs typically require 64 bits of storage, offering a compact and sortable identifier ideal for distributed systems, whereas UUIDs consume 128 bits, doubling storage requirements and potentially reducing database efficiency. The smaller size of Snowflake IDs leads to faster indexing and query performance, particularly in high-throughput environments, while UUIDs provide global uniqueness at the expense of increased storage and processing overhead. Snowflake's time-based structure enhances chronological ordering and deduplication processes, contrasting with UUID's random or pseudo-random nature that can cause fragmentation and slower storage access.
Use Cases: When to Choose Snowflake ID or UUID
Snowflake IDs are ideal for distributed systems requiring high-throughput, time-ordered unique identifiers that prevent collisions across multiple nodes, making them suitable for real-time data ingestion, event logging, and microservices architectures. UUIDs provide globally unique, random or pseudo-random identifiers useful in scenarios demanding interoperability between diverse systems, such as database keys, session IDs, and offline synchronization where decentralization and uniqueness without coordination are critical. Choose Snowflake IDs when ordered, scalable, and compact identifiers are needed, and opt for UUIDs when universal uniqueness and system-agnostic compatibility take precedence.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Identifier
Choosing between Snowflake ID and UUID depends on specific application needs; Snowflake IDs provide time-sortable, compact, and decentralized unique identifiers ideal for distributed systems requiring ordered IDs. UUIDs offer globally unique, standardized 128-bit identifiers suited for systems needing broad interoperability and no central coordination. Snowflake ID is preferred for performance and scalability in high-throughput environments, while UUID is advantageous when compatibility and global uniqueness are paramount.
Snowflake ID Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com